Each generated Java Wrapper class inherits methods from the EntireX Java ACI.
This document describes what can be performed with the methods inherited from the class RPCService.
The library name sent with the RPC request to the EntireX RPC or the
Natural RPC Server is specified in the Software AG IDL file (see library-definition under Software AG IDL Grammar in the IDL Editor documentation). When the RPC is executed, this
library name can be overwritten.
 To overwrite the library, a Java Wrapper client must
To overwrite the library, a Java Wrapper client must
Call the setLibraryName method of the
generated Java Wrapper class with the new library name as a
parameter.
 To force the library to be considered by Natural RPC Server
To force the library to be considered by Natural RPC Server
Call the setNaturalLogon method of the
generated Java Wrapper class with the parameter set to True.
| Warning: Natural and EntireX RPC servers behave differently regarding the library name. |
See Natural Logon or Changing the Library Name.
You can extend the generated Java Wrapper Class of the
client. By default, the generated client class is a subclass of
com.softwareag.entirex.aci.RPCService. The customization
component allows you to specify a class used as the superclass of the generated
client class. This user-defined class (customization class) must be a subclass
of com.softwareag.entirex.aci.RPCService.
When a customization class is specified, the calls to the user-exit
methods onEnter, onLeave,
onException and onRetry are
generated.
 To generate a customized Java Wrapper client
To generate a customized Java Wrapper client
Implement your customization class. If you use a package for your customization class, specify package and class in the following step. Place the source for the customization class in the package folder, using the folder of the IDL file as package-root. The customization class needs a default constructor and one additional constructor with 4 arguments. See the example below.
Specify the name of your customization class in the
EntireX Workbench, under ,
, . This name
is stored in the entirex.properties file (which is in your
home directory) using the key entirex.wrapper.custom.class.
Generate the wrapper client classes
 To use the customized Java Wrapper client
To use the customized Java Wrapper client
Add (public) arbitrary methods and fields to your customization class. These methods and fields are inherited by the generated client class. Add your own processing instructions to these methods.
 To perform all Broker-related processing in the generated
Java Wrapper client
To perform all Broker-related processing in the generated
Java Wrapper client
Overwrite the constructors of RPCService. You
can instantiate wrapper classes without specifying a Broker object and server
address as a parameter. Use the method setbroker() to
set or change the reference to the Broker object, and the method
setServerAddress() to set or change the server
address.
Use the four user exit methods onEnter,
onLeave, onException and
onRetry. These methods have default implementations in
RPCService and can be overwritten in your customization
class. These exits are called at the beginning and the end of each generated
method of the Java Wrapper class and when a broker exception is
thrown. See RPCService.
package ExamplePackage;
import com.softwareag.entirex.aci.Broker;
import com.softwareag.entirex.aci.BrokerException;
import com.softwareag.entirex.aci.RPCService;
public class ExampleCustomization extends RPCService {
public ExampleCustomization ()
{
super();
}
public ExampleCustomization (Broker broker, String serverAddr, String
libName, boolean compress)
{
super(broker, serverAddr, libName, compress);
}
protected void onEnter(String progname) throws BrokerException {
// insert your implementation here.
}
protected void onLeave(String progname, int sendLen, int receiveLen) throws
BrokerException {
// insert your implementation here.
}
protected void onException(String progname, BrokerException exception) throws
BrokerException {
// insert your implementation here.
}
protected boolean onRetry(String progname, BrokerException exception) throws
BrokerException {
// insert your implementation here.
return false;
}
}
It is assumed that you are familiar with the concepts of conversational and non-conversational RPC. See Conversational RPC.
 To enable conversational RPC
To enable conversational RPC
Create a Conversation object and set this with
setConversation on the wrapper object.
Different wrapper objects can participate in the same conversation if they use the same instance of a conversation object.
 To abort a conversational RPC communication
To abort a conversational RPC communication
Abort an RPC conversation by calling the
closeConversation method
 To close and commit a conversational RPC communication
To close and commit a conversational RPC communication
Commit the RPC conversation by calling the
closeConversationCommit method.
| Warning: Natural RPC Servers and EntireX RPC Servers behave differently when ending an RPC conversation. |
See Conversational RPC.
A Natural RPC Server may run under Natural Security to protect RPC requests. See Natural Security under Common Features of Wrappers and RPC-based Components in the RPC Programming documentation.
 To authenticate a Java Wrapper client against Natural
Security
To authenticate a Java Wrapper client against Natural
Security
Specify a user ID and password in the logon
method of class Broker.
If different user IDs and/or passwords are used for EntireX Security
and Natural Security, use the methods setRPCUserId or
setRPCPassword to set the user IDs and/or passwords
for Natural Security.
 To force a Java Wrapper client to log on to a specific
Natural library
To force a Java Wrapper client to log on to a specific
Natural library
Call the setLibraryName method of the
generated wrapper objects with the new library name as a parameter.
Call the setNaturalLogon method of the
generated wrapper objects with the parameter set to true.
See also Natural Logon or Changing the Library Name.
Example:
Assume that library is a wrapper object that is generated from an IDL
library. This object extends
com.softwareag.entirex.aci.RPCService. For this object, call the
methods as shown:
library.setRPCUserId("testuser");
library.setRPCPassword("password");
library.setLibraryName("NATLIB"); // this is necessary only if the Natural Library
// name is different from the library name in the IDL.
library.setNaturalLogon(true);
The order of the four methods is arbitrary.
RPC client applications can use Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) as the transport medium. The term "SSL" in this section refers to both SSL and TLS. RPC-based clients are always SSL clients. The SSL server can be either the EntireX Broker, Broker SSL Agent, or Direct RPC in webMethods Integration Server (IS inbound). For an introduction see SSL/TLS and Certificates with EntireX in the EntireX Security documentation.
 To use SSL
To use SSL
To operate with SSL, certificates need to be provided and maintained. Depending on the platform, Software AG provides default certificates, but we strongly recommend that you create your own. See SSL/TLS Sample Certificates Delivered with EntireX in the EntireX Security documentation.
Specify Broker ID and SSL parameters.
SSL transport will be chosen if the Broker ID starts with the string ssl://. Example of a typical URL-style Broker ID:
Broker broker = new Broker("ssl://yourbroker:10000?trust_store=castore","userID");
If no port number is specified, port 1958 is used as default.
If the SSL client checks the validity of the SSL server only, this is known as one-way SSL. The mandatory trust_store parameter
specifies the file name of a keystore that must contain the list of trusted certificate authorities for the certificate of
the SSL server.
By default a check is made that the certificate of the SSL server is issued for the hostname specified in the Broker ID.
The common name of the subject entry in the server's certificate is checked against the hostname. If they do not match, the
connection will be refused.
You can disable this check with SSL parameter verify_server=no.
If the SSL server additionally checks the identity of the SSL client, this is known as two-way SSL. In this case the SSL server requests a client certificate
(the parameter verify_client=yes is defined in the configuration of the SSL server).
Two additional SSL parameters must be specified on the SSL client side: key_store and key_passwd.
This keystore must contain the private key of the SSL client. The password that protects the private key is specified with
key_passwd.
The ampersand (&) character cannot appear in the password.
SSL parameters are separated by ampersand (&). See also SSL/TLS Parameters for SSL Clients.
Example of one-way SSL:
Broker broker = new Broker("ssl://yourbroker:10000?trust_store=castore&verify_server=no","userID");
Example of two-way SSL:
Broker broker = new Broker("ssl://yourbroker:10000?trust_store=castore&key_store=keystore&key_passwd=pwd","userID");
Make sure the SSL server to which the RPC component connects is prepared for SSL connections as well. The SSL server can be EntireX Broker, Broker SSL Agent, or Direct RPC in webMethods Integration Server (IS inbound). See:
When communicating with EntireX Broker over the internet, direct access to the EntireX Broker's TCP/IP port is necessary. This access is often restricted by proxy servers or firewalls. Java-based EntireX applications can pass communication data via HTTP or HTTPS. This means that a running EntireX Broker in the intranet is made accessible by a Web server without having to open additional TCP/IP ports on your firewall (HTTP tunneling). This section covers the following topics:
The Broker HTTP(S) Agent builds the bridge between Web server and EntireX Broker in the intranet.
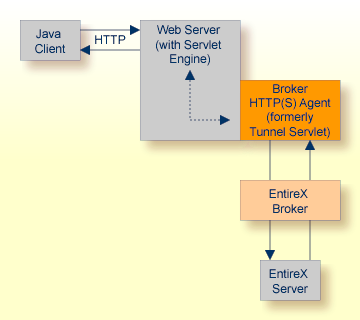
The figure above shows how the communication works. In this scenario, a Java client program communicates via HTTP and EntireX Broker with an EntireX server. By using a Broker ID starting with "http://" (passing the URL of the installed Broker HTTP(S) Agent) each Broker request is sent to a Web server, which immediately processes the Broker HTTP(S) Agent, passes the contents to EntireX Broker, receives the answer and sends it back via HTTP. For the two partners (client and server) it is transparent that they are communicating through the Web. Java server programs can also communicate via HTTP if necessary.
For the configuration, see Settting up and Administering the EntireX Broker HTTP(S) Agent under UNIX | Windows.
 To enable HTTP support
To enable HTTP support
Pass the URL of your Broker HTTP(S) Agent installation as Broker ID to your Broker objects.
For Example:
import com.softwareag.entirex.aci.Broker;
...
// "http://www.yourhost.com/servlets/tunnel" is the URL to reach your broker over HTTP
Broker broker = new Broker("http://www.yourhost.com/servlets/tunnel","userID");
...
// other code not affected
...
The Broker HTTP(S) Agent optionally accepts parameters as part of the URL. It is possible to define values for Broker and log that override the corresponding values in the configuration of the Broker HTTP(S) Agent.
 To enforce logging of the Broker HTTP(S) Agent
To enforce logging of the Broker HTTP(S) Agent
Type, e.g. the following:
Broker broker = new Broker("http://www.yourhost.com/servlets/tunnel?log=yes","userID");
 To use HTTPS instead of HTTP
To use HTTPS instead of HTTP
Replace "http://" by "https://" at the beginning of the Broker ID.
Using HTTPS requires a Web server with SSL support enabled. Check your Web server's documentation for information on how to configure SSL support.
Many Java implementations do not support HTTPS. If this is the case, your application will receive a BrokerException with error code 00130325.
RPC clients inherit all methods and functionality regarding character conversion, provided by the Java ACI. For more information see Using Internationalization with Java ACI.
Enable character conversion in the broker by setting the service-specific attribute CONVERSION to "SAGTRPC".
See also Configuring ICU Conversion under
z/OS |
UNIX |
Windows |
BS2000 |
z/VSE.
More information can be found under Internationalization with EntireX.