This page describes implementation issues and how to use sample security exits in EntireX Broker. It assumes you are familiar with EntireX Broker from both an administrative and an application perspective, and with the ACI programming interface in particular. See Introduction to ACI-based Programming.
This document covers the following topics:
Prerequisites for Running EntireX Broker in a Secure Environment
Required/Recommended Actions in the Exit (depending on Security Type)
The diagram shows a data flow for sample security exits, with Broker Kernel located, for example, on z/OS. See also Description of Steps in Data Flow.
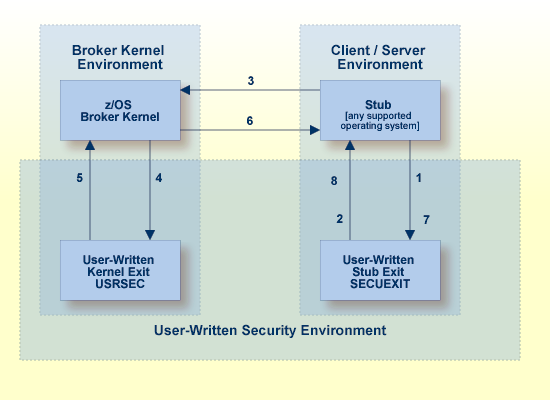
To run EntireX Broker in a secure environment, the following prerequisites must be met:
The security system in the EntireX Broker kernel must be activated by setting SECURITY=YES
in the broker attribute file.
The security routines must be accessible to the Broker. The method you use to achieve this depends on the operating system where your user-written USRSEC is implemented.
Note:
EntireX Broker will not start if SECURITY=YES is
specified but the security routines cannot be activated.
If you run a secure environment, we recommend you performing an explicit
LOGON with the AUTOLOGON=NO
definition in the attribute file. All security violations are logged to the
EntireX Broker log file.
 To implement the kernel security exit under z/OS
To implement the kernel security exit under z/OS
Write the exits USRSEC. The code must always be reentrant and
reusable.
The kernel security exit USRSEC is loaded automatically during
startup of Broker. Use module and entry name USRSEC for this exit. A security
module sample source is delivered with the ETB source library.
Under z/OS, link the exit as reentrant and reusable.
Ensure that the security exit is accessible in the Broker
STEPLIB.
 To implement security exits for Broker stubs under z/OS
To implement security exits for Broker stubs under z/OS
Write the stub security exits ETBUPRE and ETBUEVA. The code must
always be reentrant, except for batch, where the code must be reusable.
Link these exits ETBUPRE and ETBUEVA to the stub of the target
application. The stub contains weak externals for both entries.
 To implement the kernel security exit under UNIX
To implement the kernel security exit under UNIX
Write your own usrsec.c based on the samples delivered with EntireX.
Build your own usrsec.s[o|l], using the provided makefiles. (A sample makefile, makexa, is provided.).
Ensure that usrsec.s[o|l] is made available to the Broker kernel at execution time. The attribute file parameter SECURITY-PATH must be used to specify the location of usrsec.s[o|l].
 To implement security exits for Broker stubs under UNIX
To implement security exits for Broker stubs under UNIX
Write your own secuexit.c, based on the samples delivered with EntireX.
Build your own secuexit.s[o|l], using the provided makefiles. (A sample makefile, makexa, is provided.).
Ensure that secuexit.s[o|l] is made available to the application in the same directory as the Broker stub.
 To implement the kernel security exit under Windows
To implement the kernel security exit under Windows
Write your own usrsec.c based on the samples delivered with EntireX.
Build your own usrsec.dll, using the provided makefiles.
 To implement security exits for Broker stubs under Windows
To implement security exits for Broker stubs under Windows
Write your own secuexit.c, based on the samples delivered with EntireX.
Build your own secuexit.dll, using the provided makefiles.
This section describes how to write your own security exits. It describes the interfaces, indicates what can be modified and what has to be done within an exit. It also provides some helpful tips.
This section covers the following topics:
You must provide the following functions:
The Preparation exit etbupre() and the
Evaluation exit etbueva() for the Broker stub. These
two functions are linked statically to the Broker stub routines.
The Kernel exit usrsec() which is loaded by
the kernel. This exit is more generic than the other two. It is called with the
function that has been performed and a function-dependent Broker ACI control
block that provides all the necessary information. This function is loaded
dynamically by EntireX Broker during startup. One parameter of the kernel exit
is the function that is performed.
The functions map to the exit type is as follows:
| Exit Type | Function | Function to perform |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication exit | ETB_SEC_LOGON | Checks authentication for the user. |
| ETB_SEC_LOGOFF | Release user-specific information if necessary. | |
| ETB_SEC_NEWPUID | Application call with different physical USER ID. | |
| ETB_SEC_NEWST | Application call with a different SECURITY TOKEN | |
| Authorization exit | ETB_SEC_SEND | Check whether user is allowed to use the addressed service. |
| ETB_SEC_REGISTER | Check whether the user is allowed to offer that service. | |
| Encryption exit | ETB_SEC_ENCRYPT | Encrypt the given data. See Note 1 below. |
| ETB_SEC_DECRYPT | Decrypt the given data. See Note 1 below. |
Notes:
In the following text, "encryption" or "authentication" exit refers to the functions listed above.
With ACI_VERSION=4 or above, the security configuration of the caller's
stub is checked against the security configuration of the broker kernel. The
request will be rejected with the error message 00200379 - API:
Inconsistent Security Installation, if security
is present in the stub and it is not present in the kernel;
or
is not present in the stub and it is present in the kernel.
Note:
If you have written your own security - instead of using
Security Solutions in EntireX - and it is implemented only on the kernel, you will have
to add a dummy security exit to the stub.
The following security-related parameters are provided. These are fields in the Broker ACI Fields:
The USER ID is defined by the application. It is available in all ACI
exits as well as in the kernel exits, except the encryption and decryption
exits. Theoretically the preparation exit can be used to retrieve the login
name by an operating system specific mechanism. This would allow a user
identification without the application being involved. See the description of
the USER-ID
field in the Broker ACI control block.
The PASSWORD is defined by the application. It is available in all ACI
and kernel exits except the encryption exit. The PASSWORD, if provided by the
application in plain text, should be encrypted in the Preparation exit before
sending it across insecure network connections. If the PASSWORD is needed in
the application again, it must be decrypted after receipt in the Evaluation
exit. The authentication exit must ensure that the PASSWORD is properly
decrypted if necessary before sending it to an external security system.
The EntireX Broker provides minimal encryption of the PASSWORD field,
that is, the field is not transmitted in plain text. If your environment
requires absolute security, however, you will need to provide both Broker stub
and EntireX Broker kernel exits to perform encryption and decryption. See the
description of the
PASSWORD
field in the Broker ACI control block.
The SECURITY TOKEN can be created by the application and sent to
EntireX Broker. That allows for a kind of credential algorithm. The security
token is passed to all kernel exits and can therefore contain security
information which is also important for the authorization and encryption exits.
The SECURITY TOKEN can be altered in the authentication exit to provide a
context token for that application and that session. It is transmitted back to
the application and can then be used in all subsequent calls. For each
subsequent call, the EntireX Broker checks whether the SECURITY TOKEN is
identical to the one returned from the last call to the authentication exit,
which could be the ETB_SEC_LOGON, the ETB_SEC_NEWPUI or the ETB_SEC_NEWST
function. After an ETB_SEC_LOGOFF call, a subsequent call is always a
ETB_SEC_LOGON call. See the description of the
SECURITY-TOKEN
field in the Broker ACI control block.
CLIENT-UID is returned to a server application after a RECEIVE and
contains the user ID of the sending client. This allows for further security
checks (logging, separate checks, etc.). See the description of the
CLIENT-UID
field in the Broker ACI control block.
All security-related ERROR CODEs start with the ERROR CLASS 0008. The
following four digits in the ERROR CODE can be assigned by any exit if a
security violation occurs. These digits only reach the application if the
current operation is aborted by the security exit with a security violation,
i.e. an appropriate return code. See ERROR-CODE under Broker ACI Fields.
The security exits can also pass an error message back to the application. This error text must not be longer than 40 bytes.
See KERNELSECURITY under Broker ACI Fields.
The exits in the stub have the following interface:
int etbupre (ETBCB *pEtbCb,
void *pSendBuf,
void *pReserved,
char *pErrText)
| Parameter | Format | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Address of ETBCB | Pointer to ETBCB control block. | I/O | ETBCB's user_id and password are used to generate the credential which will be saved in field security_token for function LOGON. |
| Address of send buffer | void pointer | I/O | Send buffer (3) supplied by caller, only available for function SEND, length of send buffer is member of ETBCB. |
| Reserved | void pointer | I | Must be NULL. |
| Address of error text | char pointer | O | The error text is an array of 40 characters containing the error text that will be returned by the stub routine. |
0 (okay) or non-zero (error)
The real error code must be written to the Broker control block as an
8-byte character array (without trailing 0 byte!). The Message Class 0008 - EntireX ACI - Security Error is reserved for all errors in function
etbupre. The error number is user-defined.
Additionally, the error text can be returned to the user in the error text
array.
If no data encryption is desired, no action is required.
Generate a credential if function is LOGON and move it to the field
security_token.
Encrypt the send buffer if function is SEND. The encryption process
must not change the length of the buffer. See Notes below.
The exit gets control for each function of ACI version 2 and above. The exit must exist.
Notes:
SEND buffer after issuing the SEND command, since the contents of the SEND buffer will be encrypted when sending more than 32 KB of data. We recommend you code all applications so that you do not
rely on the contents of the SEND buffer after calling Broker. This will be required in the future for all SEND commands regardless of whether the data exceeds 32 KB. Therefore, the application's SEND buffer must not be in read-only memory, where encryption is activated.
int etbueva (ETBCB *pEtbCb,
void *pRecBufEncr,
void *pReserved,
char *pErrText)
| Parameter | Format | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Address of ETBCB | Pointer to ETBCB control block. | I/O | ETBCB's security token is used for data decryption. |
| Address of receive buffer | void pointer | I/O | Receive buffer (2) provided by EntireX Broker. Only available for functions RECEIVE and
SEND WAIT=x (implicit receive). Length of receive buffer is member of ETBCB. |
| Reserved | void pointer | I | Must be NULL. |
| Address of error text | char pointer | O | The error text is an array of 40 characters containing the error text which will be returned by the stub routine. |
0 (okay) or non-zero (error)
The real error code must be written to the Broker control block as an
8-byte character string (without trailing 0 bytes!). The Message Class 0008 - EntireX ACI - Security Error is reserved for all errors in function
etbueva. The error number is user-defined.
In addition, the error text can be returned to the user.
If no data decryption is wanted, no action is required.
Decrypt (1) the receive buffer if functions are
RECEIVE or SEND with
WAIT. The decryption process must not change the
length of the buffer.
The exit gets control for each function of ACI Version 2 and above. The exit must exist.
Notes:
All authentication, authorization, encryption (1) and decryption exits are
combined within one exit module named USRSEC. The
various security checks are indicated by a type parameter in the CALL
interface. USRSEC is provided with EntireX Broker as
the default security exit. It is invoked if SECURITY=YES is set in the attribute file.
Prior to EntireX, the
USRSEC exit was available only with the SAF Gateway
security package.
The general syntax of this user exit is defined as follows:
long usrsec (ETB_SECPAR *pParSec,
void *pVarious,
char *pErrText,
char *pWorkArea,
long lWorkArea)
| Parameter | Format | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Address of security parameter block | Pointer to structure ETB_SECPAR | I | Contains the security type flag. |
| Address of type-dependent security parameter block | void pointer | I | See control block structures
ETB_SECPAR_<type>.
|
| Address of error text | char pointer | O | The error text is an array of 40 characters containing the error text which will be returned to the user. |
| Address of work area | char pointer | O | Volatile work area. |
| Length of work area | long integer value | I | Size of the work area in number of bytes. |
0 (okay) or user-defined error number
Message Class 0008 - EntireX ACI - Security Error and the error number will be returned to the user. In addition, the error text can be returned to the user.
Notes:
| Security Type | Required Action | Recommended Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
ETB_SEC_ENCRYPT |
Copy decrypted to encrypted buffer and set the length of encrypted buffer. This is necessary because exit is called whether the receive data has to be encrypted or not. | Encrypt receive data if needed. | 1,2 |
ETB_SEC_DECRYPT |
Copy encrypted to decrypted buffer and set the length of decrypted buffer. This is necessary because exit is called irrespective of whether send data is encrypted or not. | Decrypt receive data if needed. | 1,2 |
ETB_SEC_LOGON |
Decrypt the password and check combination of user ID and password against the security system. Generate a context token according to the credentials of the user and EntireX Broker. Create a security handle for a user session (e.g. ACEE on z/OS). | ||
ETB_SEC_LOGOFF |
None | Delete the security handle of the user session. | |
ETB_SEC_NEWPUID |
None | An application has changed the physical user ID between two calls. If necessary, a new security token can be created. | |
ETB_SEC_NEWST |
None | For some reason, the security token of an application has changed and no longer matches the original. The security token should be recalculated and approved or the application should be rejected. | |
ETB_SEC_REGISTER |
None | Check whether user_id is authorized to offer the requested SERVICE (check security_token data if necessary). | |
ETB_SEC_SEND |
None | Check whether user_id is authorized to offer the requested SERVICE (check security_token data if necessary). | |
ETB_SEC_SECURE |
None | Check the security token. | |
ETB_SEC_INIT |
None | Create global context if required. | |
ETB_SEC_FINI |
None | Delete global context if created. | |
ETB_SEC_INFO |
None | Check CIS information request. | |
ETB_SEC_CMD |
None | Check CIS command request. |
Notes: