The application properties dialog box can be accessed by right-clicking on the relevant application and selecting . Here you edit the basic properties as well as advanced properties:
This node is the first node of the application properties and provides the most basic application information. Right-click on an application to access the general properties.
- Application name
A unique name defined when first creating the application. The application name is read only here but can be changed by right-clicking on the application and selecting .
- Description
A brief description of the application.
- Initialization mode
- Automatic
Automatically loaded when the server is started.
- When first accessed
Loaded when first accessed, in other words, when the code that initializes startup is first called (default).
Host Parameters are described in detail in Host Configuration Parameters.
- Host name
The name of the host that is to be connected to your application (obligatory field).
- Address
The host's TCP/IP address (read only).
- Port
The TCP/IP port to which the host is listening (read only).
- Device Type
The device type of terminal that ApplinX emulates (read only).
- Protocol
The protocol used to access the host (read only).
- Model
The number of characters per column and per row, in the host's window (read only).
- Code Page
The code page number of the required language for this application (read only).
- Non-activity timeout
ApplinX can be defined to disconnect after a certain period of non-activity. When selecting unlimited, the session will stay connected even when there is no activity.
- Wait condition timeout
The default amount of time, in milliseconds, for which the application waits to receive a screen from the host. For example, in paths, if the user defined a target screen, and it was not reached within this timeout, the user will get an exception. An additional example is in the frameworks, where the user will receive the last screen, and will continue waiting (as the host is still locked). Possible values are from 1000 to 999999 ms.
- Flicker
An amount of time, defined in milliseconds, in which the application waits for the host to send information. This is necessary, as information may be sent in a few chunks of data, before declaring that it has received the entire screen. This is a value defined for all the application screens, and can be bypassed using the Wait Conditions. (By default, this value is set to 0). Possible values are from 0 to 10000 ms. Refer to Handling Flickering of Host Screens.
- Blank screen timeout
The amount of time, defined in milliseconds, in which the application waits after receiving a blank screen, giving the host the opportunity to continue sending the next screen before returning to the client. This is very similar to the flicker parameter, the difference being that the flicker feature waits the complete amount of time defined as oppose to the blank screen timeout which finishes once the screen stops being blank. In addition, this setting only applies to blank screens, and in this way, does not slow down the performance of the entire application. (Default value: 500 ms). Possible values are from 0 to 10000 ms.
- Work offline
Indicates whether to simulate a communication with the host by using a pre-recorded file. By default, this feature is not enabled.
- Files on server
Lists the trace files which are on the server. Click and browse to copy a file from your local machine to the server.
- Simulate host delay
Allows a session replayed by a GCT to simulate the host's communication delay or to predefine a time delay to wait before showing the information (this is because generally, the application is faster when replayed). Available values: No delay, Simulate host, 500- 10000 ms (by default No delay is selected).
The Record Trace File feature enables creating a file, which will trace the connection communication (connection pool or user) between the ApplinX server and the host, for each connection. It is possible to define whether a single trace file will be created, replacing the previously saved file or if the data will be saved to a new file for every new connection or session. Identifying the separately saved files is possible by inserting identifying parameters in the file name (the session ID, connection time and/or connection ID).
- Record display sessions (trace files)
Select this option to enable recording trace files.
- Compress (create files in zip format)
Select this option to compress the file.
- Encrypt (using server private key)
Select this option to encypt the file. In order to encrypt files, you must first define the encryption key (In the Server properties, General tab).
- Suppress hidden fields
Conceals passwords and hidden fields in the trace file.
Note:
The "Suppress hidden fields" option is not supported when recording using Terminal Emulation Proxy.- File name
The name of the trace file. You can create a separate File for each session, or connection and the name can include the session ID, creation time and/or connection ID.
%u will insert the session ID.
%t will insert the time stamp of the connection.
%c will insert the connection ID.
- Location of folder
Browse and select the location of the folder where the files will be stored. Determine whether sub folders will be created for each year/month/day.
- Open recordings folder
Opens the Windows Explorer and displays the location and list of existing trace files.
Note:
The following section is not yet supported.
- Limit folder size
Select this check box to determine that the folder will be limited to a certain size and determine the maximum size of the folder.
- Send notification when folder size reaches...
Select the check box so that mail will be sent once the folder reaches a certain percent of the maximum size.
Enter the email address to which the notification should be sent.
- Limit number of files to be stored in each sub folder
Select the check box to determine that the sub folders will be limited to contain a specific number of files and determine this number.
- Create new folder when the sub folder reaches file limitation
Select the check box to create a new sub folder once the number of files in the current sub folder reaches the number determined in the previous field.
The Send Options enable to configure how and whether a field is sent to the host when there are mismatches between the field and the host field.
- Throw exception when field content does not match host field attributes
When the field does not match the host field attributes, for example, when the value to be entered is longer than the field length, or the field is not found, or the cursor position is not in an unprotected field, an error will occur.
- Add trailing spaces to sent fields
ApplinX trims field content (removes padding spaces), so that the content is displayed properly in HTML input fields, and so that the user will receive only the meaningful content. However, some Mainframe hosts are sensitive to spaces and expect to receive from the client the spaces that the client received (unless they were overwritten by text entered by the user). To compensate for ApplinX' trimming behavior and instruct it to send spaces to the host as needed, select this check box. This is relevant for 3270 only.
- When field content is longer than host field length...
When the field content is longer than the host field it is possible to select the option that this field will not be sent to the host, or that the contents of the field will be cut to match the host field size.
Available in SOA applications only.
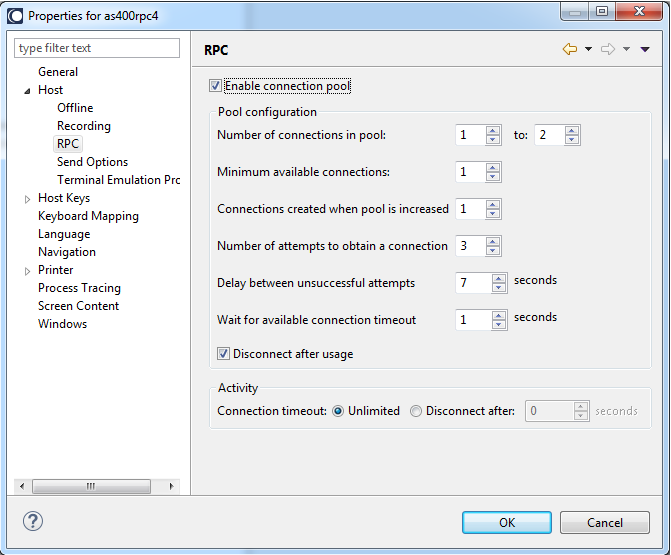
In the RPC tab, connection parameters for the ApplinX Program Calls. This is enabled only for AS/400 hosts.
- Enable connection pool
Selecting this check box indicates that the server should maintain a pool of connections.
- Number of connections in pool
The minimum and maximum number of connections it is possible to have in the pool at one given time.
- Minimum available connections
The minimal number of connections in the pool that are ready to serve a transaction. If the number of available connections in the pool falls below this number, new connections will be created until the minimum is reached.
- Connections created when pool is increased
The number of connections created each time the pool size is increased.
- Number of attempts to obtain a connection
The number of attempts to create a connection.
- Delay between unsuccessful attempts
The time, in milliseconds, before retrying to obtain a connection.
- Wait for available connection timeout
If no connections are available in the connection pool, the length of time to wait for an available connection before a timeout message is sent.
- Connection timeout
The total time, in minutes, that a connection can exist. Setting the value to "Unlimited" sets no timeout. After the set time elapses the connection is terminated.
- Disconnect after usage
This checkbox determines whether to restart the connection once a user finishes using a connection or to terminate the connection when it is returned to the pool. When checked, the connection is terminated after usage.
This feature enables redirecting emulation network traffic to pass through the port configured in this screen (only relevant for AS/400 and Mainframe hosts).
- Use Terminal Emulation Proxy
Select this check box to use the Terminal Emulation Proxy option.
Note:
When recording using Terminal Emulation Proxy, the "Suppress hidden fields" option is not supported.- Terminal Emulation Proxy port
Enter the port number through which you would like to redirect the emulation network traffic.
- Unprotected field navigation
Determine whether the arrow keys or any other key selected from the drop-down list manipulates the cursor when the unprotected fields are set (default: tab key).
- Set cursor position
This is by default not selected. Determine whether to set the cursor position. If so, whether the arrow keys or any other key selected from the drop-down list sets the cursor position (default: tab key).
- Use arrows to navigate to protected positions
Check this option when setting the cursor position with a key (not arrow keys). Allows you to set the cursor position in protected positions using arrow keys (default: checked when set cursor position is checked and key option is selected).
- Use arrows to navigate within an unprotected field
Check this option when setting the cursor position with a key (not arrow keys), to set the cursor position inside unprotected positions using arrow keys. If this is checked, navigation to the first position of the unprotected field is achieved using the selected key. Continue navigation inside unprotected positions with arrow keys (default: tab key; checked when set cursor position is checked and key option is selected).
- Automatically skip between unprotected fields
When checked, indicates the cursor skips automatically to the next unprotected field upon reaching the end of the current field (default) (happens when the field is completely filled with text).
- Wait for unprotected field
When navigating to a certain field for sending its contents, the host sometimes moves the cursor to protected positions before finally placing them inside an unprotected field. When checked, ApplinX waits for the cursor to reach an unprotected field before continuing the navigation process. When unchecked, ApplinX continues the navigation process immediately after the cursor changes its position (even if the new position is protected).
- Detailed log
When checked, a detailed description is logged to the ApplinX Server log file (default). It is highly recommended to check this during development time, however for production purposes it would be preferred to leave this check box unchecked to improve performance.
- Send characters separately
Some VT hosts require input to be sent one character at a time. When checked, input characters are sent separately. When unchecked, input characters may be sent in one buffer.
- Filler Char
Represents a character in the application that is treated like a blank. The default for new applications is underscore ("_"). The ApplinX server may use this character when, for example, erasing data from fields.
The Host Keys tab serves to define the host keys patterns (for example, PF/F/PA) that should be searched for in the application. To configure the host keys, click the Host Keys node in the Application dialog box. Click on the Manual node to customize host keys. Refer to Define Host Keys for additional information regarding to working with host keys.
- Rows to search
Specify where to commence the search for PF keys. The number of patterns that can be defined for each application is unlimited. There are a number of predefined patterns which are available by clicking on the arrow next to the hyperlink.
- Keys in successive rows only
Searches for host keys in successive rows only.
- Search keys outside window
Shows and enables keys from the entire screen - not only from the active window.
- Remove rows from screen
Removes the rows where the pattern was recognized.
- Pattern table
Lists the defined patterns.
- Pattern name
The name of the pattern.
- Key prefix
The host keys' prefix (for example, PF/F/PA). It is assumed that one or two digits appear after the prefix. Maximum of two types of prefixes for each pattern is allowed.
- Number of spaces between key and description separator
The number of spaces between the prefix and the internal separator. If a specific number is used, then only sets with that exact number of spaces will be included. Select "Any" to enable any number of spaces.
- Key-description separator
The character or string separating the key and the description (for example "=").
- Pattern separator
Separates between each combination of key + description (for example, ",").
- Key direction
By default defined as LTR (left to right).
- Caption
The caption that will appear on the customized host key.
- Host key
Determines the host key that will be sent. The host key should be in square brackets and can be selected from the standard host keys list to the right of the Host key field.
- Cursor position
Once the host key is sent the cursor is placed in the position defined here. When these fields are left empty, the cursor remains in the current position.
Use the Keyboard Mappings node to map host keys to keyboard keys.
- Keyboard key/s
The combination of keyboard keys such as Shift+W. The values in this field are entered into the field as they are pressed on the keyboard.
Note:
When using the keyboard keys within the web application, the CTRL+N and CTRL+K keys are blocked by default as they cause multiple browser windows to use the same session (this can be manually set in the config/gx_keyboardMappings.xml file).- Command
Determines the host key that will be sent. The host key should be in square brackets and can be selected from the standard host keys list to the right of the Host key field.
- Hexadecimal code (VT hosts only)
A sequence of hexadecimal numbers assigned to each key. Examples for possible values: 0x7F or 0x08 (default in ApplinX). If [backspace] doesn't work as expected in ApplinX, try configuring 0x7F.
The Language node enables you to define the language used in the application as well as direction settings, relevant mainly for right-to-left languages.
- Language
The application's language.
The following settings are relevant for right-to-left languages. The option you select is the default setting for all the screens, but can be changed for a specific screen in the relevant screen identification properties.
- Screen direction
Relevant for mainframe hosts only. The screen direction of right-to-left languages differs according to the original host settings, and when incorrectly set, can cause the screen to be illegible. In order to correct this, define the suitable screen direction.
- Typing direction
Right-to-left languages may display typed-in text in the client application text fields, aligned to the left of the field. In order to display the text aligned to the right, select the right-to-left option. Numeric type fields typing direction will always be left-to-right.
- Tab direction
When pressing the button the cursor moves to the next consecutive field. The direction the cursor moves (moving to the next field to the left or moving to the next field to the right) must be correctly defined in order to preserve the screen logic.
- Enable map steps recording while navigating in session
Once selected, the application map will record the navigation steps between the screens.
- Exception path
An Exception path is initiated once a Path Procedure which is being executed reaches a screen that is not defined as the To Screen of the step that was executed or as the From Screen of the next step to be executed. When such a screen is reached, ApplinX immediately searches (ignoring the wait condition timeout) for the Exception Path that has been defined. If an Exception path is found, it is executed. ApplinX will then try to continue the original path from the point before the Exception Path was initiated. The attempt to find and execute a suitable Exception path will be repeated as many as 30 times, after which the original path will fail to be executed.
ApplinX supports printer sessions only on AS/400 and mainframe hosts. It connects to the host, retrieves the print buffers and analyzes them. The host handles the printer's queue and the connection of printer sessions to display sessions. ApplinX connects to the host as a printer session to receive the print buffers and allows you to work with them.
Note:
This is not available when working with a SOA license, and is only
available when working with a Web enabled license.
Check the Enable printer check box to enable this feature. It is enabled by default when creating a new application.
- Device name
The name of the printer device as defined in the host.
- Associate
The name of the display device (on the host) that the printer should connect to.
Note:
Applicable for mainframes only. The host handles the linkage of printer session to the display device.- Message queue
The message queue where printer messages are sent. The default message queue is contained in library QSYSOPR (enabled for AS/400 hosts only).
- Message library
The name of the library that contains the message queue (enabled for AS/400 hosts only).
- Delay response to host
Adds a delay before the ApplinX server sends a response to the host, as a number of hosts react in an unpredictable fashion when a very fast response is received from the emulator (e.g. creating problems with the printer session). This parameter should be set only after experiencing such problems.
- Create trace file
Indicates whether to log the communication with the host into a file. If you include %u or %t (or both) in the trace file name, you can create files for diverse users with different time information and session ID.
Note:
This trace file may only be used as a replay file for a printer session.- File name
The name of the trace file. You can create a separate file for each printing session, or connection and the name can include the session ID and/or creation time.
%u will insert the session ID.
%t will insert the time stamp of the connection.
By default, this feature is not enabled.
- Open recordings folder
Opens the Windows Explorer and displays the location and list of existing trace files.
Refer to the Printer Session chapter for more information regarding the Printer Session.
- Work offline
Indicates whether to simulate a communication with the host by using a pre-recorded file. By default, this feature is not enabled.
- Files on server
Lists the trace files which are on the server. Click and browse to copy a file from your local machine to the server.
- Simulate host delay
Allows a session replayed by a GCT to simulate the host's communication delay or to predefine a time delay to wait before showing the information (this is because generally, the application is faster when replayed). Available values: No delay, Simulate host, 500 ms, 1000 ms, 2000 ms, 3000 ms, 4000 ms, 5000 ms, 6000 ms, 7000 ms, 8000 ms, 9000 ms, 10000 ms (by default No delay is selected).
The Application Process Tracing is used to provide a log of performance times of processes such as procedures, paths and programs. This can give a more specific indication (pinpoint the exact process) as to the cause of application performance problems. The application process tracing information can be saved as a txt and/or csv file. These files are located in the Software AG\ApplinX\host-applications\<application name>\auditing directory.
Note:
The Host times that the tracing application process displays, are
only relevant for hosts that are not character mode hosts.
- Enable process tracing
Select this check box to activate process tracing in your application.
- Type
Select the type of tracing you require: either basic logging, which logs the data at the entity level (logs when a procedure, path or program started and when they were completed) or in-depth logging, which logs more detailed data, at the step or node level.
- Output
Select whether to log each process from the beginning to the end or just to log a summary of the process. When logging just the process summary, it is possible to define to only log processes that took longer than a certain amount of time to be completed.
- File type
Indicates whether to display the logged data in a textual informative format (txt) and/or to display the logged data in Comma Separated Values (CSV) format.
- File name
The name of the trace file. You can create a separate File for each session, or connection and the name can include the creation time and/or connection ID.
%t will insert the time stamp of the connection.
%c will insert the connection ID.
By default, this feature is not enabled.
- Open auditing folder
Opens the Windows Explorer and displays the location and list of existing files.
Since version 9.8, ApplinX uses an internal database based on the H2 database as a repository. External databases are no longer supported as repositories and are migrated to the internal DB configuration.
The Database Manager is a migration tool, allowing you to convert your databases' structure to the current structure needed by the installed version of ApplinX.
- Replace padding characters with space
Some hosts fill input fields with a character such as underscores or dots (following the actual content of the field). You may define that ApplinX replaces this character in the input field with spaces when the server sends the field's contents to the client. It is possible to define up to two padding characters.
The radio buttons enable applying this to all fields or only to input (unprotected) fields (input fields also include application fields with "both" protection type - protected and unprotected).
- Remove from both sides of text
This field determines whether the padding character will be removed from both sides of the field or just from one side (in LTR applications the character will be removed from the right side, and in RTL applications the character will be removed from the left side). In numeric type input fields, the characters are removed from both sides of the content (as it is clearly not a number).
- Trim Fields
Some hosts fill input fields with spaces (following the actual content of the field). You may instruct ApplinX to remove the spaces from the content of the input field.
The radio buttons enable applying this to all fields or only to input (unprotected) fields or input fields and application fields with "both" protection type - protected and unprotected).
- Remove from both sides of text
This field determines whether the spaces will be removed from both sides of the field or just from one side (in LTR applications the character will be removed from the right side, and in RTL applications the character will be removed from the left side). In numeric type input fields, the characters are removed from both sides of the content (as it is clearly not a number).
- Return Content of Hidden Fields
Some hosts have hidden fields in the screen. Usually these fields' visibility depends on the context of the screen. By default, ApplinX does not return the content of these fields because the user in an emulator cannot see them. However, sometimes their content can be important and one may want to access it (for example, hidden fields can be used as screen identifiers, or as a part of a Path Procedure's logic). Check the Return content of hidden fields check box to return the content of all hidden fields in the application.
- Split fields when an attribute changes (color, blinking etc.)
This field determines whether when an attribute changes in the middle of a field, this field will be split.
In the Designer, you can describe the way a window is displayed in the host. The Window definitions are used to correctly identify screens and to open host windows as separate pop-up windows. Click the or button to make any changes.
Note:
When the host is a Natural UNIX host, this tab is disabled, as the
windows' definitions are included in the Natural-Unix protocol and do not
require being defined via ApplinX.
- List of host windows
The list of host windows is displayed here. Add or remove windows by clicking on the relevant button. When adding a window you are required to select the type of modal windows the host sends. There are two types: Reversed Video or Frame. For applications that have more than one level of windows (a window within a window), where each level is defined with a different Window Type, be sure to define the windows in the correct order.
- Attributes
- Frame is intensified
One of the parameters that assist in recognizing windows. This parameter determines whether the frame will be recognized as a window when the frame is intensified.
- Frame with title
One of the parameters that assist in recognizing windows. This parameter determines whether the frame will be recognized as a window if the frame has a title.
- Identify window even though unprotected fields exist outside window area
This field determines whether or not an area that seemingly could be identified as a window will be recognized as one, even though there are unprotected fields outside the window area. Note: When a window is identified within a screen, and working with modal windows, it is not possible to edit unprotected fields outside the window area.
- Content
- Remove window frame
Characters appear on the first line of the screen without the window frame. Suitable typically for NATURAL mapping applications.
- Display window title
Displays the window title in the window frame to be viewed.
- Frame characters
- Vertical
The character used for the host's modal window vertical lines. The character can be either typed in, or selected from the list of characters.
- Horizontal
The character used for the host's modal window horizontal lines. The character can be either typed in, or selected from the list of characters.
- Corners
The character used for the host's modal window corners. The character can be either typed in, or selected from the list of characters.
- Synchronize corners
Defines that all four corners of the window frame are the same character (default). When selecting this option, define the character for each of the corners (upper-left, lower-left, upper-right and lower-right).