Import one or more library modules.
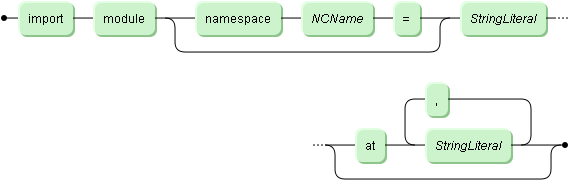
A ModuleImport imports declarations of functions and
variables from one or more library modules. The first string literal specifies
the target namespace for which you can optionally define a namespace prefix.
The ModuleImport imports all modules that share this target
namespace. By using the at keyword you can provide an additional
location hint with a string literal that must be a valid URL. The
following rules apply for importing modules:
It is an error if more than one module import in a prolog specifies the same target namespace.
Module imports are not transitive which effectively means that you can access only the function and variable declarations directly contained in the imported module. So if module A imports module B and module B imports module C then module A cannot access the function and variable declarations of module C.
The graph of module imports must not contain cycles. So if module A imports module B and module B imports module C then module C must not import module A.
This imports the module:
import module namespace math = "http://example.org/math-functions";
The following construct(s) refer to this construct: