The Tamino Manager contains commands that you can use to create and manage replication databases. For further information about database replication and when to use it, please refer to the document Replication Guide.
The first step in creating a replication database is to create an exact copy (slave) of the database to be replicated (master) from the most recent backup of that database. To do so, you first have to create a database from a (non-initial) backup of your current database. For further information about creating a database from a backup, please refer to the section Create a Database From a Backup.
| Warning: Do not start a replication database before you have performed the step Setting a Replication Database |
Once the database has been created from backup, its name has to be added to the list of permitted replication databases for the master database. A master database can have one or more replication databases. The database to which the replication database name is to be added must be active (running).
![]() To add/remove a replication database name
To add/remove a replication database name
Expand the database object to which you want to add a replication database name.
Select the object and choose from the context menu. The Add Replication Database page appears.
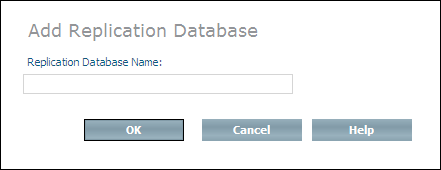
Enter the name of a slave database in the Replication Database Name text box (the one you have created from backup) and choose . It is possible to enter the name of a replication database that has not yet been created from backup, but will be in the future. Thus, you can create a "pool" of replication database names to be used at a later point in time, so that you do not have to repeat this step each time a new replication database is to be created.
Note:
The first time you add an entry to the list it is not necessary
to restart the master database.
If you want to remove the name of a database from the list of permitted replication databases, select the object for the master database - the Permitted Replication Databases page appears.
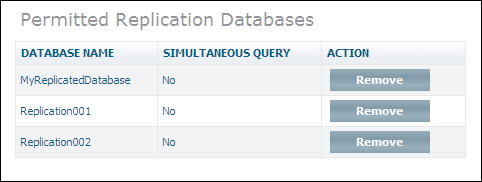
Choose to remove the database name from the list.
Once the name of the replication database has been added to the master database, the replication database must be set as a replication database. This is done by specifying the name of the master database that is to be replicated. The replication database must be inactive (stopped).
![]() To set a replication database
To set a replication database
Expand the database object that has been defined as the replication database (the one you have created from backup), select and choose from the context menu. The Set replication database page appears.
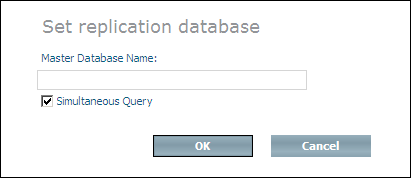
Enter the name of the master database in the Master Database Name text field. If you want to enable queries to this database while replication is in progress, select the Simultaneous Query checkbox. and choose .
Note:
Once a database has been set to a replication
database, the subtree under the database object in question changes and
contains only the child objects ,
, , ,
and . Also, the only commands that can be performed on a
replication database are Start Database, Stop Database and Delete Database. You
can view the replication status of a database by selecting the object
.
If, for any reason, the master database is lost, you can reset the replication database to a normal database, which can then be used as a substitute for the lost master. The replication database to be reset must be inactive (stopped).
![]() To reset a replication database
To reset a replication database
Expand the database object of the replication database, select and choose from the context menu . The Confirm Reset Replication Database page appears.
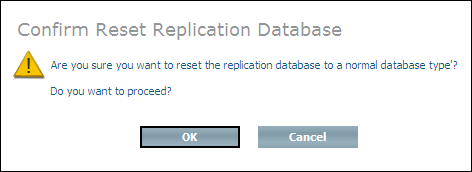
Choose to reset the replication database to a normal database.
Note:
Once you have reset a replication database, replication cannot be
continued.
Depending on whether you work with a normal database or with a replication database, the options that are available with Replication Management differ.
If you select the object for a replication database, information similar to the following is displayed:
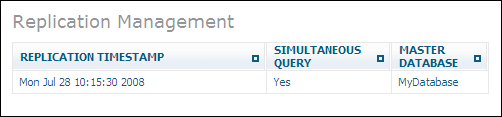
The window shows the name of the replication database's master database, the timestamp when the replication database was created, and if simultaneous query is enabled. The command is not available.
If you select the object for a normal (master) database, information similar to the following is displayed:
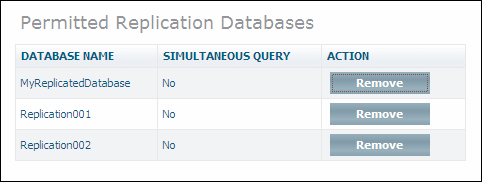
The window lists the names of the replication databases that are allowed for the master database. It also shows if simultaneous query is enabled. The buttons and are not available.