The Tamino Data Loader is used to load and unload large amounts of data in an efficient manner. This document covers the following topics:
The Tamino Data Loader ensures the efficient loading and unloading of large amounts of data into and from Tamino. Particularly the initial load of mass data during the migration phase from other data management systems that are to be replaced by Tamino (the so called legacy data) is a special challenge, which can be solved quickly and safely by the Tamino Data Loader.
Also, the Tamino Data Loader guarantees the permanent topicality of data when large amounts of data, which are for example provided regularly by external applications, are added to the database. Normal operations of the Tamino Server are not affected by this, and hence the error-free use of Tamino is ensured 24 hours a day.
The Tamino Data Loader can load not only XML data but also non-XML data, such as text, audio or video documents. These documents can of course also be subsequently unloaded.
The selection of documents to be loaded is very easily done by specifying a combination of file lists, wildcards and regular expressions. Thus, a variety of documents and files can be loaded in one single run.
Also the selection of documents to be unloaded from Tamino can be done by using search expressions, thus manipulating and reducing the data to be unloaded in a very flexible manner. It is thus possible to efficiently hand over unloaded data to follow-up applications. The Tamino Data Loader can take the role of a filter in this process and pass the unloaded data directly to an application without intermediate storage of documents.
This section gives you general information that you need before you start working with the Tamino Data Loader:
The Tamino Data Loader has two interfaces that provide the same functionality: a command line interface and a graphical user interface. On a Windows platform, the command line interface is available in the submenu of Tamino, whereas the graphical interface is started from the Tamino Manager. The Tamino Manager is also available in Tamino's submenu. On UNIX platforms, a script is available. See the startup procedures for your platform as described in the section Starting Tamino > Starting Tamino on UNIX Systems for details.
The Tamino Data Loader needs an active Tamino Server with the appropriate collection and doctype defined into which the documents are to be loaded, or from which they will be unloaded. For information about collections and doctypes, see the Getting Started document. The collection and doctype need to be defined before the data loading can start. This can be done using the Schema Editor.
By default, the Tamino Data Loader exclusively locks the complete
doctype when loading data. This means that queries and all other Tamino
operations on this doctype will be refused. However, the Tamino Data Loader
provides a parameter called concurrentwrite that allows
concurrent read and write access to the doctype while data is loaded. In the
graphical interface, you can switch the parameter on or off by simply
activating or deactivating a button. In the command line interface, you can
explicitly specify the parameter concurrentwrite.
It is possible to cancel an inactive data loading operation with the
function ino:CancelMassLoad of the X-Machine
-admin command. For further information, see the
documentation about the
X-Machine _admin command.
To use the Tamino Data Loader from the command line, open the command
line interface as described in the startup procedures for your platform as
described in the section Starting Tamino.
Use the command inoload with the appropriate
parameters (consisting of a keyword and an option) to start data loading. To
list the online help texts for the parameters, enter inoload -help
at the prompt.
The command line syntax is:
inoload [-keyword [option]]...
Note that there is a minus sign before the keyword, and a space between keyword and option. Keywords and options are not case sensitive.
Here is an example for starting the Tamino Data Loader from the command line interface:
![]() To start the Data Loader from the command line
To start the Data Loader from the command line
At the prompt, enter for example the following command:
inoload -database my-database -user [Johnid] -collection Hospital/patient -input abc.xml -norejects -log xyz.xml
Note:
Generally, it is possible to use wildcards in filenames. Wildcard
expansion depends on the operating system or shell. However, do not use blanks
in pathnames when using wildcards. Combining blanks and wildcards in pathnames
leads to errors.
In the following, you will find a detailed description of the parameters that are available:
| Parameter Name and Syntax | Default Value |
|---|---|
| -function [load|unload|delete|define|undefine|unloadschema] | load |
| -database database name | none |
| -server machine name:XML port | none |
| -user uid | if not provided, anonymous |
| -password password | none |
| -log log filename | STDERR (standard error) |
| -version | none |
| -verbose | none |
| -quiet | none |
| -help or -h | none |
This parameter specifies which function you want to use
(load or unload data, delete data, define, undefine or unload a schema or
doctype). The default value is load (which can be
omitted for load operations).
This parameter specifies the name of the Tamino database. It is a
mandatory parameter without a default value. For example: -database
my-database
This parameter specifies the name of the machine where the Tamino
Server is running. The port is the XML port of the database and can be found in
the Tamino Manager under . It is a mandatory parameter
without a default value. The parameter server has the
same meaning as (and is mutually exclusive to) the parameter
database. It is provided for platforms where only TCP/IP
communication is available.
This parameter specifies the Tamino user identification. If it is not provided, the user remains anonymous. If Tamino Security is used, it is a mandatory parameter.
This parameter specifies the password for the Tamino user identification, if a user identification is specified.
This parameter specifies whether to write a file with processing information (log messages). It also specifies the filename of the log file. The log file is in Tamino response format.
This parameter shows the current version of the Tamino Data Loader.
This parameter specifies that all messages are written to the log file.
With this parameter, only important error messages are written to the log file. If you specify this parameter, only important error messages are written.
With this parameter, online help is displayed.
| Parameter Name and Syntax | Default Value |
|---|---|
| -collection collection/doctype | none |
| -input input filespec | STDIN (standard input) |
| -norejects | tolerate having rejected documents |
| -mediatype media type | none |
| -docname [none|full|filename|autoext] | autoext |
| -concurrentwrite | no concurrent read/write |
This parameter specifies the collection name and doctype to load data into. It is a mandatory parameter.
This parameter specifies the input for the load operation. As input, it is possible to enter a filename or a list of filenames, separated by a space. Note that it is possible to use wildcards in filenames. However, do not use blanks in pathnames when using wildcards. Combining blanks and wildcards in pathnames leads to errors. If no input parameter is provided, then the input is assumed to come from standard input.
Files that cannot be loaded by the Tamino Data Loader are called rejected files. When the Data Loader finds a file to be rejected during the load process, the file is renamed and a copy of it placed in the same directory as the input file (unless it is a read-only device, such as a CD-ROM). The new file name consists of the original file name plus the string -mlderr, followed by the process id, using the following format: input filename-mlderrpid.input filename ext. Files that contain only one document do not produce rejected files.
This parameter specifies that rejected documents are not tolerated while loading. If it is used and an error occurs, the mass loading is stopped with no documents being loaded, and the collection is left in the same state as before the load operation started. Rejected documents are written to the directory where also the files to be loaded reside.
This parameter specifies a text string for a valid media type. Information about valid media types can be found in the section Known Media Types.
This parameter
specifies how to generate the ino:docname on the basis of the corresponding
filename for load operations. The ino.docname is the identifier of a loaded
document. When storing documents and other data in Tamino, Tamino allows
assigning a document name to such an object. This name is stored in the
internal attribute ino:docname. The following
values are available:
| Value of parameter for docname | Description (for load operations) |
|---|---|
| none | No ino:docname is created for the documents in Tamino. The media type is set if the file extension is known to Tamino. If no file extension is found, the media type is not set. If a media type is explicitly specified as parameter, that media type is set for the document. |
| full | The ino:docname is set to the filename including its path. The media type is set if the file extension is known to Tamino. If no file extension is found, the media type is not set. If a media type is explicitly specified as parameter, that media type is set for the document. |
| filename | The ino:docname is set to the filename without the path but including the file extension, if one exists. The media type is set if the file extension is known to Tamino. If no file extension is found, the media type is not set. If a media type is explicitly specified as parameter, that media type is set for the document. |
| autoext | The ino:docname is set to the filename without the path and without the file extension. If an extension exists and the extension is known to Tamino, the corresponding media type is set. If the extension is not known to Tamino, the extension is used as media type, where the character sequences %2E and %2F are replaced by . (dot) and / (slash) respectively in the media type name. If the extension #nomimetype is found, no media type will be set |
This parameter specifies that the Data Loader allows other clients to have concurrent read and write access to the doctype while data is being loaded.
| Parameter Name and Syntax | Default Value |
|---|---|
| -collection collection/doctypename | none |
| -docname [none|full|filename|autoext] | autoext |
| -output output filespec | STDOUT (standard output) |
| -outputformat [singlefile|multifiles] | singlefile |
| -filter | no filter (unload all) |
| -concurrentwrite | no concurrent read/write |
This parameter specifies the collection and doctype to unload data from. It is mandatory.
This parameter specifies how to generate the filename on the basis of the ino:docname for unload operations. Existing files are overwritten. The following values are available:
| Value of parameter for docname | Description (for unload operations) |
|---|---|
| none | The filename of the stored document is created from the ino:id as "#doc" + ino:id. The filename is followed by an extension if a media type is set for that document and if Tamino knows an extension for that media type. If the document is stored in an XML doctype, then .xml is always used as the extension. |
| full | The filename of the stored document is created
from ino:docname, where that may also include creation of subdirectories, if
paths are part of the filename. If the parameter output
is set, only the filename without the path is used for storing the documents.
If the document being unloaded does not have an ino:docname, the filename of
the stored document is created from the ino:id as "#doc" + ino:id. The filename
is followed by an extension if a media type is set for that document and if
Tamino knows an extension for that media type. If the document is stored in an
XML doctype, then .xml is always used as the extension.
|
| filename | The filename of the stored document is created from ino:docname, where any paths are stripped if they exist. If the document being unloaded does not have an ino:docname, the filename of the stored document is created from the ino:id as "#doc" + ino:id. The filename is followed by an extension if a media type is set for that document and if Tamino knows an extension for that media type. If the document is stored in an XML doctype, then .xml is always used as the extension. |
| autoext | The filename of the stored document is created from ino:docname, where any paths are stripped if they exist. If the ino:docname does not include a file extension, an extension is automatically added to the filename if an extension is known for that media type. If the document being unloaded does not have an ino:docname, the filename of the stored document is created from the ino:id as "#doc" + ino:id. The filename is followed by an extension if a media type is set for that document. If Tamino knows an extension for that media type, that extension is used, otherwise the full media type name is used as the extension, where the special characters . (dot) and / (slash) are replaced by %2E and %2F respectively. If the ino:docname contains an extension, but there is no media type set for the document, the extension #nomimetype is appended, which will result in no media type being set when that file is loaded into Tamino again with the autoext option. |
Note:
The ino:docname is not necessarily a valid filename (depending on
the platform you are using). Unloading documents with the ino:docname can thus
fail. If the ino:docname has a slash or backslash (/ or \), it is substituted
by a hash (#).
This parameter specifies the file or directory name, to which the unloaded documents are to be written.
This parameter specifies whether to write the unloaded documents into
one single file, or each document to a separate file. The value
multifile is only available in connection with an output
file specification of a directory. The documents are written into several
files, one for each document.
This parameter specifies a filter to select the documents to be
unloaded. Use a query string if you want to assemble the data to be unloaded.
The filter expression has to start and end with square brackets [], for
example: -filter [filterexpression]. Use X-Query syntax for the
filter expression.
This parameter specifies that the Data Loader allows other clients to have concurrent read and write access to the doctype while data is being unloaded.
| Parameter Name and Syntax | Default Value |
|---|---|
| -collection collection/doctypename | none |
| -filter | no filter (delete all) |
| -concurrentwrite | no concurrent read/write |
If no filter is specified, the delete function deletes all documents. Depending on the amount of data to be deleted, the process can take some time. So if you want to delete all files, you can use the undefine function with a collection name or doctype name specified (all documents belonging to the doctype or collections are also deleted) and then redefine the collection/doctype (see Undefine Parameters.
This parameter specifies the name of the collection and/or doctype, from which data is to be deleted.
This parameter specifies a filter to select the documents to be
deleted. Use a query string if you want to select the data to be deleted. The
filter expression has to start and end with square brackets [], for
example: -filter [filterexpression]. Use X-Query syntax for the
filter expression.
This parameter specifies that the Data Loader allows other clients to have concurrent read and write access to the doctype while data is being deleted.
This parameter specifies the file or directory containing schemas to be defined. The default value is STDIN.
If you define a list of schemas (e.g. with wildcards), the definition document has to be defined first, then the other schemas.
The undefine function undefines a collection, schema and/or doctype and deletes all documents that belong to the collection/doctype (see also Delete Parameters. The collection name is mandatory; schema and doctype names are optional. If you want to delete all files, you can use the undefine function with a collection name or doctype name specified (all documents belonging to the doctype or collections are also deleted) and then redefine the collection/doctype.
This parameter specifies the name of the collection, schema and/or doctype to be undefined.
The option unloadSchema unloads the specified
schema into a single file. The name of the file into which the schema is
unloaded is collectionname#schemaname.tsd. If all
doctypes are unloaded, an additional schema - the so-called definition
document - is
unloaded into a file, containing attributes of the collection. The filename is
collectionname.tsd. In combination with
unloadSchema, the doctype does not need to be specified;
all schemas in the specified collection will be unloaded.
It is not possible to unload single doctypes that belong to one schema.
The following parameters are available:
This parameter specifies the collection and schema to be unloaded. It is a mandatory parameter.
This parameter specifies where to write the unloaded schema file to. The default value is STDOUT.
Data loading and unloading can also be done with a graphical user interface in the Tamino Manager. If you select a doctype in a collection, using , the option is available in the context menu.
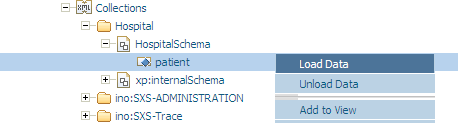
Choose from the context menu to display the following screen in the right window of the Tamino Manager:
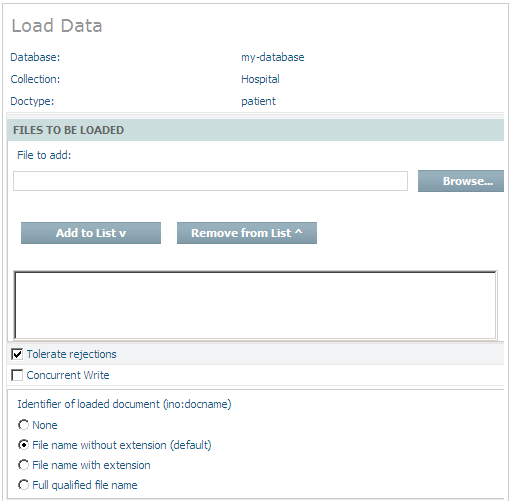
The upper part of the window shows information about the database, collection and doctype into which the data is to be loaded. The part below that information is used for entering information about the load operation. The following fields are available:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| File to add | Enter the filename of the file(s) to be loaded or browse to the file location by choosing the button. |
| Add to List / Remove from List | Choose this button to add the file(s) to be loaded to the list box in the middle of the window. With the button, files can be removed from the list. To scroll the list, use the and buttons. |
| Tolerate rejections | Tolerate having rejected documents. If this
option is checked, the parameter norejects is not used.
Thus invalid documents are rejected but the load is continued. If this option
is not checked, the parameter norejects is used. Thus in
the case of invalid data, the load operation is stopped, and the doctype is
reset to the state before the load (if Concurrent Write is not
checked).
|
| Concurrent Write | Select this option if you want to have read/write access to the database while loading data. |
| Identifier of loaded document (ino:docname) | When storing documents and other data in Tamino,
Tamino allows assigning a document name to such an object. This name is stored
in the internal attribute ino:docname. This
method of object identification is also used for non-XML data. The following
options are available:
|
Specify input as appropriate in the fields of the screen and choose the button to start the load operation.
When an error occurs in the processing of a document, the line and
column numbers given in the error report will be relative to the load document
that was in error (line and column computation start at the tag
ino:object). Processing messages are written to the
log file. The log file is a well-formed XML document.
If you want to load data and are using the Tamino X-Node feature, insert or update operations are only possible with the concurrent read/write option being switched on. This means that it is not possible to insert data into external databases or to update them if you are using the Tamino Data Loader in default mode, which is without concurrent read/write. You need to explicitly switch the parameter on. The same applies for triggers.
Unloading data, however, is always possible, with or without concurrent read/write.
Generally, however, it is only possible to unload X-Node documents that have been saved via Tamino and thus have an ino:id. X-Node documents that have not been saved via Tamino and have no ino:id cannot be unloaded with the Data Loader.
Tamino also supports another method of loading data, which is to use one single input file which consists of all the files you want to load. In this case, the input file must have the following format (the output file format is the same):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ino:request xmlns:ino="http://namespaces.softwareag.com/tamino/response2">
<ino:object [ino:docname="docname"] [ino:id="id"] >
<!-- document contents for first XML document including PI's and Comments -->
</ino:object >
<ino:object [ino:docname="docname"] [ino:id="id"] >
<!-- document contents for second XML document including PI's and Comments -->
</ino:object >
.....
</ino:request>
The square brackets ("[", "]") around the
ino:docname and
ino:id attribute indicate that the attributes
are optional.
The XML prolog may be specified only once at the start of the input
file. The prolog and entities will be used by the Data Loader, but are not
stored by Tamino. If there is no XML prolog, then the file must have a
character encoding of UTF-8, UTF-16, or UTF-32. Make sure that all occurrences
of ino:docname attributes are unique. Delivering duplicate
ino:docname attributes leads to an error
message, stating that an internal error has occurred, followed by a rollback of
the whole loading process.
If you want to keep the doctype declaration of your documents to be loaded, it must be wrapped in the following way:
<ino:object> <ino:documentprolog> <![CDATA[ <!-- here comes the doctype declaration --> ...]]> </ino:documentprolog> <rootelement> ... </rootelement> </ino:object>
This format guarantees that the input file is still well-formed.
The following lists are used by the Tamino Data Loader to determine the file extension for loading and unloading files:
Input files: Using the file extension to determine the media type
Output files: Using the media type to determine the file extension
The following list is used to determine the media type, using the file extension, for loading data:
| File Extension | Media Type |
| ai | application/postscript |
| aif | audio/x-aiff |
| aifc | audio/x-aiff |
| aiff | audio/x-aiff |
| asc | text/plain |
| au | audio/basic |
| avi | video/x-msvideo |
| avx | video/x-msvideo |
| bcpio | application/x-bcpio |
| bin | application/octet-stream |
| bmp | image/x-bmp |
| cdf | application/x-netcdf |
| class | application/octet-stream |
| cpio | application/x-cpio |
| cpt | application/mac-compactpro |
| csh | application/x-csh |
| css | text/css |
| dcr | application/x-director |
| dir | application/x-director |
| dl | video/x-dl |
| dll | application/octet-stream |
| dms | application/octet-stream |
| doc | application/msword |
| dvi | application/x-dvi |
| dxr | application/x-director |
| eps | application/postscript |
| etx | text/x-setext |
| exe | application/octet-stream |
| ez | application/andrew-inset |
| flc | video/x-fli |
| fli | video/x-fli |
| gif | image/gif |
| gtar | application/x-gtar |
| gz | application/x-gzip |
| hdf | application/x-hdf |
| hqx | application/mac-binhex40 |
| htm | text/html |
| html | text/html |
| ice | x-conference/x-cooltalk |
| ico | image/x-ico |
| ief | image/ief |
| iges | model/iges |
| igs | model/iges |
| jpe | image/jpeg |
| jpeg | image/jpeg |
| jpg | image/jpeg |
| js | application/x-javascript |
| latex | application/x-latex |
| lha | application/octet-stream |
| lzh | application/octet-stream |
| m3u | audio/x-mpegurl |
| man | application/x-troff-man |
| me | application/x-troff-me |
| mesh | model/mesh |
| mid | audio/midi |
| midi | audio/midi |
| mov | video/quicktime |
| movie | video/x-sgi-movie |
| mp2 | audio/mpeg |
| mp3 | audio/mpeg |
| mpe | video/mpeg |
| mpeg | video/mpeg |
| mpg | video/mpeg |
| mpga | audio/mpeg |
| ms | application/x-troff-ms |
| msh | model/mesh |
| mv | video/x-sgi-movie |
| mxu | video/vnd.mpegurl |
| nc | application/x-netcdf |
| oda | application/oda |
| pbm | image/x-portable-bitmap |
| pdb | chemical/x-pdb |
| application/pdf | |
| pgm | image/x-portable-graymap |
| pgn | application/x-chess-pgn |
| png | image/png |
| pnm | image/x-portable-anymap |
| ppm | image/x-portable-pixmap |
| ppt | application/vnd.ms-powerpoint |
| ps | application/postscript |
| qt | video/quicktime |
| ra | audio/x-realaudio |
| ram | audio/x-pn-realaudio |
| ras | image/x-cmu-raster |
| rgb | image/x-rgb |
| rm | audio/x-pn-realaudio |
| roff | application/x-troff |
| rpm | audio/x-pn-realaudio-plugin |
| rtf | text/rtf |
| rtx | text/richtext |
| sgm | text/sgml |
| sgml | text/sgml |
| sh | application/x-sh |
| shar | application/x-shar |
| silo | model/mesh |
| sit | application/x-stuffit |
| skd | application/x-koan |
| skm | application/x-koan |
| skp | application/x-koan |
| skt | application/x-koan |
| snd | audio/basic |
| so | application/octet-stream |
| spl | application/x-futuresplash |
| src | application/x-wais-source |
| stc | application/vnd.sun.xml.calc.template |
| std | application/vnd.sun.xml.draw.template |
| sti | application/vnd.sun.xml.impress.template |
| stw | application/vnd.sun.xml.writer.template |
| sv4cpio | application/x-sv4cpio |
| sv4crc | application/x-sv4crc |
| swf | application/x-shockwave-flash |
| sxc | application/vnd.sun.xml.calc |
| sxd | application/vnd.sun.xml.draw |
| sxg | application/vnd.sun.xml.writer.global |
| sxi | application/vnd.sun.xml.impress |
| sxm | application/vnd.sun.xml.math |
| sxw | application/vnd.sun.xml.writer |
| t | application/x-troff |
| tar | application/x-tar |
| tcl | application/x-tcl |
| tex | application/x-tex |
| texi | application/x-texinfo |
| texinfo | application/x-texinfo |
| tgz | application/x-gzip |
| tif | image/tiff |
| tiff | image/tiff |
| tr | application/x-troff |
| tsv | text/tab-separated-values |
| txt | text/plain |
| ustar | application/x-ustar |
| vcd | application/x-cdlink |
| vfw | video/x-msvideo |
| vrml | model/vrml |
| wav | audio/x-wav |
| wbmp | image/vnd.wap.wbmp |
| wbxml | application/vnd.wap.wbxml |
| wml | text/vnd.wap.wml |
| wmlc | application/vnd.wap.wmlc |
| wmls | text/vnd.wap.wmlscript |
| wmlsc | application/vnd.wap.wmlscriptc |
| wp | application/wordperfect5.1 |
| wrl | model/vrml |
| xbm | image/x-xbitmap |
| xls | application/vnd.ms-excel |
| xml | text/xml |
| xpm | image/x-xpixmap |
| xsl | text/xml |
| xwd | image/x-xwindowdump |
| xyz | chemical/x-xyz |
| zip | application/zip |
The following list is used to determine the file extension, using the media type, for unloading data:
| Media Type | File Extension |
| application/andrew-inset | ez |
| application/mac-binhex40 | hqx |
| application/mac-compactpro | cpt |
| application/msword | doc |
| application/octet-stream | bin |
| application/oda | oda |
| application/pdf | |
| application/postscript | ps |
| application/vnd.ms-excel | xls |
| application/vnd.ms-powerpoint | ppt |
| application/vnd.sun.xml.calc | sxc |
| application/vnd.sun.xml.calc.template | stc |
| application/vnd.sun.xml.draw | sxd |
| application/vnd.sun.xml.draw.template | std |
| application/vnd.sun.xml.impress | sxi |
| application/vnd.sun.xml.impress.template | sti |
| application/vnd.sun.xml.math | sxm |
| application/vnd.sun.xml.writer | sxw |
| application/vnd.sun.xml.writer.global | sxg |
| application/vnd.sun.xml.writer.template | stw |
| application/vnd.wap.wbxml | wbxml |
| application/vnd.wap.wmlc | wmlc |
| application/vnd.wap.wmlscriptc | wmlsc |
| application/wordperfect5.1 | wp |
| application/x-bcpio | bcpio |
| application/x-cdlink | vcd |
| application/x-chess-pgn | pgn |
| application/x-cpio | cpio |
| application/x-csh | csh |
| application/x-director | dir |
| application/x-dvi | dvi |
| application/x-futuresplash | spl |
| application/x-gtar | gtar |
| application/x-gzip | gz |
| application/x-javascript | js |
| application/x-koan | skd |
| application/x-latex | latex |
| application/x-netcdf | cdf |
| application/x-sh | sh |
| application/x-shar | shar |
| application/x-shockwave-flash | swf |
| application/x-stuffit | sit |
| application/x-sv4cpio | sv4cpio |
| application/x-sv4crc | sv4crc |
| application/x-tar | tar |
| application/x-tcl | tcl |
| application/x-tex | tex |
| application/x-texinfo | texinfo |
| application/x-troff | roff |
| application/x-troff-man | man |
| application/x-troff-me | me |
| application/x-troff-ms | ms |
| application/x-ustar | ustar |
| application/x-wais-source | src |
| application/zip | zip |
| audio/basic | au |
| audio/midi | midi |
| audio/mpeg | mp3 |
| audio/x-aiff | aiff |
| audio/x-mpegurl | m3u |
| audio/x-pn-realaudio | ram |
| audio/x-pn-realaudio-plugin | rpm |
| audio/x-realaudio | ra |
| audio/x-wav | wav |
| chemical/x-pdb | pdb |
| chemical/x-xyz | xyz |
| image/gif | gif |
| image/ief | ief |
| image/jpeg | jpg |
| image/png | png |
| image/tiff | tif |
| image/vnd.wap.wbmp | wbmp |
| image/x-bmp | bmp |
| image/x-cmu-raster | ras |
| image/x-ico | ico |
| image/x-portable-anymap | pnm |
| image/x-portable-bitmap | pbm |
| image/x-portable-graymap | pgm |
| image/x-portable-pixmap | ppm |
| image/x-rgb | rgb |
| image/x-xbitmap | xbm |
| image/x-xwindowdump | xwd |
| model/iges | iges |
| model/mesh | mesh |
| model/vrml | vrml |
| text/css | css |
| text/html | html |
| text/plain | txt |
| text/richtext | rtx |
| text/rtf | rtf |
| text/sgml | sgml |
| text/tab-separated-values | tsv |
| text/vnd.wap.wml | wml |
| text/vnd.wap.wmlscript | wmls |
| text/xml | xml |
| text/x-setext | etx |
| video/mpeg | mpeg |
| video/quicktime | mov |
| video/vnd.mpegurl | mxu |
| video/x-dl | dl |
| video/x-fli | flc |
| video/x-fli | fli |
| video/x-msvideo | avi |
| video/x-sgi-movie | movie |
| x-conference/x-cooltalk | ice |