How a My webMethods Server Cluster Works
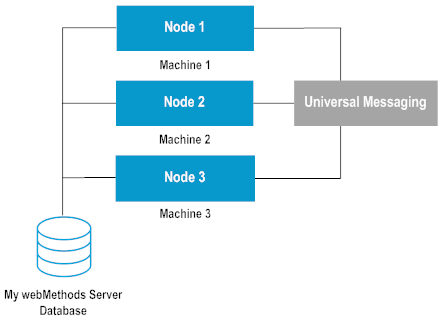
A My webMethods Server cluster is an active/active environment in which multiple server instances run at the same time, sharing the My webMethods Server database. A My webMethods Server cluster achieves high scalability by distributing the workload among multiple servers. This model is different from an active/passive environment, which makes use of a standby server. A My webMethods Server cluster achieves high availability through the use of shared resources, allowing the cluster to continue to function when a node is taken out of service.
To create a cluster, you need to install an instance of My webMethods Server on each machine in the cluster. All nodes of the cluster share the same My webMethods Server database, which contains shared configuration information and data, stored by the system content service.
The system content service stores and retrieves files and objects published by webMethods users and applications, running on My webMethods Server. The system content service is installed with My webMethods Server and does not require additional configuration. Published content is available to all nodes in the cluster.
You should install the same set of webMethods applications (such as Task Engine), My webMethods user interfaces, and language packs on each node in the cluster. If an application is not installed on a particular node, the components of the application are not functional on that node.
The nodes in the cluster exchange information when they run, using the following channels:

The
My webMethods Server database - cluster bookkeeping is maintained this way.

HTTP - when a cluster node delegates the execution of a command to another node, it uses the HTTP port of the target server.

The
Universal Messaging server -
My webMethods Server nodes use the
Universal Messaging server to exchange JMS events for cache synchronization between the nodes.
Cluster architecture