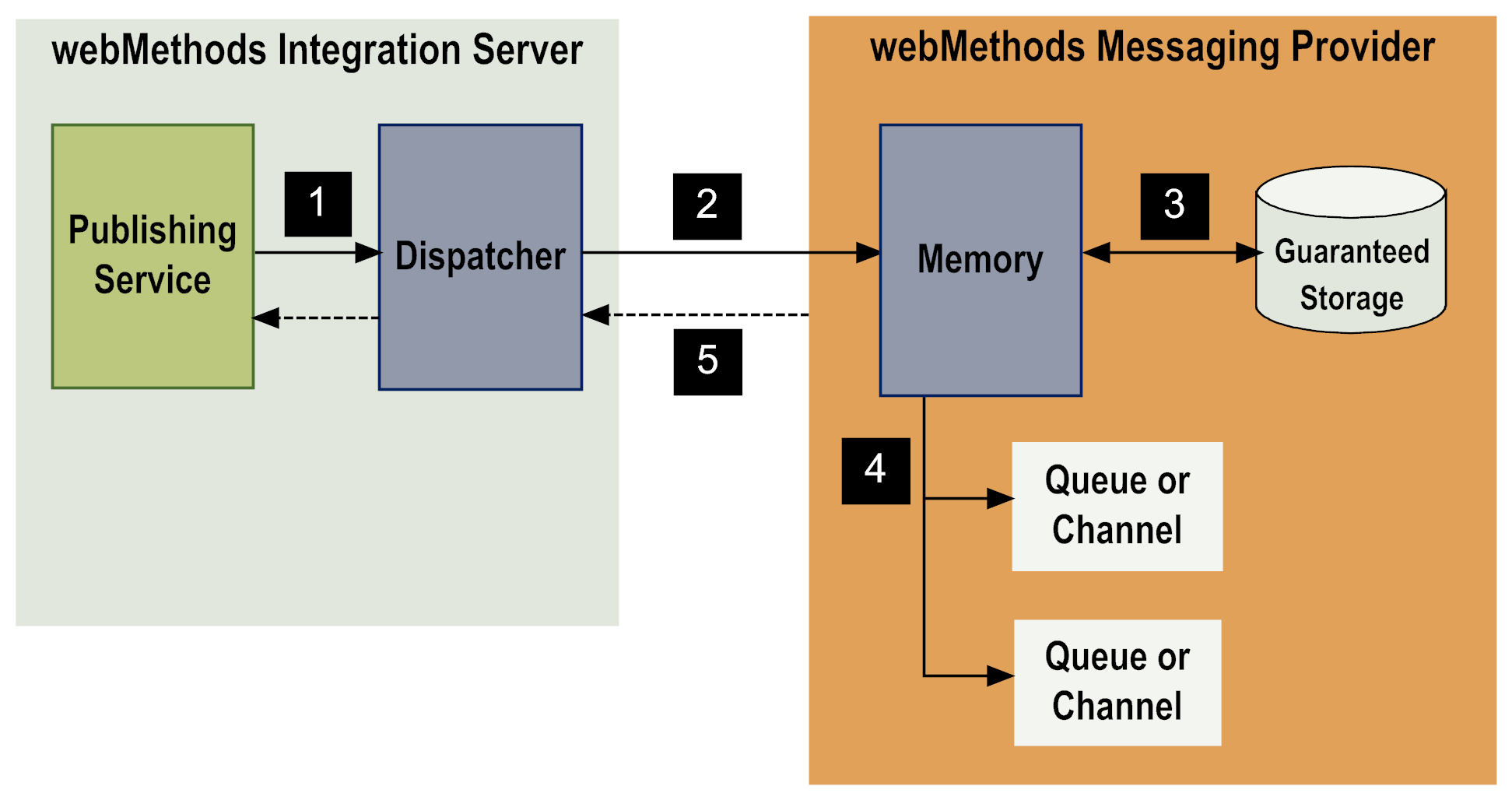
Step | Description |
1 | A publishing service sends a document to the dispatcher (or an adapter notification publishes a document when an event occurs on the resource the adapter monitors). If validation is configured for the publishable document type, Integration Server validates the document against its publishable document type before sending the document to the dispatcher. If the document is not valid, the service returns an exception specifying the validation error. |
2 | The dispatcher sends the document to the webMethods messaging provider. Note: If the webMethods messaging provider is not available, the document is guaranteed, and use of the client side queue is configured, the dispatcher routes the document to the outbound document store. For more information, see Publishing Documents When the webMethods Messaging Provider Is Not Available. |
3 | The webMethods messaging provider examines the storage type for the document to determine how to store the document. |
4 | The webMethods messaging provider routes the document to subscribers by doing one of the following: The Broker places documents in a queue for a subscriber. Universal Messaging places documents on a channel. A document remains enqueued on the webMethods messaging provider until it is picked up by the subscriber. If the time-to-live for the document elapses, the webMethods messaging provider discards the document. For more information about setting time-to-live for a publishable document type, see webMethods Service Development Help. If there are no subscribers for the document and the messaging provider has been configured to handle dead letters (sometimes called dead events), the webMethods messaging provider routes the document to the dead letter queue or dead event store. For more information about configuring the messaging provider to handle documents for which there are no subscribers, refer to the documentation for the webMethods messaging provider that is in use. Note: If the Broker is the webMethods messaging provider and a deadletter subscription exists for the document, the Broker deposits the document in the queue containing the deadletter subscription. For more information about creating deadletter subscriptions, see webMethods Service Development Help. |
5 | Integration Server returns control to the publishing service, which executes the next step. |