This document describes how to generate COBOL source files from Software AG IDL files. It covers the following topics:
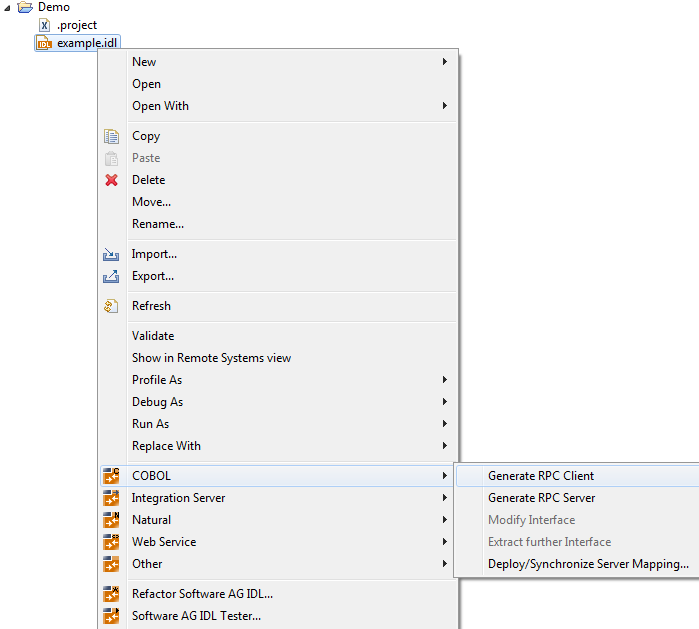
From the context menu, choose and to generate the COBOL source files.
Note:
In command-line mode, use command -cobol:client or
-cobol:server. See Using the COBOL Wrapper in Command-line Mode. Note that
existing files will always be overwritten.
Results for RPC client:
The folders client and include are created as subfolders to the IDL-specific Output Folder defined in the Generation Settings - Properties.
The client folder contains the following:
client interface objects
optionally the generic RPC service module, which is only generated if the option Generate Generic RPC Service Module COBSRVI is set, see Generation and Usage of Generic RPC Service Module COBSRVI.
The include folder contains the following:
the associated copybooks
the RPC communication area copybook ERXCOMM
optionally its extension copybook ERXVSTR
optionally the copybooks COBINIT and COBEXIT
For further information on the usage of copybooks generated in this folder, see Using the Generated Copybooks.
Results for RPC server:
The folder server is created as a subfolder to the IDL-specific Output Folder defined in the Generation Settings - Properties. It contains the RPC server skeletons.
| Warning: Take care not to overwrite an existing RPC server implementation with an RPC server skeleton. We recommend moving your RPC server implementation to a different folder. |
If required, a server mapping file is generated, too. See When is a Server Mapping File Required? under Server Mapping Files for COBOL in the Designer documentation. The following dialog is displayed.
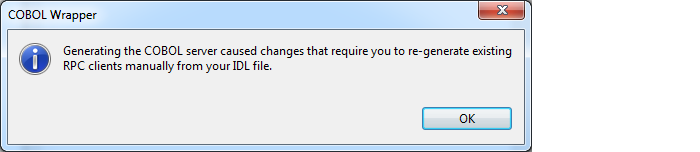
You need to rebuild all RPC clients communicating with this RPC server program. Select the appropriate wrapper (see EntireX Wrappers in the Designer documentation) and re-generate the client interface objects. For the EntireX Adapter you need to update your generated IS adapter as described under To update an existing connection in Step 3: Create or Update an Adapter Connection in the Integration Server Wrapper documentation.
This section covers the following topics:
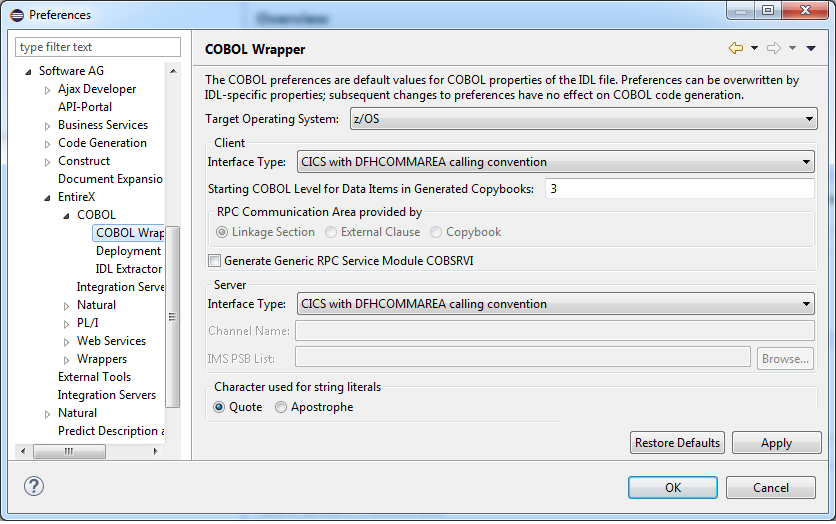
Whenever a new IDL file is created, defaults for the properties are copied from the preferences. See Generation Settings - Preferences. To set individual properties per IDL file for COBOL Wrapper generation, use the Properties wizard of the IDL file. The Target Operating System and the Interface Type are essential. They determine if other parameters such as RPC Communication Area provided by can be set or have to remain fixed. The parameter IDL-specific Output defines the location to store the source file subfolders. Target Operating System determines whether file extensions are generated or not.
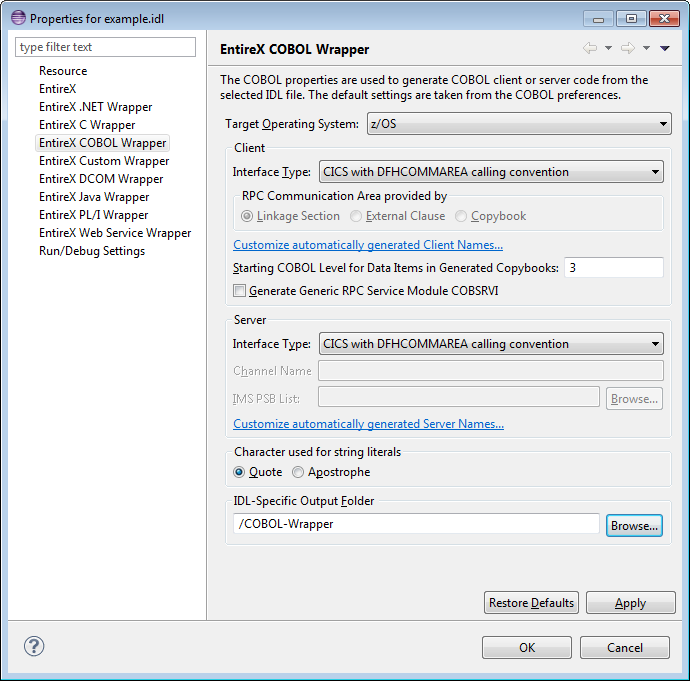
In the following, we give a detailed description of the properties that need to be set for each type of generation:
Select the target operating system for which COBOL code is to be generated. See Platform Coverage for a full list of supported operating system versions.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| z/OS | IBM z/OS operating system. |
| z/VSE | IBM z/VSE operating system. |
| BS2000 | Fujitsu Siemens BS2000 operating system. |
| IBM i | IBM i operating system. |
With this option you can specify how string literals are specified in the generated COBOL code. See your COBOL compiler documentation for information on how string literals are enclosed.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Quote | String literals will be enclosed in double quotes in the generated COBOL code. |
| Apostrophe | String literals will be enclosed in apostrophes (single quotes) in the generated COBOL code. |
This field specifies the folder where the COBOL files will be stored, by default in the same folder as the IDL file. For a non-default location, enter another folder name or choose .
| Interface Type | Target Operating System | More Information | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Calling Convention | z/OS, z/VSE | Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Calling Convention (z/OS and z/VSE).
|
1 |
| CICS with Standard Linkage Calling Convention | z/OS, z/VSE | Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for CICS with Call Interfaces (z/OS and z/VSE). | 2 |
| Batch with Standard Linkage Calling Convention | z/OS, BS2000, z/VSE, IBM i | Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for Batch (z/OS, BS2000, z/VSE and IBM i). | 2 |
| IMS BMP with Standard Linkage Calling Convention | z/OS | Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for IMS (z/OS). | 2 |
| IMS MPP with Standard Linkage Calling Convention | z/OS | Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for IMS (z/OS). | 2 |
| IDMS/DC with Standard Linkage Calling Convention | z/OS | Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for IDMS/DC with Call Interfaces (z/OS). | 2 |
Notes:
COBSRVI with a DFHCOMMAREA interface.
COBSRVI with a standard linkage interface.
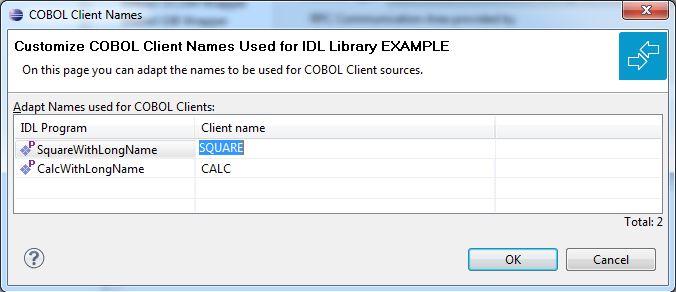
If you open the link Customize automatically generated Client Names
on the Properties page you can adapt the names for the COBOL client interface objects (subprograms).
When you call the page the first time, COBOL names are suggested based on the IDL program (program-definition)
or IDL program alias names. The page varies,
depending on whether the target COBOL environment supports long COBOL names or not:
Max. 8 characters (short names) are supported as COBOL names:
Note:
If your IDL file contains more than one IDL library, the additional column IDL Library is displayed.
Customization of client names for IBM i is the same as for z/OS and z/VSE. See z/OS and z/VSE.
Max. 30 characters are supported as COBOL names. By default, names are generated with a maximum of 8 characters (short names).
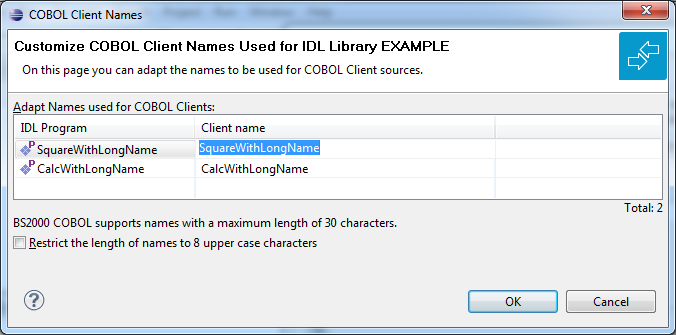
Notes:
With this option you can specify the starting COBOL level used in the generated copybooks for COBOL data items.
See Using the Generated Copybooks for syntax examples.
Specify a valid COBOL level in the range 1-49. The COBOL programming language maximum of 49 subtracted by the specified level must provide enough levels to hold all IDL levels. Note that IDL types may consume more than one COBOL level, for example:
IDL unbounded groups require a COBOL level for every dimension. If they are defined on IDL level 1, an extra COBOL level is required
IDL unbounded arrays require a COBOL level for every dimension plus one extra COBOL level
some basic (scalar) IDL data types need extra COBOL levels
Notes:
The RPC communication area copybook ERXCOMM and its extension ERXVSTR are used to specify parameters that are
needed to communicate with the broker and are not specific to client interface
objects. These are for example the broker ID, client parameters such as
userID and password and the
server address such as class/servername/service etc.
| Value | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
External Clause |
This kind of RPC communication area usage applies to the scenarios
CICS |
Batch |
IMS.
The RPC communication area copybooks are defined in the working storage section as COBOL data items with the
EXTERNAL clause in the RPC client application.
They are passed with the EXTERNAL clause to and the generated client interface object(s).
|
1 |
Linkage Section |
This kind of RPC communication area usage applies to the scenarios CICS | Batch | IMS. The RPC communication area copybooks are defined in the working storage section as COBOL data items. They are passed via additional parameter between your RPC client application and the generated client interface object(s). | 2 |
Copybook |
This kind of RPC communication area usage is available in the z/OS operating system.
Refer to the scenarios
CICS |
Batch |
IMS.
The RPC communication area copybooks are provided inside the generated client interface object(s). It is not visible
in the RPC client application - it is local to the client interface objects.
Default values are retrieved from Designer preferences or IDL-specific properties and
can be overwritten in the copybook COBINIT
(see folder include).
|
2 |
Notes:
DYNAM compiler option; for other compilers, to your compiler documentation.
The generic RPC service module COBSRVI can be optionally generated in the folder client in the container folder. It acts as a runtime for RPC communication. See Generic RPC Services Module under Introduction to the COBOL Wrapper. The module depends on target environment (CICS, Batch...), client interface type (see Client Interface Types) and operating system (z/OS, z/VSE...). Use this option to control the generation of this module.
Handling depends on the interface type:
CICS with DFHCOMMAREA calling convention
For this interface type, the generic RPC service module is installed once within CICS as a CICS program and shared by all
RPC clients using this interface type.
Details and the architecture of this scenario are described under Using the COBOL Wrapper for CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Calling Convention (z/OS and z/VSE).
Check this option if you want to install or replace the installed generic RPC service module in CICS with the version generated by the COBOL Wrapper. This makes sense in the following situations:
You have not installed the RPC examples on z/OS, because installation of this module is part of Installing RPC Examples for z/OS.
You need an update of the generic RPC service module because of a newer COBOL Wrapper version, for example an Eclipse update without mainframe update. For compile job and CICS CSD definitions see Delivered Modules for z/OS | z/VSE.
Clear this option if you have already installed the generic RPC service module in CICS (already installed RPC examples for z/OS or previous COBOL Wrapper project) and do not want to re-install it in CICS. This prevents the generation of the generic RPC service module.
The preferred approach is to check this option. This will generate the generic RPC service module. The generated module is part of your client application. Its usage is described under Using the COBOL Wrapper with a Call Interface (CICS | Batch | IMS).
Clear this option if you can reuse the generic RPC service module from a previous COBOL Wrapper project. This will prevent the generation of the generic RPC service module. It is important that Target Operating System, Client Interface Types and Characters Used for String Literals are the same.
If you open the link Customize automatically generated Server Names
on the properties page you can, adapt the names for the COBOL server (subprograms).
When you call the page the first time, COBOL names are suggested based on the IDL program
(program-definition) or IDL program alias names.
For further details on customizing names for the server side, see the platform-specific section under
Customize Automatically Generated Client Names; the information here also applies to server names:
Notes:
| Interface Type | Target Operating System | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CICS with DFHCOMMAREA calling convention | z/OS, z/VSE | Use this option if you want to build a CICS RPC server application with a DFHCOMMAREA interface.
Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Calling Convention (z/OS and z/VSE).
|
| CICS with Channel Container calling convention | z/OS | Use this option if you want to build a CICS RPC server application with a channel container interface. To specify a channel name, see Channel Name. Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for CICS with Channel Container Calling Convention (z/OS). |
| CICS with DFHCOMMAREA large buffer interface | z/OS, z/VSE | Use this option if you want to build a CICS RPC server application with a large buffer interface.
Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Large Buffer Interface (z/OS and z/VSE).
|
| Batch with standard linkage calling convention | z/OS, BS2000, IBM i | Use this option if you want to build an application for an RPC Server for Batch. Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for Batch (z/OS, BS2000 and IBM i). |
| IMS BMP with standard linkage calling convention | z/OS | Use this option if you want to build an RPC Server for IMS application for IMS BMP mode (no MPP) with standard call interfaces. If your server uses PCB pointers, see IMS PSB List below. Follow the steps under Using the COBOL Wrapper for IMS BMP (z/OS). |
IMS PSB List applies to the server interface type "IMS BMP with standard linkage calling convention" only. If your server uses PCB pointers and requires that they are passed through the linkage section, an IMS PSB list is required. Your IDL must comply with the rules under IMS PCB Pointer IDL Rules. If no PCB pointers are required, omit the IMS PSB list. See Server Interface Types for more information.
Channel Name applies to the server interface type "CICS with Channel Container calling convention" only.
If a channel name is specified, the server is
called with the given channel name
generated with COBOL code to check for channel name validity.
If no channel name is specified, the server is
called with the "EntireXChannel" channel name
generated without COBOL code to check for channel name validity.
Your IDL must comply with the rules described under CICS Channel Container IDL Rules. See Server Interface Types for more information.
Use the Preferences page of the COBOL Wrapper to set the workspace defaults for the target operating system, interface types etc. The settings (except Type of COBOL mapping) are used as the defaults for the IDL properties when a new IDL file is created; see Generation Settings - Properties.