RPC client applications can use Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) as the transport medium. The term "SSL" in this document refers to both SSL and TLS. RPC-based clients are always SSL clients. The SSL server can be either the EntireX Broker, Broker SSL Agent, or Direct RPC in webMethods Integration Server (IS inbound). For an introduction see SSL/TLS and Certificates with EntireX in the Platform-independent Administration documentation. This document describes using SSL with the COBOL Wrapper on the following platforms:
SSL delivered on a z/OS mainframe will typically use the Resource Access Control Facility (RACF) as the certificate authority (CA). Certificates managed by RACF can only be accessed through the RACF keyring container. A keyring is a collection of certificates that identify a networking trust relationship (also called a trust policy). In an SSL client/server network environment, entities identify themselves using digital certificates called through a keyring. Server applications on z/OS that wish to establish network connections to other entities can use keyrings and their certificate contents to determine the trustworthiness of the client or peer entity. Note that certificates can belong to more than one keyring, and you can assign different users to the same keyring. Because of the way RACF internally references certificates, they must be uniquely identifiable by owner and label, and also unique by serial number plus data set name (DSN).
For establishing an SSL connection on z/OS, IBM's Application Transparent Transport Layer Security (AT-TLS) can be used, where the establishment of the SSL connection is pushed down the stack into the TCP layer.
With the COBOL Wrapper you can use IBM's Application Transparent Transport Layer Security (AT-TLS), where the establishment of the SSL connection is pushed down the stack into the TCP layer.
Configure the AT-TLS rules for the policy agent (PAGENT) ![]() using an appropriate client
using an appropriate client ![]() and the z/OS Management Facility (z/OSMF)
and the z/OS Management Facility (z/OSMF) ![]() .
Together with SSL parameters (to provide certificates stored in z/OS as RACF keyrings) define AT-TLS rules, for example by
using the application
.
Together with SSL parameters (to provide certificates stored in z/OS as RACF keyrings) define AT-TLS rules, for example by
using the application ![]() job name and remote TCP port number.
If the rules match, the TCP connection is turned into an SSL connection
job name and remote TCP port number.
If the rules match, the TCP connection is turned into an SSL connection ![]() .
Refer to your IBM documentation for more information, for example the IBM Redbook Communications Server for z/OS VxRy TCP/IP Implementation Volume 4: Security and Policy-Based Networking.
.
Refer to your IBM documentation for more information, for example the IBM Redbook Communications Server for z/OS VxRy TCP/IP Implementation Volume 4: Security and Policy-Based Networking.
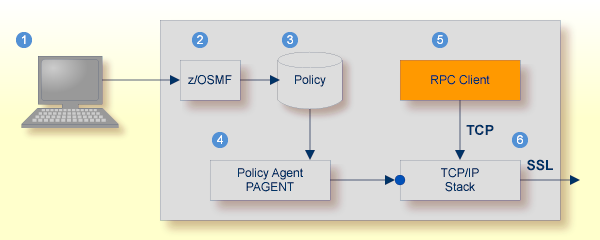
| Client to interact with z/OS Management Facility (z/OSMF). | |
| AT-TLS rules are defined with z/OSMF policy management. | |
| Policy Repository with AT-TLS rules stored as z/OS files. | |
| Policy Agent, MVS task PAGENT, provides AT-TLS rules through a policy enforcement point (PEP) to TCP/IP stack. | |
| Application using TCP connection. | |
| If AT-TLS rules match, the TCP connection is turned into an SSL connection. |
Notes:
 To set up SSL with AT-TLS
To set up SSL with AT-TLS
To operate with SSL, certificates need to be provided and maintained. Depending on the platform, Software AG provides default certificates, but we strongly recommend that you create your own. See SSL/TLS Sample Certificates Delivered with EntireX in the EntireX Security documentation.
Set up the RPC component for a TCP/IP connection. On mainframe platforms, use Transport-method-style Broker ID. Example:
ETB024:1699:TCP
Configure AT-TLS to turn the TCP/IP connection to an SSL connection, see above.
Make sure the SSL server to which the RPC component connects is prepared for SSL connections as well. The SSL server can be EntireX Broker, Broker SSL Agent, or Direct RPC in webMethods Integration Server (IS inbound). See:
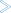
Establishing an SSL connection on z/VSE requires BSI's Automatic Transport Layer Security (ATLS). This facility is similar to z/OS Application Transparent - Transport Layer Security (AT-TLS). ATLS is supported by the BSI stack only.
Together with SSL parameters (to provide certificates), define ATLS rules for socket interception in the ATLS daemon startup
job BSTTATLS ![]() .
If the rules match, the socket connection is turned into an SSL connection
.
If the rules match, the socket connection is turned into an SSL connection ![]() .
Refer to your IBM documentation for further information. For an overview, refer to the IBM Redbook Enhanced Networking on IBM z/VSE; for a more detailed description, refer to BSI SSL Installation, Programming and User's Guide.
.
Refer to your IBM documentation for further information. For an overview, refer to the IBM Redbook Enhanced Networking on IBM z/VSE; for a more detailed description, refer to BSI SSL Installation, Programming and User's Guide.
| BSI TCP/IP Stack, either BSTTINET (IPv4) or BSTT6NET (IPv6). | |
| ATLS rules are defined manually. See Sample ATLS Daemon Configuration below. | |
| BSTTATLS is associated with a TCP/IP stack. | |
| Application using TCP connection. | |
| BSTTATLS intercepts outbound TCP connection and converts it to SSL connection. For inbound, SSL connections can also be intercepted and converted to TCP connections. |
 To set up SSL with ATLS
To set up SSL with ATLS
To operate with SSL, certificates need to be provided and maintained. Depending on the platform, Software AG provides default certificates, but we strongly recommend that you create your own. See SSL/TLS Sample Certificates Delivered with EntireX in the EntireX Security documentation.
Set up the RPC component for a TCP/IP connection. On mainframe platforms, use Transport-method-style Broker ID. Example:
ETB024:1699:TCP
Configure ATLS to turn the TCP/IP connection to an SSL connection, see above.
Make sure the SSL server to which the RPC component connects is prepared for SSL connections as well. The SSL server can be EntireX Broker, Broker SSL Agent, or Direct RPC in webMethods Integration Server (IS inbound). See:
* Converting inbound EntireX Broker connection * Converts listen port 1971 to SSL listen port 1972 OPTION SERVER ATTLS 1971 AS 2071 SSL * * Converting outbound client connection * Converts connect to 192.168.2.100:1972:TCP to 192.168.2.100:2072:SSL OPTION CLIENT ATTLS 1972 TO 192.168.2.100 AS 2072 SSL
Note:
We recommend setting SETPARM value SUBTASK to a value greater than 0 in the ATLS daemon startup job (valid values 0-16, default=0). For example:
// SETPARM SUBTASK=8
See also BSI SSL Installation, Programming and User's Guide.
RPC client applications built with the COBOL Wrapper do not support Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) as the transport medium under UNIX, Windows or BS2000.