In the architecture of modern e-business applications (such as SOA), loosely coupled systems are becoming more and more important. Reliable messaging is one important technology for this type of system.
Reliable RPC is the EntireX implementation of a reliable messaging system. It combines EntireX RPC technology and persistence, which is implemented with units of work (UOWs).
Reliable RPC allows asynchronous calls ("fire and forget")
Reliable RPC is supported by most EntireX wrappers
Reliable RPC messages are stored in the Broker's persistent store until a server is available
Reliable RPC clients are able to request the status of the messages they have sent
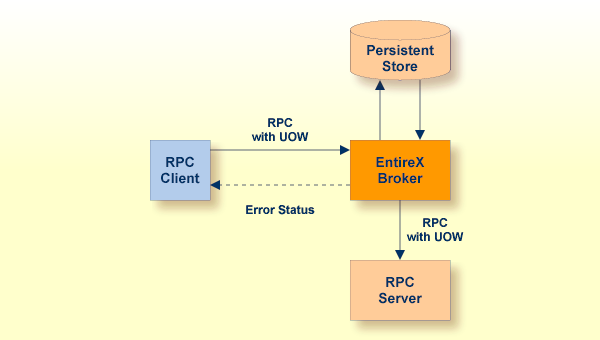
Reliable RPC is used to send messages to a persisted Broker service. The
messages are described by an IDL program that contains only IN parameters. The
client interface object and the server interface object are generated from this
IDL file, using the EntireX COBOL Wrapper.
Reliable RPC is enabled at runtime. The client has to set one of two different modes before issuing a reliable RPC request:
AUTO_COMMIT
CLIENT_COMMIT
While AUTO_COMMIT commits each RPC message implicitly after sending it, a
series of RPC messages sent in a unit of work (UOW) can be committed or rolled
back explicitly using CLIENT_COMMIT mode.
The server is implemented and configured in the same way as for normal RPC.
The following steps describe how to write a COBOL reliable RPC client
program with the scenario Using the COBOL Wrapper for CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Calling Convention (z/OS and z/VSE):
Note:
Reliable RPC requires an explicit broker logon. See Using Broker Logon and Logoff.
The customer data structures (all below COBOL label SM-COMA) must match the interfaces of the
generated client interface objects with regard to format and lengths, otherwise unpredictable results will occur.
See the following code snippet:
* Declare the customer data of the generated RPC interface (See Note 1)
01 SENDMAIL.
02 SM-COMA.
03 SM-TOADDRESS PIC X(60).
03 SM-SUBJECT PIC X(20).
03 SM-TEXT PIC X(100).
* Declare RPC communication area
02 ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA.
COPY ERXCOMM.
Notes:
EXEC CICS LINK Clients for usage examples.
See the following code snippet and refer to Step 2: Initialize the RPC Communication Area under Writing EXEC CICS LINK Clients for additional hints and information.
* Initialize RPC communication area INITIALIZE ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA. MOVE "2000" to COMM-VERSION.
The following settings to the RPC communication area are required as a minimum to use the COBOL Wrapper. These settings have to be applied in your RPC client program. It is not possible to generate any defaults into your client interface objects:
* assign the broker to talk with MOVE "localhost:1971" to COMM-ETB-BROKER-ID. * assign the server to talk with MOVE "RPC" to COMM-ETB-SERVER-CLASS. MOVE "SRV1" to COMM-ETB-SERVER-NAME. MOVE "CALLNAT" to COMM-ETB-SERVICE-NAME. * assign the user ID for Broker logon MOVE "ERXUSER" to COMM-USERID.
MOVE "LO" TO COMM-FUNCTION.
EXEC CICS LINK
PROGRAM ("COBSRVI")
COMMAREA (ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
LENGTH (LENGTH OF ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
RESP (CICS-RESP1)
RESP2 (CICS-RESP2)
END-EXEC.
IF WORKRESP = DFHRESP(NORMAL)
IF (COMM-RETURN-CODE = 0) THEN
* Perform success-handling
ELSE
* Perform error-handling (See Note 1)
END-IF
ELSE
* Perform error-handling
END-IF.
Notes:
COMM-RETURN-CODE in the RPC communication area contains the error provided by the COBOL Wrapper.
For the error messages returned, see Error Messages and Codes.
Before reliable RPC can be used, the reliable state must be set to
either ERX_RELIABLE_CLIENT_COMMIT or ERX_RELIABLE_AUTO_COMMIT.
"C" - CLIENT_COMMIT
"A" - AUTO_COMMIT
* Set the reliable RPC mode MOVE "C" TO COMM-RELIABLE-STATE.
The RPC message is sent using the EXEC CICS LINK interface.
* Send the RPC message
MOVE DFHRESP(NORMAL) TO CICS-RESP1.
MOVE DFHRESP(NORMAL) TO CICS-RESP2.
MOVE ZEROES TO COMM-RETURN-CODE.
EXEC CICS LINK
PROGRAM ("SENDMAIL")
RESP (CICS-RESP1)
RESP2 (CICS-RESP2)
COMMAREA (SENDMAIL)
LENGTH (LENGTH OF SENDMAIL)
END-EXEC.
IF WORKRESP = DFHRESP(NORMAL)
IF (COMM-RETURN-CODE = 0) THEN
* Perform success-handling (See Note 1)
ELSE
* Perform error-handling (See Note 2)
END-IF
ELSE
* Perform error-handling
END-IF.
Notes:
UOWID is available in the RPC communication area field COMM-ETB-UOW-ID.
See The RPC Communication Area (Reference).
COMM-RETURN-CODE in the RPC communication area contains the error provided by the COBOL Wrapper.
For the error messages returned, see Error Messages and Codes.
To determine that reliable RPC messages are delivered, the reliable RPC message status can be queried. See Understanding UOW Status and Broker UOW Status Transition for more information.
MOVE DFHRESP(NORMAL) TO CICS-RESP1.
MOVE DFHRESP(NORMAL) TO CICS-RESP2.
MOVE "RS" TO COMM-FUNCTION.
MOVE ZEROES TO COMM-RETURN-CODE.
EXEC CICS LINK
PROGRAM ("COBSRVI")
RESP (CICS-RESP1)
RESP2 (CICS-RESP2)
COMMAREA (ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
LENGTH (LENGTH OF ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
END-EXEC.
IF WORKRESP = DFHRESP(NORMAL)
IF (COMM-RETURN-CODE = 0) THEN
* Perform success-handling (See Note 1)
ELSE
* Perform error-handling (See Note 2)
END-IF
ELSE
* Perform error-handling
END-IF.
Notes:
COMM-ETB-UOW-STATUS.
See The RPC Communication Area (Reference).
COMM-RETURN-CODE in the RPC communication area contains the error provided by the COBOL Wrapper.
For the error messages returned, see Error Messages and Codes.
Send a second reliable RPC message. See Step 6.
Check the reliable RPC message before the commit call. See Step 7.
Now both reliable RPC messages are committed. This will deliver all reliable RPC messages to the server if it is available.
MOVE DFHRESP(NORMAL) TO CICS-RESP1.
MOVE DFHRESP(NORMAL) TO CICS-RESP2.
MOVE "RC" TO COMM-FUNCTION.
MOVE ZEROES TO COMM-RETURN-CODE.
EXEC CICS LINK
PROGRAM ("COBSRVI")
RESP (CICS-RESP1)
RESP2 (CICS-RESP2)
COMMAREA (ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
LENGTH (LENGTH OF ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
END-EXEC.
IF WORKRESP = DFHRESP(NORMAL)
IF (COMM-RETURN-CODE = 0) THEN
* Perform success-handling (See Note 1)
ELSE
* Perform error-handling (See Note 2)
END-IF
ELSE
* Perform error-handling
END-IF.
Notes:
COMM-RETURN-CODE in the RPC communication area contains the error provided by the COBOL Wrapper.
For the error messages returned, see Error Messages and Codes.
Send a third reliable RPC message. See Step 6.
Check the reliable RPC message before the rollback call. See Step 7.
Roll back the current reliable RPC message.
MOVE DFHRESP(NORMAL) TO CICS-RESP1.
MOVE DFHRESP(NORMAL) TO CICS-RESP2.
MOVE "RR" TO COMM-FUNCTION.
MOVE ZEROES TO COMM-RETURN-CODE.
EXEC CICS LINK
PROGRAM ("COBSRVI")
RESP (CICS-RESP1)
RESP2 (CICS-RESP2)
COMMAREA (ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
LENGTH (LENGTH OF ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
END-EXEC.
IF WORKRESP = DFHRESP(NORMAL)
IF (COMM-RETURN-CODE = 0) THEN
* Perform success-handling
ELSE
* Perform error-handling (See Note 1)
END-IF
ELSE
* Perform error-handling
END-IF.
When the rollback call is returned, check whether it was successful or not.
MOVE DFHRESP(NORMAL) TO CICS-RESP1.
MOVE DFHRESP(NORMAL) TO CICS-RESP2.
MOVE "RS" TO COMM-FUNCTION.
MOVE ZEROES TO COMM-RETURN-CODE.
EXEC CICS LINK
PROGRAM ("COBSRVI")
RESP (CICS-RESP1)
RESP2 (CICS-RESP2)
COMMAREA (ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
LENGTH (LENGTH OF ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
END-EXEC.
IF WORKRESP = DFHRESP(NORMAL)
IF (COMM-RETURN-CODE = 0) THEN
* Perform success-handling
ELSE
* Perform error-handling (See Note 1)
END-IF
ELSE
* Perform error-handling
END-IF.
Notes:
COMM-RETURN-CODE in the RPC communication area contains the error provided by the COBOL Wrapper.
For the error messages returned, see Error Messages and Codes.
MOVE "LF" TO COMM-FUNCTION.
EXEC CICS LINK
PROGRAM ("COBSRVI")
COMMAREA (ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
LENGTH (LENGTH OF ERX-COMMUNICATION-AREA)
RESP (CICS-RESP1)
RESP2 (CICS-RESP2)
END-EXEC.
IF WORKRESP = DFHRESP(NORMAL)
IF (COMM-RETURN-CODE = 0) THEN
* Perform success-handling
ELSE
* Perform error-handling (See Note 1)
END-IF
ELSE
* Perform error-handling
END-IF.
Notes:
COMM-RETURN-CODE in the RPC communication area contains the error provided by the COBOL Wrapper.
For the error messages returned, see Error Messages and Codes.
There are no server-side methods for reliable RPC. The server does not send back a message to the client. The server can run deferred, thus client and server do not necessarily run at the same time. If the server fails, it returns an error code greater than zero. This causes the transaction (unit of work inside the Broker) to be cancelled, and the error code is written to the user status field of the unit of work. For writing reliable RPC servers, see Using the COBOL Wrapper for the Server Side.
To execute a reliable RPC service with an RPC server, the parameter logon
(LOGN under CICS) must be set to YES.
See logon under z/OS (CICS | Batch | IMS) | BS2000.
A Broker configuration with PSTORE is recommended. This enables the Broker
to store the messages for more than one Broker session. These messages are
still available after Broker restart. The attributes
STORE, PSTORE,
and PSTORE-TYPE in the Broker attribute file can
be used to configure this feature. The lifetime of the messages and the status
information can be configured with the attributes
UOW-DATA-LIFETIME and
UOW-STATUS-LIFETIME. Other attributes such as
MAX-MESSAGES-IN-UOW,
MAX-UOWS and
MAX-UOW-MESSAGE-LENGTH may be used in addition
to configure the units of work. See Broker Attributes.
The result of the generic RPC function call "RS" - get reliable status depends on the
configuration of the unit of work status lifetime in the EntireX Broker
configuration. See COMM-FUNCTION. If the status is not stored longer than the message, the
function call returns the error code 00780305 (no matching UOW
found).