This document covers the following topics:
Task 1: Create the Consumer REST API Descriptor, Connections and Listeners
Task 2: Generate Client Interface Objects and Build Client Application
This scenario uses the following tools of the Designer:
from the Service Development perspective: New REST API Descriptor
from the EntireX perspective: IDL Extractor for Integration Server and COBOL Wrapper
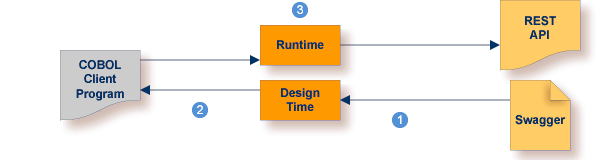
To call the REST API from COBOL, take an existing description of a REST API  and
generate the integration logic
and
generate the integration logic  to call it from a COBOL application
to call it from a COBOL application  , as shown below.
, as shown below.
 |
Create the consumer REST API descriptor in Integration Server. See Service Development Help in the webMethods Integration Server documentation. Then generate Integration Server connections and listeners. See Using the IDL Extractor for Integration Server. |
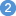 |
Generate client interface objects and build COBOL client application. |
 |
Execute the call from the COBOL client to the REST API. |
This scenario makes the following important assumptions:
For Task 1:
You have an Integration Server with EntireX Adapter installed.
You have an Integration Server with EntireX Adapter installed.
You can call the REST API at runtime using different methods:
This section covers the following topics:
After you have created the consumer REST API descriptor, follow the instructions for extracting a webMethods Integration Server (IS) service under Using the IDL Extractor for Integration Server.
This process creates the following EntireX metafiles:
an IDL file, containing definitions of the interface between client and server; see Software AG IDL File in the IDL Editor documentation
a webMethods IS Connection
a webMethods IS Listener, depending on connection type. See Listeners in the EntireX Adapter documentation.
Connection types are described under Creating Listener Objects in Integration Server.
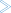 To create a consumer REST API Descriptor
To create a consumer REST API Descriptor
Switch to the Service Development perspective. Create a package and folder in Designer where the API descriptor is placed into.
Invoke the wizard to create a new REST API Descriptor in Eclipse. From the File menu, choose New > REST API Descriptor.
Or:
Choose from the toolbar or context menu of a view showing resources.
Or:
Press Ctrl-N to start the selection of the New Wizards.
Follow the instructions on the screen. Provide the description of the REST API (Swagger file) and create the REST API descriptor for a Consumer.
For more information on REST API descriptors see Service Development Help in the webMethods Integration Server documentation.
First create a project in Designer. This project is the container into which all extracted and generated EntireX artifacts are placed. Name this project COBOL placeOrder client.
 To start the IDL Extractor for Integration Server
To start the IDL Extractor for Integration Server
Switch to the EntireX perspective.
Invoke the IDL Extractor for webMethods IS, which is a New Wizard in Eclipse. From the menu, choose . Select IDL Extractor for webMethods IS in the following page.
Or:
Choose from the toolbar or context menu of a view showing resources.
Or:
Press to start the selection of the New Wizards.
If you are using the wizard for the first time without any predefined Integration Server connections, enter the TCP/IP address of the webMethods IS to extract from. Otherwise select the connection to the Integration Server.
Press .
 To extract the IDL from the selected package
To extract the IDL from the selected package
Under Source (Integration Server), select the package you want to extract from.
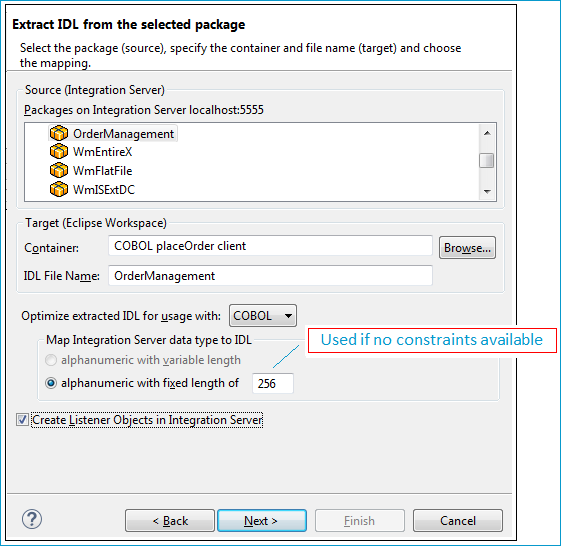
For Target (Eclipse Workspace), specify project COBOL placeOrder client. Extraction results will be placed in this container. You can keep the IDL File Name as it has been derived from the package name by default. Since COBOL is your desired endpoint, select Optimize extracted IDL for usage with: COBOL.
Note:
COBOL only supports fixed-length data items, whereas webMethods IS has variable length types, often without any length restrictions
(constraints).
Parameters with no specified constraints will take the default fixed length. You can specify this default in field alphanumeric
with fixed length.
.
A listener is required for calling webMethods IS from an RPC client, so check Create Listener Objects in Integration Server.
Press .
 To create Listener Objects in Integration Server
To create Listener Objects in Integration Server
Select a Listener connection type used for inbound connection to the Integration Server.
An EntireX RPC Listener connection is the standard way and is always available.
If your interface contains only In parameters, an EntireX Reliable RPC Listener connection is available.
If it is enabled by the license for the webMethods Integration Server:
an EntireX Direct RPC Listener connection is available
if your interfaces contain only In parameters, an EntireX Direct Reliable RPC Listener connection is available
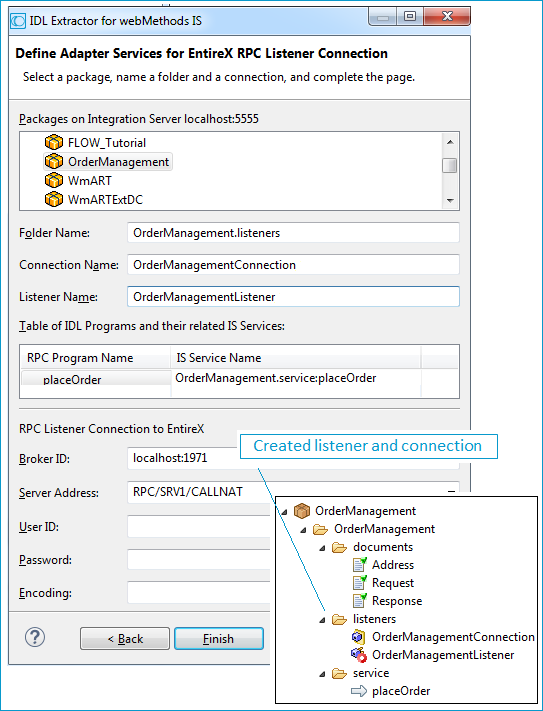
On this page, you set the properties for the listener objects to create; these objects will wait for the incoming COBOL requests. Select the package and specify the folder name into which the listener is generated. If the folder does not exist, it will be created automatically.
Keep the defaults given for RPC Listener Connection to EntireX. The Broker ID is a TCP/IP or SSL/TLS address and Server Address is an EntireX-specific namespace to locate a target server (here: OrderManagementListener).
When creating a connection, a package dependency is added such that the selected package depends on webMethods EntireX (the package WmEntireX) with the version currently used.
Press . The listener and the connection appear in the package navigator. For the package navigator, switch to the service development perspective by choosing .
 To test the extraction results
To test the extraction results
For EntireX RPC (see Task 3 in the Introduction) and an RPC Listner Connection, make sure EntireX Broker is running.
Enable the EntireX Adapter Listener.
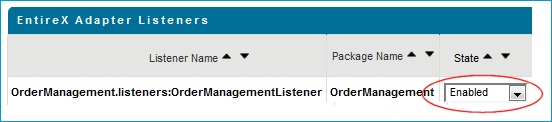
Activate the EntireX perspective by choosing , and from the context menu of the IDL file, choose .
This step depends on the method used to call the server (see Task 3 in the Introduction).
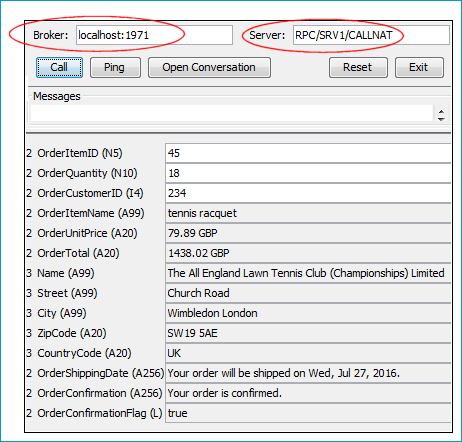
For EntireX RPC, enter the same TCP/IP address for Broker that you supplied when you created the RPC Listener Connection to EntireX (localhost:1971).
For Direct RPC, that is, you generated a Direct RPC Listener Connection, enter the TCP/IP address from the Integration Server (localhost:1971).
For , enter the values you specified for the server address (RPC/SRV1/CALLNAT).
This section covers the following topics:
 To set generation options (properties) for the COBOL Wrapper
To set generation options (properties) for the COBOL Wrapper
To generate suitable COBOL code for your environment, first set the correct target operating system. Make sure the EntireX perspective is active () and call the properties of the COBOL Wrapper.
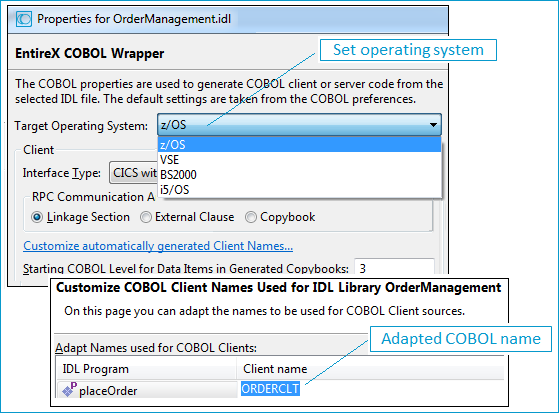
From the context menu of the IDL file, choose . On the COBOL Wrapper Properties page, set the Target Operating System
Adapt the name of the generated COBOL program: Choose Customize automatically generated Client Names. Take ORDERCLT as the COBOL program's name.
Set the appropriate interface type for the generated client interface objects to your application. The options available for CICS are Standard Linkage Calling Convention and DFHCOMMAREA Calling Convention. These are described below.
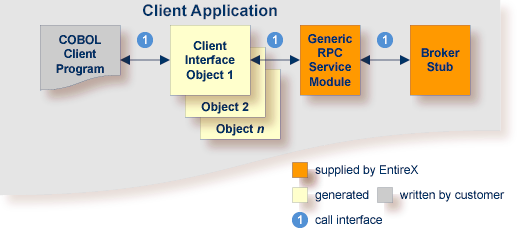
The COBOL Wrapper can be used with a call interface, even in CICS. This means you can build a client application where the COBOL client program, every generated client interface object, the generic RPC services module and the broker stub are linked together, similar to the batch scenario. See Using the COBOL Wrapper for Batch (z/OS, BS2000, z/VSE and IBM i). Using a call interface within CICS may be useful in the following situations:
The restriction of the COMMAREA length (about 31 KB) prevents you from using the scenario Using the COBOL Wrapper for CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Calling Convention (z/OS and z/VSE) (see above).
You do not require a distributed program link (CICS DPL) to your client interface object(s).
You prefer a call interface instead of EXEC CICS LINK to your client interface objects.
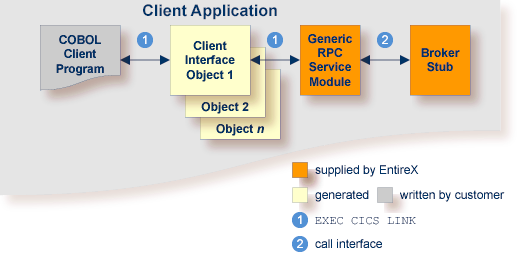
In this scenario, the generic RPC services module and the broker stub are linked together to a CICS program. The COBOL client program, every generated client interface object and the generic RPC services module together with the broker stub are installed each as separate individual CICS programs. Use the COBOL Wrapper with this calling convention in the following situations:
You want to have an EXEC CICS LINK DFHCOMMAREA interface to your client interface object(s).
The restriction of the COMMAREA length suits your purposes. Because the RPC communication area is also transferred in the COMMAREA, the effective length that can be used for IDL data is shorter than the CICS COMMAREA length. Nearly 31 KB can be used for IDL data.
You wish to separate the generic RPC service module and the broker stub from the client interface object(s).
You require a program link to the client interface object(s).
 To generate COBOL code
To generate COBOL code
For COBOL code generation, make sure the EntireX Perspective is active: Choose . From context menu of the IDL file, choose . This generates the COBOL client ORDERCLT in folder client and a copybook in folder include:
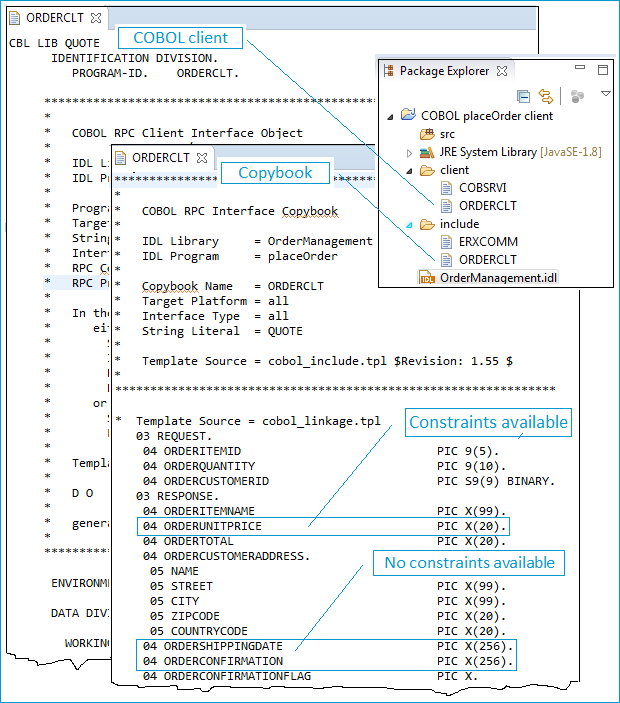
The copybook is the COBOL programmer's API. It is for use in the COBOL application.
As you would expect, the length of generated COBOL parameters exactly matches the lengths extracted. COBOL parameters always have a fixed length defined at compile time. They are not altered at runtime to reflect actual string length as in modern programming languages. This means that if you choose your default length (see Extracting the Interface of the webMethods IS Service) you have to choose the maximum possible data size to ensure all data can be transmitted. However, this may needlessly increase the message size if no constraints are set for fields of shorter data length. Choose your defaults and contstraints carefully.
Depending on the chosen interface type of your client interface objects (CICS with Standard Linkage Calling Convention or CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Calling Convention under Setting Generation Options (Properties) for the COBOL Wrapper, refer to
Using the COBOL Wrapper for CICS with Call Interfaces (z/OS and z/VSE)
Using the COBOL Wrapper for CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Calling Convention (z/OS and z/VSE)
 To execute the call
To execute the call
For EntireX RPC (see Task 3 in the Introduction) and an RPC Listner Connection, make sure EntireX Broker is running.
Enable the EntireX Adapter Listener.

Activate the EntireX perspective by choosing , and from the context menu of the IDL file, choose .
This step depends on the method used to call the server (see Task 3 in the Introduction).
For EntireX RPC, enter the same TCP/IP address for Broker that you supplied when you created the RPC Listener Connection to EntireX (localhost:1971).
For Direct RPC, that is, you generated a Direct RPC Listener Connection, enter the TCP/IP address from the Integration Server (localhost:1971).
For , enter the values you specified for the server address (RPC/SRV1/CALLNAT).
