This document describes how to use the Software AG IDL Extractor for Natural. It covers the following topics:
Extracting IDL from Natural Subprogram Sources in NaturalONE
Extracting Software AG IDL File from a New Natural RPC Environment
Extracting Software AG IDL File from an Existing Natural RPC Environment
In a NaturalONE project in Software AG Designer, IDL can be extracted directly from Natural subprogram sources (CALLNATs), using the following steps:
Step 2: Select the Natural Library from NaturalONE Project (Optional)
Step 3: Select the Natural Subprograms from NaturalONE Project
There are various ways of starting the IDL Extractor for Natural Wizard:
To extract the IDL, select the NaturalONE project in the Designer.
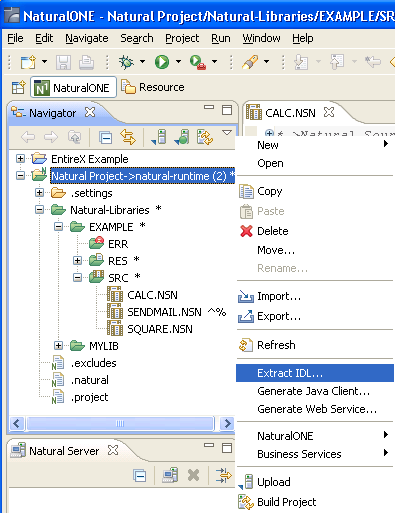
From the context menu, choose and continue with Step 2: Select the Natural Library from NaturalONE Project (Optional).
To extract the IDL, select the NaturalONE library in the Designer.
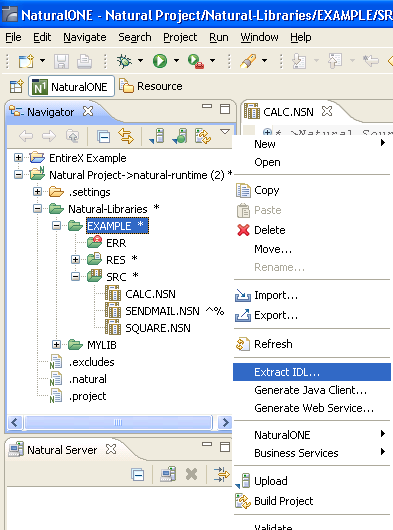
From the context menu, choose and continue with Step 3: Select the Natural Subprograms from NaturalONE Project.
To extract the IDL, select one or multiple Natural subprogram sources (.NSN) in the Designer.
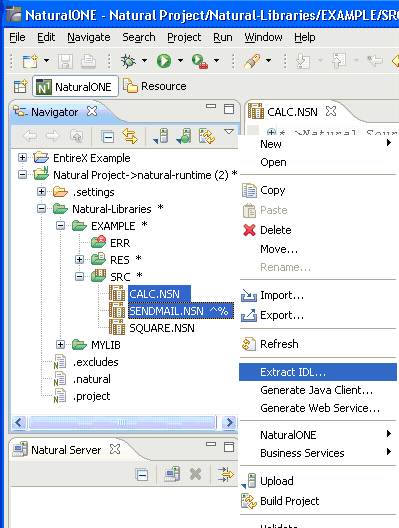
From the context menu, choose and continue with Step 3: Select the Natural Subprograms from NaturalONE Project.
Alternatively, you can start the IDL Extractor for Natural from the context menu of the Natural source folder or any parent folder in the project, including the Natural library and the Project folder.
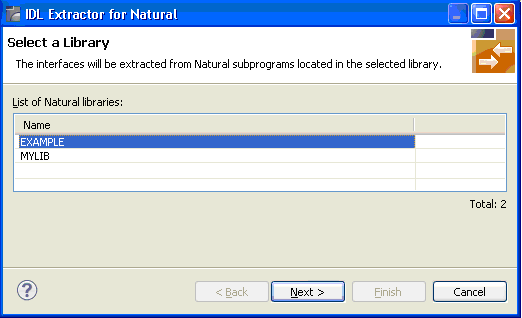
Select the Natural library from the list and choose to continue with Step 3: Select the Natural Subprograms from NaturalONE Project.
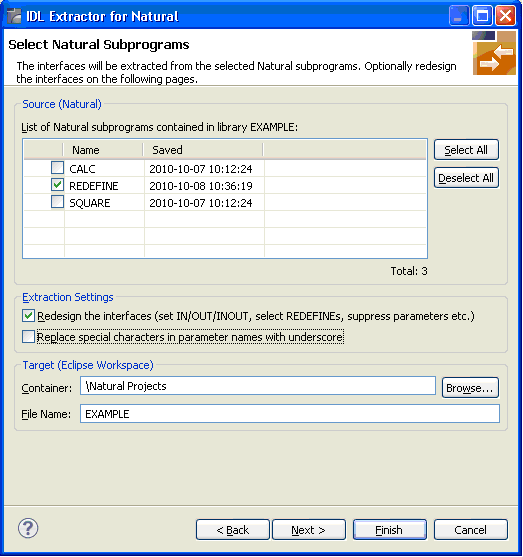
In the Source pane, select at least one program from the list of Natural subprograms (CALLNATs). You can also choose or .
In the Extraction Setting pane, check Redesign the interfaces if you want to design the extracted interfaces to the Natural subprograms. The button will be enabled. See User-defined Mapping. If you do not check Redesign the interfaces, see Natural to IDL Mapping for default mappings.
By checking Replace special characters in parameter names with underscore under Extraction Setting, the special characters ("$", "#", "&", "@", "/") allowed in Natural parameters can be replaced by underscores, see also Extracting IDL Parameter Names.
In the Target pane, select the container where the IDL file will be stored. Enter the file name of the new IDL file. If the IDL file exists, it will be overwritten. Preserving the IDL File and optional mapping file allows you to customize the IDL (alias names, in/out/inout modifiers) for subsequent optimized client generation steps. See Server Mapping Files for Natural in the Designer documentation.
Choose to redesign the interfaces. See Step 6: Redesign the Interface for Natural Subprograms (Optional). To enable the button, check Redesign the interfaces.
Choose to start extraction with a default mapping. For more information see Extraction Result.
This section covers the following topics:
Step 4: Select Natural Library from RPC Environment (Optional)
Step 6: Redesign the Interface for Natural Subprograms (Optional)
Press and continue with Step 3: Edit RPC Environment.
If no RPC environments are defined, you only have the option to . The RPC environments are managed in the Preferences.
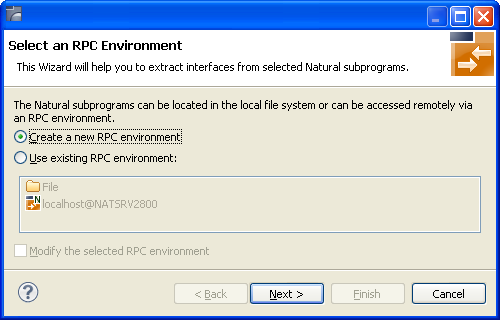
Choose Create a new RPC Environment and press to create a new RPC environment. Continue with Step 3: Edit RPC Environment.
Note:
The folder File and the RPC environment
localhost@NATSRV2800 (default RPC server for NaturalONE)
are available only if NaturalONE plugins are installed.
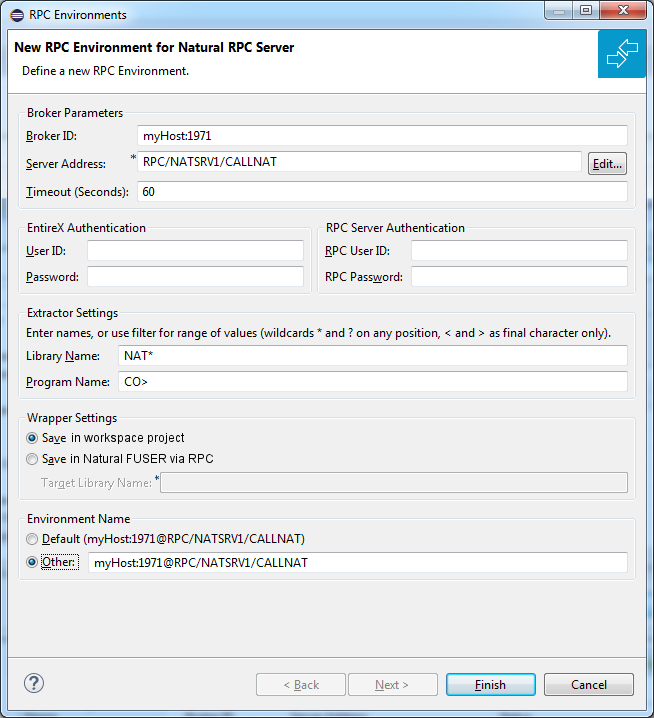
Define the new RPC environment on this page. Required fields are Broker ID, Server Address and the Environment Name. The timeout value must be in the range 1-9999 seconds (default: 60).
The EntireX Authentication fields apply to the broker.
The RPC Server Authentication fields apply to the RPC server. If the Natural RPC Server operates under Natural Security,
your user ID and password must be defined in Natural Security. If the Natural Security user ID or password differs from the broker user ID and password, use RPC Server Authentication - otherwise use EntireX Authentication for both.
access to the Natural system library SYSIDL is required
Note:
Users who do not have access rights to the Natural system library
SYSIDL are not allowed to extract IDL from your Natural environment.
With Extractor Settings, specify the Natural library and program name from which you want to extract. You have the following options to select a range of Natural libraries and programs:
wildcard asterisk "*" (any position) to list libraries or program names matching any sequence of characters.
wildcard question mark "?" (any position) to list libraries or program names matching any single character.
wildcard greater than ">" (final character only) to list libraries or program names after.
wildcard lower than "<" (final character only) to list libraries or program names before.
no wildcard to extract from the given library or program. If the library or program does not exist, an error message will be displayed.
Any Natural RPC Server can be used. Only Natural libraries that reside in the FUSER system file of the Natural RPC Server can be accessed. Special configuration is required only for operating system IBM i; see Natural RPC Server Configuration for the IDL Extractor for Natural.
Press to continue.
If Library Name (using any wildcards) matches one Natural library only, continue with Step 5: Select Natural Subprograms from RPC Environment.
If Library Name matches more than one Natural library, continue with Step 4: Select Natural Library from RPC Environment (Optional).
All Natural libraries that reside in the FUSER system file of the Natural RPC Server and that match the specification in the Extractor Settings are listed here. See Step 3: Edit RPC Environment. This step is skipped if exactly one Natural library matches the specification. In this case continue with Step 5: Select Natural Subprograms from RPC Environment.
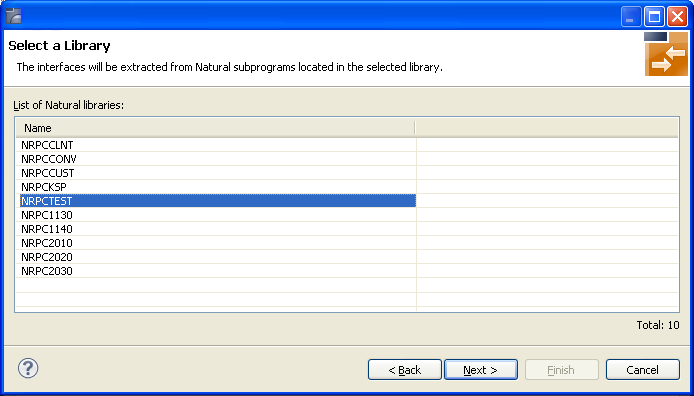
Only Natural libraries from the Natural User System file (FUSER) are displayed. If the Natural RPC server operates under Natural Security, Natural libraries are displayed only if you are allowed to access the library. This means that if a library is people-protected and you do not have access rights, it is not displayed. See also RPC Server Authentication under Step 3: Edit RPC Environment.
Select the Natural library from the list and choose to continue with Step 5: Select Natural Subprograms from RPC Environment.
All Natural subprograms that match the specification in the Extractor Settings are listed here. See Step 3: Edit RPC Environment.
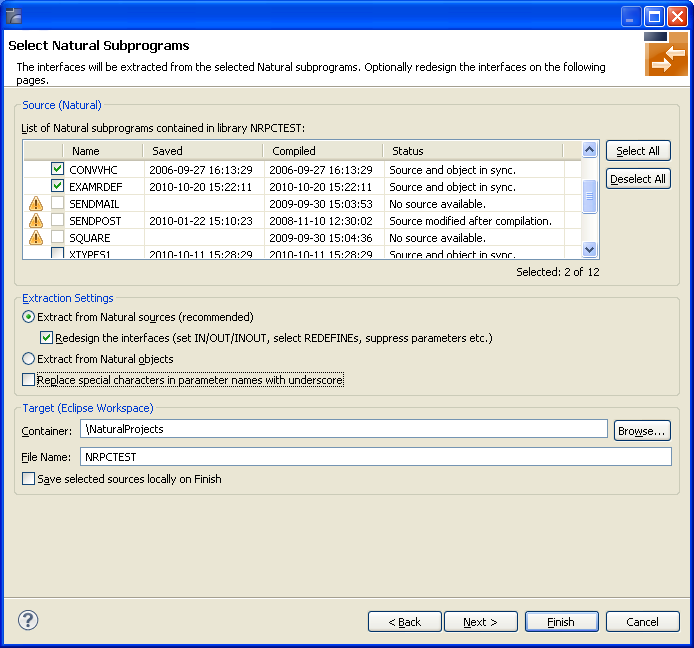
In the Source pane select at least one program from the list of Natural subprograms (CALLNATs). You can also choose or .
In the Extraction Settings pane, specify whether the IDL is to be extracted from Natural subprogram sources or compiled objects. The following restrictions apply:
Extract from Natural sources (recommended)
Extracting from a source is only possible if the compiled object and
source are in sync. For example, in the screen above, source extraction is not
possible for
SENDMAIL, because there is no source, only an object
SENDPOST, because the source is modified after last compilation
Extract from Natural objects
Extracting from an object is always possible.
Check Redesign the interfaces if you want to design the extracted interfaces to the Natural subprograms. The button will be enabled. See User-defined Mapping. If you do not check Redesign the interfaces, refer to Natural to IDL Mapping for default mappings.
Check Replace special characters in parameter names with underscore to substitute the special characters '$', '#', '&', '@', '/' by underscores. See also Extracting IDL Parameter Names in Natural to IDL Mapping.
Choose to continue. If multiple Natural subprograms have been selected in the Natural subprogram selection step, redesign the next interface. You can see the current and total number of the subprogram you are extracting from in the title (n/m).
Choose to extract the interface. For further subprograms that have been selected, a default mapping is created, see Extraction Result.
In this step, you can redesign the interface. This includes:
These tasks are described in more detail under Step 6: Redesign the Interface for Natural Subprograms (Optional).
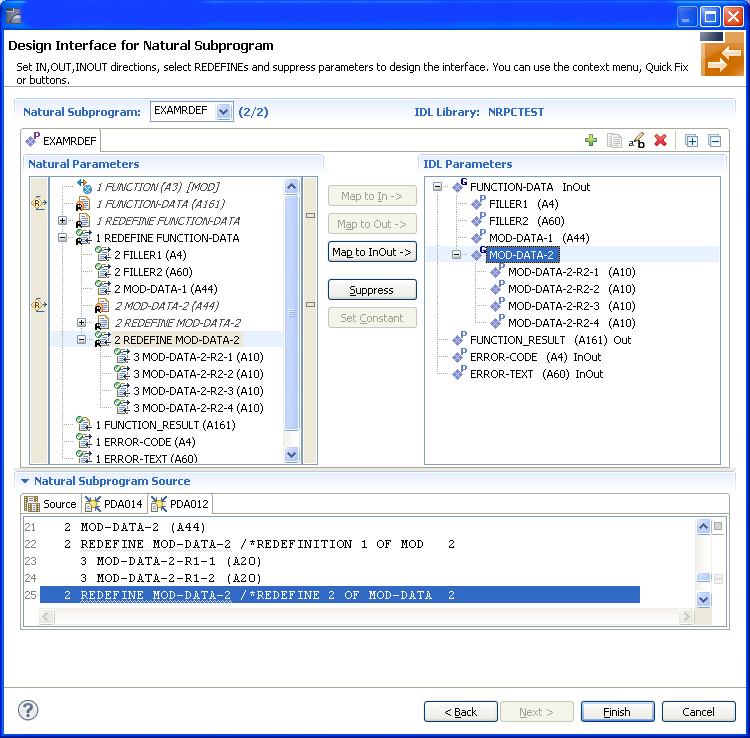
Use this page for the following tasks:
Define the direction of parameters in the extracted interface. Choose Map to In, Map to Out or Map to InOut for each parameter on level 1.
Define which parameters redefined in the Natural PDA are part of the
extracted interface. Choose Map to In, Map to
Out or Map to InOut for the
REDEFINE base parameter or any
REDEFINE path.
Hide or suppress unneeded parameters in the extracted interface. Choose Suppress.
Set parameters to constants and hide or suppress them in the extracted interface. Choose Set Constant.
This page consists of the following main parts:
Top line
The top line contains the current Natural subprogram and the IDL library
name. The combo box can be used as quick navigation if more than one Natural
subprogram is selected.
Middle
The middle part contains a tab item for each interface ( IDL program)
extracted from the Natural subprogram.
Note:
It is possible to extract more than one interface (IDL program) from a
Natural subprogram. To create, rename and remove interfaces, use the toolbar on
the right side of tab folder.
| Icon | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Create | Create a new interface (IDL program) based on the original parameters of the Natural subprogram. |
|
|
Duplicate | Create a new interface (IDL program) based on the current interface (active tab). All modifications of the current interface are copied. |
|
|
Rename | Change the name of the current interface (active tab). The name must be unique. |
|
|
Remove | Remove the current interface (active tab). At least one interface must exist. |
|
|
Expand All | Expand the Natural and IDL tree. |
|
|
Collapse All | Collapse the Natural and IDL tree. |
Middle left
Input pane. The parameters of the Natural subprogram to extract from. For
each Natural subprogram parameter you can choose one of the operations
Map to In, Map to Out, Map
to InOut, Suppress and Set
Constant. Additionally for REDEFINEs, a quick fix is available
(icons on the left side of the pane) to choose which parameters redefined in
the Natural PDA are part of the extracted interface.
Notes:
FUNCTION (A3) is set to constant; FILLER1(A4) and
FILLER2(A60) are suppressed; FUNCTION-DATA(A161) and
its first REDEFINE path are implicitly suppressed because the
second REDEFINE path with prefix MOD-DATA-2-R2 is
selected.
FUNCTION (A3) [MOD]).
 ).
).
Middle right
Output pane. The extracted interface (IDL).
Bottom
Reference. The Natural subprogram source and its PDA sources, each
displayed in a separate tab.
The panes can be resized.
To enlarge parameter lists, use the vertical bars on the side.
You can close the bottom pane if it is not needed by clicking on the triangle next to Natural Subprogram Source. In this way, you have more space for viewing the upper panes.
Use the quick navigation or choose to continue. If multiple Natural subprograms have been selected in the Natural subprogram selection step, redesign the next interface. The amount of subprograms extracted so far is indicated by the fraction next to the title (current/total).
Choose to continue. If multiple Natural subprograms have been selected in the Natural subprogram selection step, redesign the next interface. You can see the current and total number of the subprogram you are extracting from in the title (n/m).
Choose to extract the interface. For further subprograms that have been selected, a default mapping is created, see Extraction Result.

Choose Next and continue with Step 6: Redesign the Interface for Natural Subprograms (Optional).
If RPC environments are defined, you can select an existing one. RPC environments are managed in the Preferences.
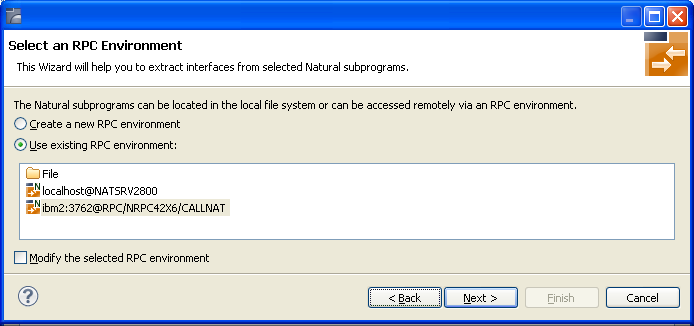
Select Use existing RPC environment and select the appropriate RPC environment from the list below.
If Modify the selected RPC environment is checked, the selected RPC environment can be modified before extraction starts.
Press to continue.
If Modify the selected RPC environment is checked, continue with Step 3: Edit RPC Environment above.
If Modify the selected RPC environment is not checked and the Natural library name matches one Natural library only (using any wildcard defined in Step 3: Edit RPC Environment), continue with Step 5: Select Natural Subprograms from RPC Environment above.
If Modify the selected RPC environment is not checked and the Natural library name matches more than one Natural library, continue with Step 4: Select Natural Library from RPC Environment (Optional) above.
Note:
The folder File and the RPC environment
localhost@NATSRV2800 (default RPC server for NaturalONE)
are available only if NaturalONE plug-ins are installed.
When the wizard has finished successfully, you can see two additional files in your Eclipse project:
.idl file
The IDL file that describes the RPC interface of the
Natural server component that implements the service's business logic.
The IDL file is opened with the IDL Editor.
See Software AG IDL File in the IDL Editor documentation.
.cvm file (optional)
This server mapping file completes the IDL file with a mapping from the
programming-language-neutral parameter definition in the IDL file to the
parameters and data types expected by the Natural subprograms (CALLNATs).
Always keep the server mapping in the same folder as its related IDL file.
See Server Mapping Files for Natural in the Designer documentation.
For more information on how Natural programs are extracted, refer to Natural to IDL Mapping.
Use the preference page for IDL Extractor for Natural to manage the default values for the IDL Extractor for Natural wizard.
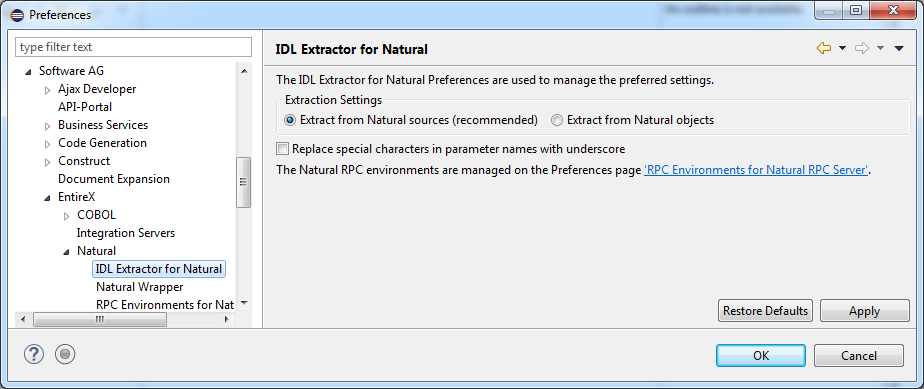
The option IDL Extraction from Source or from Object determines from which code type the IDL file is to be extracted.
With the check box Replace special characters in parameter names with underscore, the special characters ("$", "#", "&", "@" , "/") allowed in Natural parameters can be replaced by underscores. See also Rules for Coding Group and Parameter Names.
For more information on object and source extraction and character replacing, see Step 5: Select Natural Subprograms from RPC Environment.
RPC environments are managed with the RPC Environment Manager.