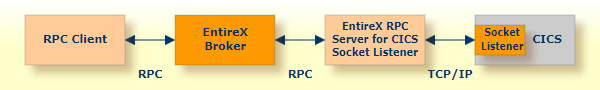
The EntireX RPC Server for CICS Socket Listener allows standard RPC clients to communicate with CICS programs running on IBM CICS®. All CICS interface types are supported: (DFHCOMMAREA, Channel Container and Large Buffer). This document covers the following topics:
The RPC Server for CICS Socket Listener acts on one side as an RPC server and on the other side as a client for CICS. The RPC Server for CICS Socket Listener is a Java-based component that can run on a different host to the one where CICS is running. This allows it to operate with a minimal footprint of EntireX on the CICS host. For details see Preparing for CICS Socket Listener. No configuration in CICS is required.
For local extraction, all source files have to be stored locally on the same machine where the Designer is running.
For existing CICS COBOL programs, use the Software AG IDL Extractor for COBOL to extract the Software AG IDL File for the RPC clients.
For existing CICS PL/I programs, use the Software AG IDL Extractor for PL/I to extract the Software AG IDL File for the RPC clients.
Remote extraction requires an RPC server running under z/OS with Extractor Service (Batch | IMS).
For COBOL, see Step 2: Select a COBOL Extractor Environment or Create a New One in the IDL Extractor for COBOL documentation.
For PL/I, see Extract Software AG IDL File from a Remote PL/I RPC Environment in the IDL Extractor for PL/I documentation.
Software AG Command Central is a tool that enables you to manage your Software AG products remotely from one location. Command Central offers a browser-based user interface, but you can also automate tasks by using commands to remotely execute actions from a terminal or custom script (for example CI servers such as Jenkins, or generic configuration management tools such as Puppet or Chef).
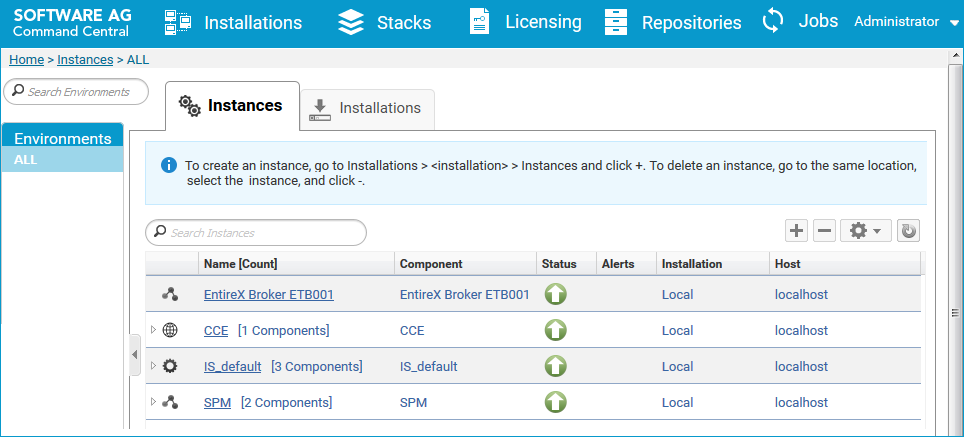
Command Central can assist with the following configuration, management, and monitoring tasks:
Infrastructure engineers can see at a glance which products and fixes are installed, where they are installed, and compare installations to find discrepancies.
System administrators can configure environments by using a single web user interface or command-line tool. Maintenance involves minimum effort and risk.
Release managers can prepare and deploy changes to multiple servers using command-line scripting for simpler, safer lifecycle management.
Operators can monitor server status and health, as well as start and stop servers from a single location. They can also configure alerts to be sent to them in case of unplanned outages.
The Command Central graphical user interface is described under Administering the RPC Server for CICS Socket Listener using the Command Central GUI. For the command-line interface, see Administering the RPC Server for CICS Socket Listener using the Command Central Command Line.
The core Command Central documentation is provided separately and is also available under Guides for Tools Shared by Software AG Products on the Software AG documentation website.
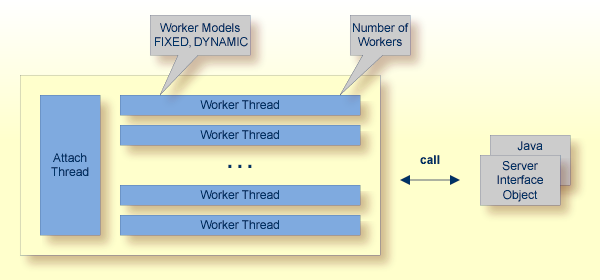
RPC requests are worked off inside the RPC server in worker threads. Every RPC request occupies during its processing a worker thread. If you are using RPC conversations, each RPC conversation requires its own thread during the lifetime of the conversation. The RPC Server for CICS Socket Listener can adjust the number of worker threads to the number of parallel requests. The RPC server provides two worker models:
FIXED
The fixed model creates a fixed number of worker threads. The number of worker threads does not increase or decrease during the lifetime
of an RPC server instance.
DYNAMIC
The dynamic model creates worker threads depending on the incoming load of RPC requests.
For configuration with the Command Central GUI, see Worker Scalability under Configuration > Server.
For technical details, see property entirex.server.fixedservers under Administering the RPC Server for CICS Socket Listener.