E-Business scenario diagram
The smooth execution of inter-company business processes is continuously gaining in significance. Here, the focus of interest lies on the operational sequence of specific procedures at the interfaces between companies on the one hand and at the interfaces between companies and their customers on the other. The contacts need to take place in a clear, quick, consistent, and direct manner.
Also, rapidly finding suitable business associates (from a corporate perspective) and providers (from a consumer point of view) is becoming increasingly more important. Maximum optimization of these processes results in a competitive advantage. The ideal platform for supporting these bilateral relationships is the Internet. As the processes in the above-mentioned environment are very complex, it is necessary to define the term e-business.
E-business describes all computer-assisted processes involving two economic agents and the attempt to gain added value by using new media.
Thus, e-business can mean simply acquiring an item using the Internet, or a highly complex project involving two companies, or creating a Web site for a corporate presentation.
Relationships between companies are referred to as Business-to-Business (or B2B), while relationships between companies and consumers are called Business-to-Consumer (or B2C).
The E-Business scenario diagram was developed to support e-business.
The ability to view a value-added chain in its entirety, that is, from the end user to each of the companies involved in a procedure, provides a basis for developing optimization potential. The objective is, for example, to improve the supply chain, to reduce procurement and distribution costs, or to optimize the information system architecture. The contents represented by the objectives can be modeled using this method.
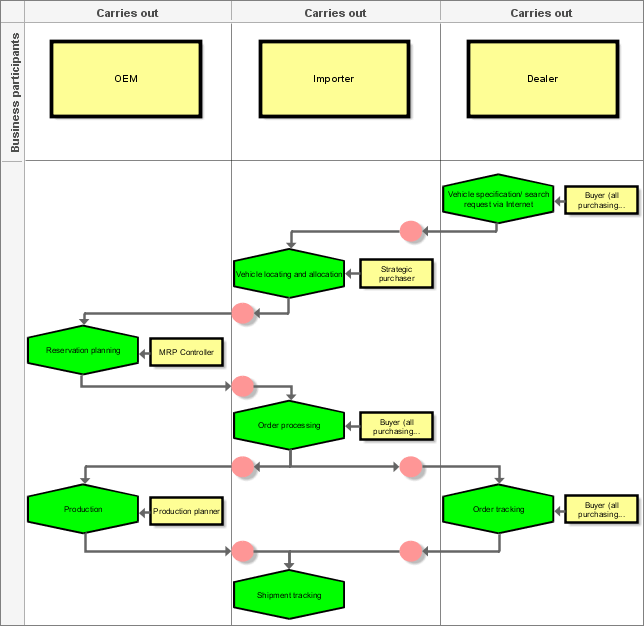
The economic agents are arranged in the upper row of the diagram and referred to as Business participants. The participating companies can be assigned using an organizational chart. Here, interest centers on the individual processes that economic agents perform as part of the overall process as well as the interfaces between these subprocesses. An individual process is a business process that plays an important role in inter-company cooperation and that can be assigned to the process model. The business process is supported by application systems (business components), such as the R/3 system.
Even the roles of the employees involved in the process can be defined. These are referred to in the model as Employee role.
The main feature of the interfaces is the transfer of process-specific information. The information is gathered in business documents and can assume the form of an XML or HTML document. The business document can also be assigned as a data model. As an alternative to this object, the objects Money transaction (for representing a cash flow), Goods shipment (for representing a flow of goods), as well as E-mail, Internet, Intranet, Extranet, and Mobile phone (for specifying the technological aspects of the data transfer) can also be used.
All operational procedures relating to a company are modeled in the row below the business participant, but in the same column.
Thus, column borders form abstract interfaces. These merit special attention, as they carry the main potential for optimization, and it is therefore always beneficial to model them.
Explanation of terms: In the sample model below, OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer and MRP for Material Resource Planning Controller.
The sample model shows how a manufacturer, an importer, and a dealer cooperate. Each party has its specific processes in the overall structure and uses business documents to exchange information via the interfaces to processes of other business associates. The persons involved in the business processes are also recorded and assigned with their roles.