Introduction
The smooth execution of inter-company business processes is increasingly gaining in significance. Here, the operational sequence of specific procedures at the interfaces between companies on the one hand and at the interfaces between companies and their customers on the other hand is in the center of interest. The contacts need to take place in a clear, quick, consistent, and direct manner.
Rapidly finding suitable business associates (from a corporate perspective) and providers (from a consumer point of view) is also of great relevance. Maximum optimization of these processes results in a competitive advantage. The ideal platform for supporting these multilateral relations is the Internet. As the processes in the above-mentioned environment are very complex, it is necessary to define the term 'e-business'.
E-business is a generic term for the use of information and communication technologies in support of a company's business activities. It includes the use of electronic media for the purpose of supporting relationships and processes involving business associates, employees, and customers (Herrmans, Sauter, 1999).
Thus, e-business can mean the creation of a Web site for a corporate presentation, the acquisition of an item via Internet, a highly complex project shared by two companies, or multilayered relationships between any number of business associates meeting in a marketplace.
It can be subdivided into the following concepts:
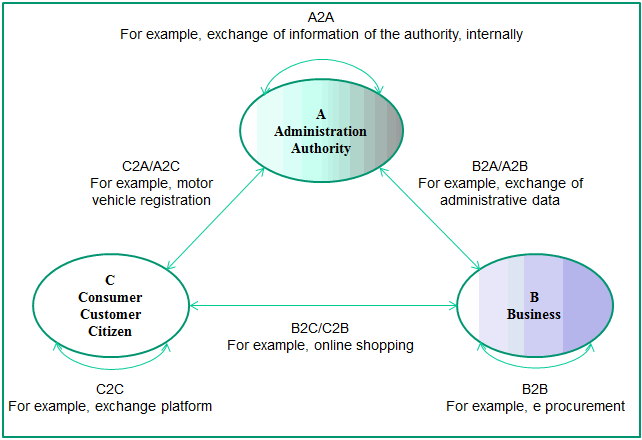
B2B (Business to Business)
Business to Business describes the transactions taking place between companies. For example, this is enabled by linking the companies' supply chains.
B2C (Business to Consumer)
Business to Consumer describes transactions taking place between companies and their customers. For example, this includes purchases by customers in online shops.
B2A/C2A (Business/Consumer to Administration)
Business/Consumer to Administration describes all transactions between companies or individuals and public administration. Contacts between companies and administration are considered to be an area with great cost-cutting potential.
In addition to differentiating between various partners, a distinction can also be made regarding the scope of relationships between the partners: one to one, one to many, many to many. Especially the marketplace scenario is of major significance.
Marketplaces
Electronic marketplaces are virtual places where any number of people buy and sell products and services (openly) and exchange information.
To support these scenarios, the E-Business scenario diagram was developed. In conjunction with other methods and various components supplied by ARIS, it enables optimal support of the implementation of e-business projects. This chapter on e-business scenario diagrams first describes the method with all objects and evaluation options and then goes on to discuss interrelationships with other methods. At the end of the chapter, a use case demonstrates the complex possibilities.