Working with Decision Tables
A decision table is a decision entity. It is a compact way to depict a complex set of rules in an IF Condition THEN Result syntax.
Decision Table Structure
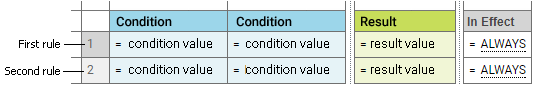
In a decision table, the conditions and corresponding results are sorted into rows and columns. A column can either represent a condition (blue color) or a result (green color) of a rule. There can be more than one condition and more than one result. Each row in a decision table represents one individual rule.
Decision Table in the Decision Entity Editor
Condition
A condition is specified by a parameter element.
Condition Value
A condition value can consist of:

An operator and a literal value.

An operator and a parameter element (marked by a dotted line).

An operator and an action that delivers an output value (marked by a dotted line and () behind the name).

An operator and a constant (marked by a dotted line).

An operator and an expression (marked by a dotted line).
Result
The following table explains the result types.
Result | Description |
Assignment Result | An assignment result is specified by a parameter element. This result type is applied, whenever you want to assign a value to a result. |
Action Result | An action result is specified by an action. This result type is applied, whenever you want to execute an action from a decision table. |
Assignment Result Value
An assignment result value can consist of:

An operator and a literal value.

An operator and a parameter element (marked by a dotted line).

An operator and an action that delivers an output value (marked by a dotted line and () behind the name).

An operator and a constant (marked by a dotted line).

An operator and an expression (marked by a dotted line).
Action Result Value
The action result value expresses the action status. There are two types:

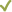
(action is enabled).

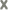
(action is disabled).
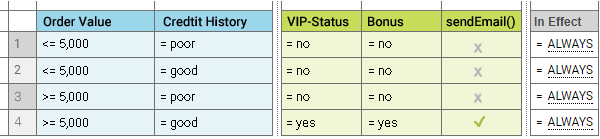
The following table shows two sample rules can be modeled in a decision table:
Rule 1: | IF a customer has a good credit history, and the annual order value is equal to or larger than $ 5,000, THEN this customer is a VIP customer. |
Rule 2: | IF a customer is a VIP customer, THEN he/she will receive a bonus at the end of a year and will be notified of this by email. |
The corresponding decision table uses two conditions, two assignment results, and one action result:
Decision Table Example