Monitoring Multiple Events in Array Lists
When configuring custom attributes for monitoring and the attributes are for an array data type (for example, DATETIME LIST), you can post the events to Optimize in arrays of events or as a single array with all the values. You specify your choice while configuring the event map (from the Administration > Integration > B2B > Business Monitoring page).
When configuring the event map:

Selecting
Post multiple events for arrays sends multiple events for the same document when there is a arraylist in custom attributes or multiple elements in system attributes.

Clearing
Post multiple events for arrays sends all attribute values in a single event for an array (for example, ordernumber1, ordernumber2, ordernumber3).
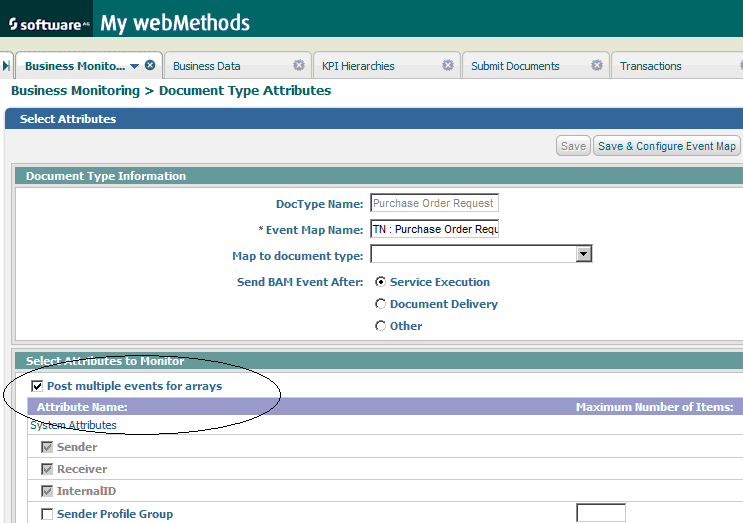
To post events to Optimize in arrays of events rather a single array with all the values, go to the Administration > Integration > B2B > Business Monitoring page, and select Post multiple events for arrays, as shown below.
Figure 4. Post Multiple Events for Arrays selection
When Post multiple events for arrays is selected, the Maximum Number of Items field is disabled for the attributes.
After you configure the event map, click the Save and Configure Event Map button. The Event Map page appears, with the individual array element.
After the event map is configured and the document type is enabled for monitoring, Trading Networks sends events to Optimize as follows:
 Optimize
Optimize determines how many events to create for this transaction based on the maximum size of arrays in the extracted monitored attributes.
For example, the attributes "Sender Profile Group," "Receiver Profile Group," and custom attributes "ArrayList1" and "ArrayList2" are enabled for monitoring. Optimize determines the maximum number of elements available in the four attributes and creates that many events. If "ArrayList1" has 20 elements and the other attributes each contain fewer than 20 elements, Optimize creates 20 events.

Individual attributes such as Sender, Receiver, and InternalID are always populated in all events. Arrays are populated in terms of their size.
For example, if five events are to be created and "ArrayList1" has five elements and "ArrayList2" has two elements, the events are populated as follows:
1st event - Sender / Receiver / InternalID / Arraylist1[0] / Arraylist2[0]
2nd event - Sender / Receiver / InternalID / Arraylist1[1] / Arraylist2[1]
3rd event - Sender / Receiver / InternalID / Arraylist1[2]
4th event - Sender / Receiver / InternalID / Arraylist1[3]
5th event - Sender / Receiver / InternalID / Arraylist1[4]