How Do I Publish Data to a Message Queue using Custom Destination?
This use case explains how to publish data to a message queue.
The use case starts when you have data to be published and ends when you have successfully configured a message queue as a destination to publish the data.
Ensure you have a JMS/AMQP environment set up with the required connection alias configured. For details on setting up the JMS/AMQP setup, see
Messaging.

To publish data to a message queue
1. Expand the menu options icon

, in the title bar, and select
Administration.
2. Click Destinations.
3. Select Custom destinations from the left navigation pane.
The Custom destination page appears.
4. Provide the name of the custom destination in the Name field.
The name must be unique and must not be the name of any pre-defined API Gateway destinations such as Elasticsearch.
5. To configure conditions that determine the data to be published in the specified destination, perform the following steps in the Conditions section:

Select one of the following options in the
Condition type field:
 AND
AND. To publish data that satisfies all your conditions.
 OR
OR. To publish data that satisfies one of your conditions.

Click
+ Add condition.

Provide the following details for your condition:
 Variable
Variable. Name of the variable based on which you want to validate your condition. This field supports the variables that are available in the Variable framework. For details on the list of variables, see
Variable Framework.
 Operator
Operator. The operator to use to relate variable and the value.
 Value
Value. The value of the variable that must be matched to satisfy the condition.

Click
Add.
The condition appears in the grid.
Repeat this process to add the required number of conditions. Click on a condition to edit it and click

next to a condition to delete it.
6. Select Mesaging in the Type field.
7. Provide the following information in the Messaging section, as required:
Property | Description |
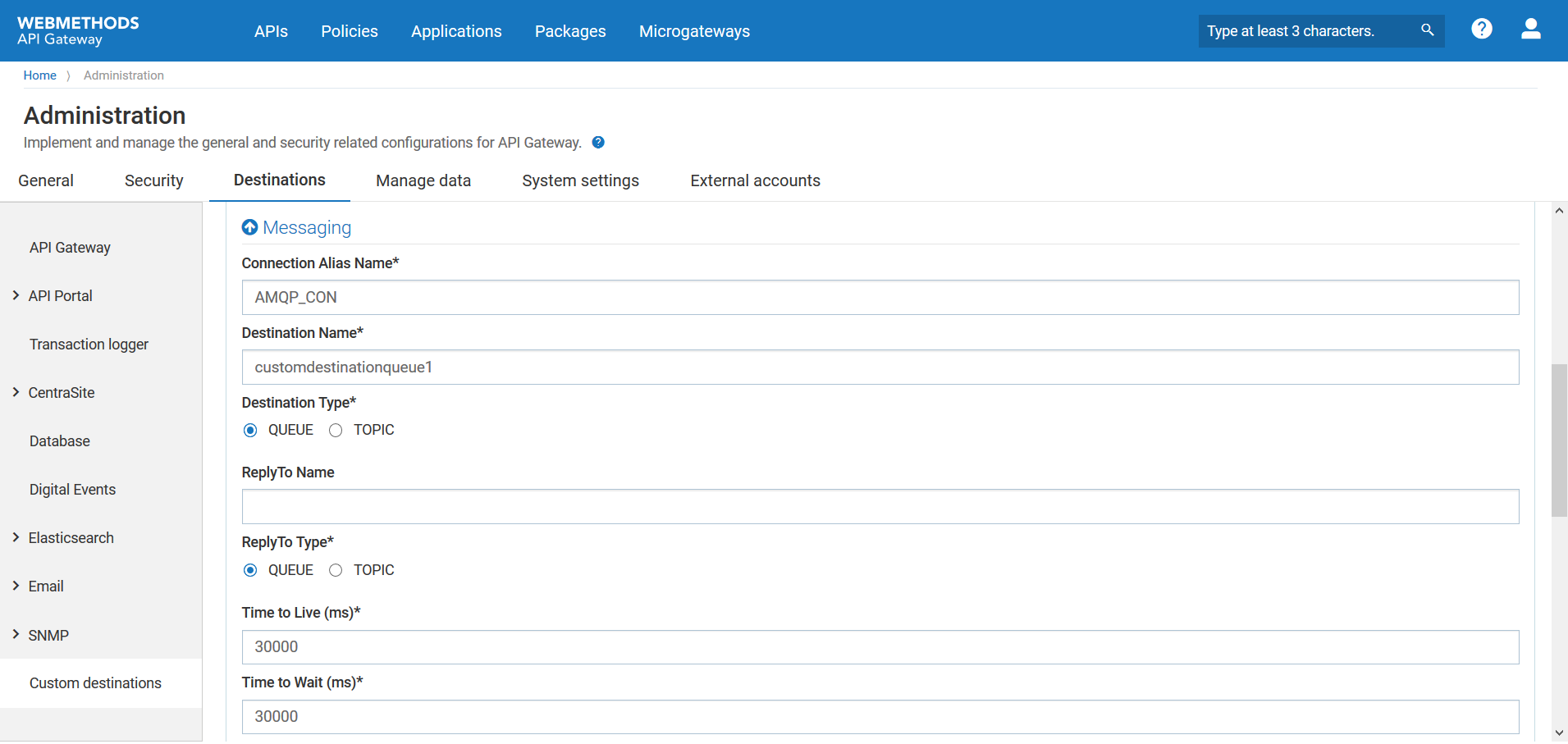
Connection Alias Name | Name of the connection alias you have configured. You can configure the connection alias under Administration > Messaging section. For details on how to configure the connection alias, see
Messaging. |
Destination Name | Specify the destination to which the request message is sent. A new destination is created with this name to publish events. |
Destination Type | Specify the destination type to which the request message is sent. |
Reply To Name | Specify the destination to which the response message is sent. |
Reply To Type | Specify the destination type to which the response message is sent. Select one of the following types:  QUEUE QUEUE. Indicates that the response message is sent to a particular queue.  TOPIC TOPIC. Indicates that the response message is sent to a particular topic. |
Time to Live (ms) | Provide a numeric value that specifies the expiration time (in milliseconds) of the JMS or AMQP message. If the time-to-live is specified as zero, expiration is set to zero, which indicates that the message does not expire. |
Time to Wait (ms) | Defines the time in milliseconds for which API Gateway listens to the Reply To Queue or Topic for the response message. |
Delivery Mode | The message delivery mode for the request message. This is the delivery mode that web service clients must specify in the JMS or AMQP message that serves as the request message for the web service. Select one of the following modes:  Non-Persistent Non-Persistent. Indicates that the request message is not persistent. The message might be lost if the JMS provider fails.  Persistent Persistent. Indicates that the request message should be persistent. The message is not lost if the JMS provider fails. |
8. Configure the custom properties of the custom extension as required.
9. From the Events section, select the data that you want to publish to the configured destination. The options available are:
 Event types
Event types. Type of events to publish to the specified destination. The available event types are:
 Error
Error: Occurs each time an API invocation results in an error.
 Lifecycle
Lifecycle: Occurs each time API Gateway is started or shut down.
 Policy violation
Policy violation: Occurs each time an API invocation violates the policy enforcement that was set for the API.
 Performance metrics data
Performance metrics data. To publish to the specified destination.
In the Publish interval of performance metrics data field, type a time interval (in minutes) to specify how often API Gateway must publish performance metrics. Provide a value from 1 through 60. The default is 60 minutes.
 Events
Events. API Gateway modules for which the audit logs to publish to the specified destination.
10. Click Add.
The custom destination is created successfully and appears in the Custom destinations page. The configured events are published to the specified destination.
Note:
To edit a custom destination, you can click the required custom destination, make changes and click Update. To delete a custom destination, click

next to required custom destination. You cannot delete a custom destination that is associated with an API.
 next to a condition to delete it.
next to a condition to delete it.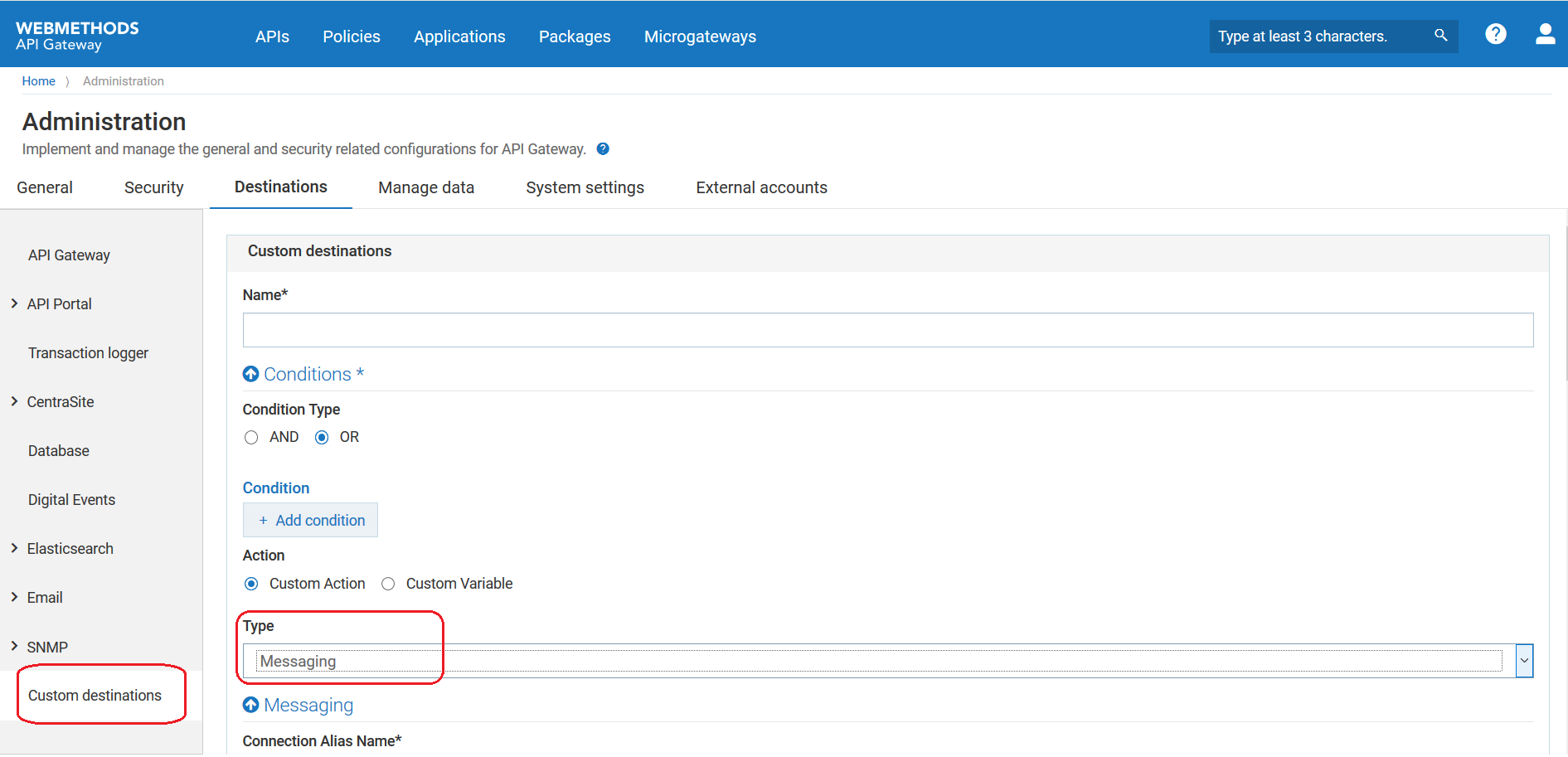
 next to required custom destination. You cannot delete a custom destination that is associated with an API.
next to required custom destination. You cannot delete a custom destination that is associated with an API.