JWT Authentication Use case and Workflow
JSON Web Token is a JSON-based open standard (
RFC 7519) means of representing a set of information to be securely transmitted between two parties. A set of information is the set of claims (claim set) represented by the JWT. A claim set consists of zero or more claims represented by the name-value pairs, where the names are strings and the values are arbitrary JSON values. The claims in a JWT are encoded as a JSON object that is used as the payload of a JSON Web Signature (JWS) structure, enabling the claims to be digitally signed. JWTs can be signed using a shared secret (with HMAC algorithm), or a public or private key pair using RSA.
API Gateway can generate a JWT token itself or validate the JWT token generated by a trusted third-party server. API Gateway uses the RSA-based JWT to provide stronger integrity protection to JWTs when API Gateway is the issuer of the token. The JSON-based access tokens contain one or more claims. A claim is any piece of information that serves as an unique identifier, and that the token issuer who generated the token has verified. API Gateway extracts the claims from the JWT, identifies the application and then authorizes access to the protected resource.
Note:
JWT authentication is supported for both REST and SOAP APIs. API Gateway does not support Base 64 encoded JWT tokens.
Use case 1: JWT authentication with API Gateway as a JWT issuer
This describes the high level workflow for the scenario where API Gateway can generate the JSON Web Token itself.
1. Configure API Gateway as an internal authorization server.
2. Enforce the Identify & Authorize policy on the API.
3. Associate an application with the API.
You can create a new application or use an existing one. Ensure that you add the required claims while creating the application, which you would use to validate the access token. For a complete procedure on creating an application with a strategy, see
Creating an Application.
4. Activate the API.
User on invoking the API uses the JWT identification method to access the protected resource.
5. You get the JWT in one of the following ways (with or without claims), which you can pass as a bearer token to invoke the API.
Use case 2: API Gateway with an external JWT issuer
This describes the high level workflow for the scenario where API Gateway accepts JSON Web Token generated by a trusted third-party server.
1. Configure an external authorization server.
2. Enforce the Identify & Authorize policy on the API.
3. Associate an application with the API.
You can create a new application or use an existing one. Ensure that you add the required claims while creating the application, which you would use to validate the access token and the external authorization server that would be the JWT issuer. For a complete procedure on creating an application with a strategy, see
Creating an Application. Refer the
Authorizations for applications created from API Portal section for information on configuring authorization server for the applications created from API Portal.
4. Activate the API.
User on invoking the API uses the JWT identification method to access the protected resource.
5. Pass the JWT as a bearer token to invoke the API.
Use case 3: JWT authentication with API Gateway for applications registered from API Portal
This use case describes the high-level workflow for the scenario where API Gateway generates the JSON Web Tokens for the applications registered from API Portal. From API Portal, you can create applications for APIs that require JWT access tokens to access them and test APIs from API Portal.
1. Configure an internal or external authorization server in API Gateway.
2. Create an API.
3. Enforce the Identify & Authorize policy on the API.
4. Provide the name of the authorization server in the watt.server.oauth.authServer.alias settings in the Administration section of API Gateway.
5. Publish the API to API Portal.
6. Log in to API Portal.
7. Open the API that you published from the API gallery page.
8. Click Get access token from the right pane of the API details page request an access token to access and use the API.
9. In the Request API access token dialog box, provide the Application name and Application description. The application is created and listed in the Applications page.
10. Click Try API.
11. Select the required application from the Application drop-down list in the left pane.
12. Select the resource, that you want to try, from the left pane.
13. In the Authorization tab, select JWT from the Authorization type drop-down list.
14. Do one of the following:

Provide your Integration Sever credentials in the
User name,
Password field, and click
Get token. Select a token from the available list of tokens, and click
Update.

Provide the JWT token or select one from the available list of tokens, and click
Update.
The bearer token value appears in the Value field of the Header tab.
Note:
If you are using a REST client like Postman or SoapUI to create an consumer application and invoke a REST API, then you must generate the application authentication using static or dynamic payload, and provide the bearer token value to invoke the API. But, if you are using API Portal to register a consumer application, this process is made simple using the Get token feature in the Try API section of API Portal.
15. Click Send. The response for the selected method appears.
JWT Authorization Workflow
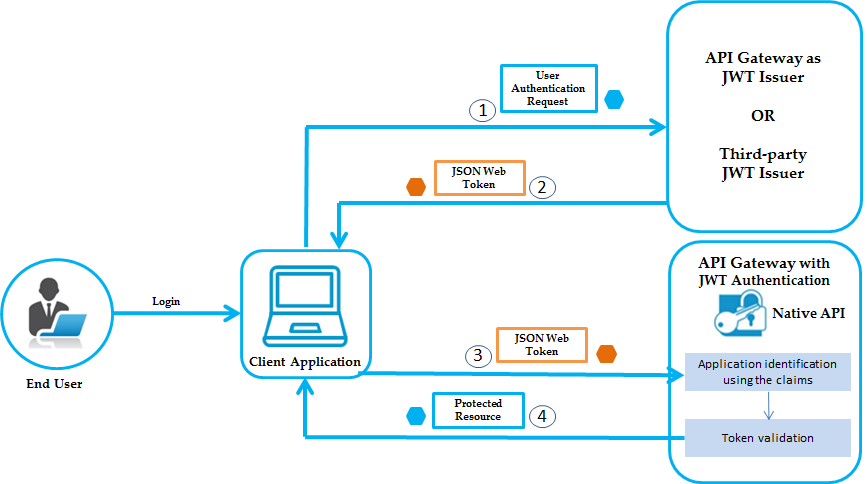
The flow of authorization requests and responses between the end user, client application, JWT issuer, and resource server is as depicted in the following figure.
The JWT authorization workflow is as follows:
1. The end user logs in, the client application sends an authentication request to API Gateway or to any third-party JWT issuer, to obtain a JWT token.
2. If API Gateway is the JWT issuer, then it validates the user or the application. If the user or application credentials are valid, API Gateway generates the JSON token using a private key that was specified in the JWT configuration, and sends the generated token to the client.
If the user credentials are invalid, API Gateway returns a specific error response.
3. Client sends the generated JSON token in the HTTP Authorization request header as a Bearer token to access the protected API in API Gateway.
4. API Gateway first identifies the application based on claims from the JWT, then validates the JWT using the public certificate of the issuer (the issuer can be API Gateway or a third-party issuer) and provides access to the protected resources.
If the validation fails, API Gateway returns a specific error response.
Note:
If API Gateway has generated the JSON token, it validates the signature using a public certificate that was specified in the JWT configuration. Else, if the HTTP request is sent from a third-party JWT issuer, API Gateway validates the token using a public certificate or the JWKS URI of the issuer.