High Availability and Disaster Recovery
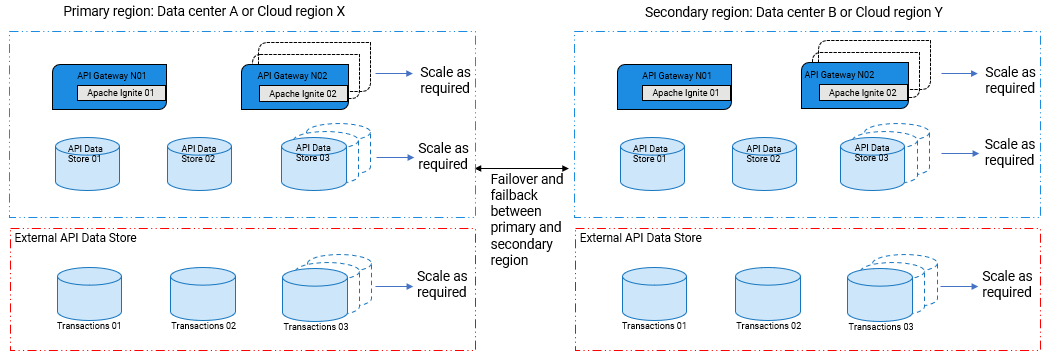
The architecture of high availability and disaster recovery (HADR) is as follows:
When an entire data center goes down due to natural disaster, equipment failure, or cyber attack, a business has to recover lost data from where the data is backed up. The disaster recovery relies upon the replication of the backed up data in a safe network or a cloud location that is not affected by the disaster.
Disaster recovery architecture can be setup using Cold standby mode or Warm standby mode.
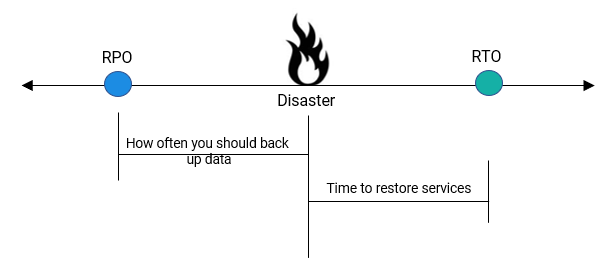
The two most important parameters for a disaster recovery plan are:
 Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
Recovery Point Objective (RPO). Describes the age of files that must be recovered from backup for a business operation to resume after a disaster. It also specifies how often you should back up data. For example, if your RPO value is 15 minutes, then the data before 15 minutes of a disaster must be restored for operations to resume.
 Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
Recovery Time Objective (RTO). Describes the duration and service level within which you must restore the most critical IT services after a disaster. For example, if your RTO value is 60 minutes, the data in the required systems must be restored within 60 minutes of a disaster event.
You can have an effective disaster recovery management in place by configuring a reliable repository and by taking data backup at regular intervals.
The recovery process during disaster recovery is categorized into two stages:
 Failover
Failover. The failover operation is the process of switching data from a primary data center to a backup facility.
 Failback
Failback. The failback operation is the process of returning data from the backup facility to the primary data center.