Container Orchestration allows automated deployment, scaling and management of ApplinX servers running in Docker containers. Multiple instances of containers can be deployed on multiple nodes running on multiple hosts. Container orchestration allows load balancing and health monitoring. It supports takeover scenarios if, for example, one node or one container dies. The management of the worker nodes is done by the master node.
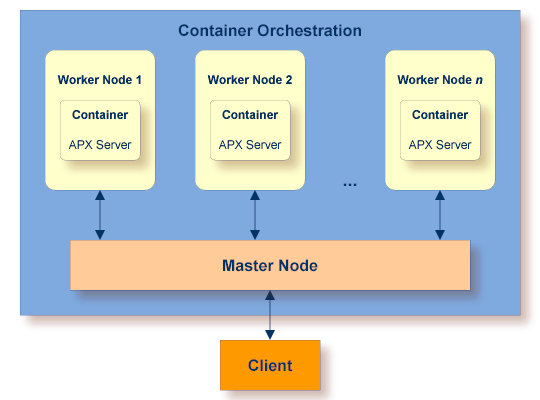
The following ApplinX components are available inside the ApplinX container (depending on the license used):
ApplinX Web Emulation
ApplinX API Enabling
The ApplinX container can be deployed in a container orchestration environment, for example Kubernetes. This document covers the following topics:
See also High Availability with Container Orchestration under Managing the ApplinX Server.
A typical container orchestration environment has at least one master node and several worker nodes. Containers can be deployed on multiple worker nodes. If one node fails, the remaining nodes keep the application alive. The deployable unit for a worker node is called a pod. A pod consists of at least one container. Containers running in the same pod share the same network namespace (same IP and port space) and the same IPC namespace (visible to each other over PID). From outside the pod, containers are only reachable via sockets.
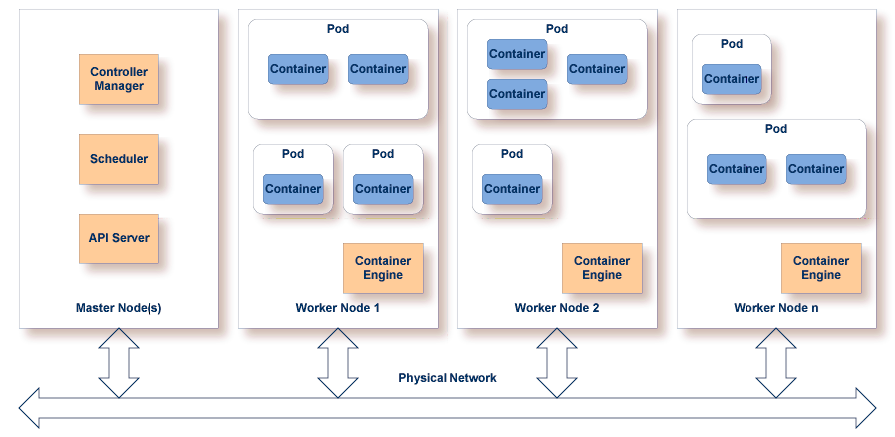
This example assumes you have a Kubernetes cluster installed.
 To Deploy ApplinX Server in a Kubernetes cluster
To Deploy ApplinX Server in a Kubernetes cluster
Create a pod containing the images of ApplinX Server. Find more details here: Building an ApplinX Docker Image in the Getting Started documentation.
Configure a deployment for multiple ApplinX Server instances.
Assign a port to a service to access the ApplinX Web Emulation - or ApplinX Server if you want to connect with the Designer or Administrator - from outside the Kubernetes cluster.
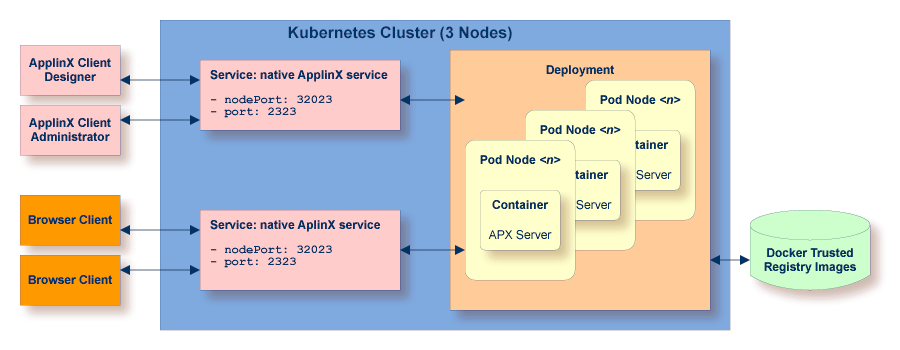
The following graphic shows the deployment of ApplinX Server in a Kubernetes cluster:
Kubernetes uses YAML files to describe the deployment of pods, services and ConfigMaps. Below is a sample configuration file applinx.aml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: applinx-service
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: applinx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
name: web-services
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
nodePort: 32080
- protocol: TCP
name: applinx
port: 2323
targetPort: 2323
nodePort: 32023
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: applinx
name: applinx-deployment
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: applinx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: applinx
spec:
containers:
- image: applinx:10.5.0.0335
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /opt/softwareag/healthcheck.sh
name: applinx
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /license
name: licenses
- mountPath: /opt/softwareag/ApplinX/tomcat/webapps/ApplinX/WEB-INF/host-applications
name: host-applications-data
- mountPath: /opt/softwareag/ApplinX/tomcat/webapps/ApplinX/WEB-INF/config
name: server-config
- mountPath: /opt/softwareag/ApplinX/tomcat/webapps/ApplinX/config
name: framework-config
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 36000
volumes:
- name: host-applications-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: host-applications-claim
- name: framework-config
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: framework-config-claim
- name: server-config
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: server-config-claim
- name: licenses
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: licenses-claim
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: framework-config-claim
labels:
app: applinx
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 20M
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: licenses-claim
labels:
app: applinx
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadOnlyMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 10M
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: host-applications-claim
labels:
app: applinx
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 200M
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: server-config-claim
labels:
app: applinx
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 20M
You can update your deployment to use a new image, for example for a version update.
 To update a version in a container orchestration environment
To update a version in a container orchestration environment
Enter the following command:
kubectl --record deployment.apps/applinx-deployment set image deployment.v1.apps/applinx-deployment applinx=applinx:10.5.0.335