The SUBCISPAGE2 control allows you to place one page into another page. You may already have read the section describing the SUBPAGE control which allows to place any HTML page into an Application Designer page. The differences between the SUBCISPAGE2 and the SUBPAGE tag are:
With SUBCISPAGE2, you embed Application Designer pages, not normal HTML pages.
Application Designer pages are normally started using a servlet "StartCISPage" which creates an embedding frame in which the Application Designer page is placed. The SUBCISPAGE2 control automatically creates this frame, you do not have to take care of this.
There is a defined communication channel allowing the "outside page" to interact with the "embedded page", and vice versa.
The embedded page is automatically linked to the Application Designer session management. It runs in the same session - and typically also in the same subsession as the embedding page.
This document covers the following topics:
The following example shows the input of an article number and its article detail data:
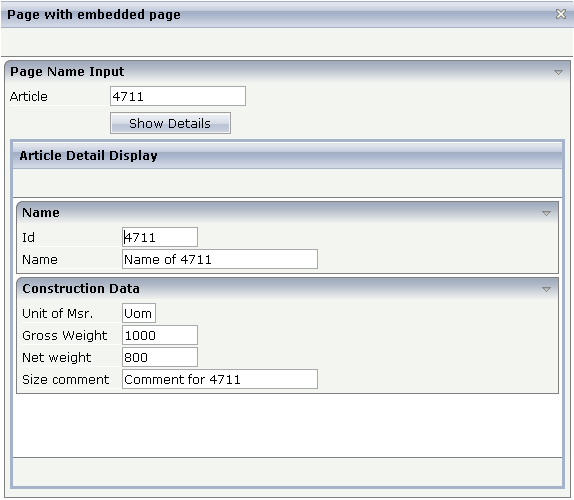
The detail data page is embedded into the whole (outer) page. The XML code of the outer page is:
<page model="OuterPageAdapter" pagename="Demo.html">
<titlebar name="Page with embedded page">
</titlebar>
<header>
</header>
<pagebody takefullheight="true">
<rowarea name="Page Name Input">
<itr>
<label name="Article" width="100">
</label>
<field valueprop="article" length="20">
</field>
</itr>
<vdist height="5">
</vdist>
<itr>
<hdist width="100">
</hdist>
<button name="Show Details" method="showDetails">
</button>
</itr>
<vdist height="5">
</vdist>
<rowtable0>
<itr width="100%">
<subcispage2 subcispageprop="innerPage" width="100%" height="350" borderwidth="1">
</subcispage2>
</itr>
</rowtable0>
<vdist height="5">
</vdist>
</rowarea>
</pagebody>
<statusbar withdistance="false">
</statusbar>
</page>
The SUBCISPAGE2 control references a property
innerPage which is provided by the adapter class
of the page. The height can be specified depending on the whole page's height
or can be fixed.
The corresponding adapter source is:
// This class is a generated one.
import com.softwareag.cis.server.Adapter;
import com.softwareag.cis.server.util.SUBCISPAGEInfo;
public class SubCisPage2Adapter
extends Adapter
{
// property >innerPage<
SUBCISPAGEInfo m_innerPage = new SUBCISPAGEInfo();
public SUBCISPAGEInfo getInnerPage() { return m_innerPage; }
// property >article<
String m_article;
public void setArticle(String value) { m_article = value; }
public String getArticle() { return m_article; }
/** */
public void init()
{
m_innerPage.showPage("ArticlePage.html");
}
/** */
public void showDetails()
{
// fetch adapter of inner page
ArticlePageAdapter ipa = (ArticlePageAdapter) findAdapter(ArticlePageAdapter.class);
ipa.init(m_article);
// trigger a refresh of the innerpage
m_innerPage.refreshContentOfCurrentPage();
}
}
The property innerPage is of type
com.softwareag.cis.server.util.SUBCISPAGEInfo. With
method SUBCISPAGEInfo.showPage, the article page is
started within the subarea. This does not have to be flexible all the time -
but it may be on request. (Maybe there are several versions of displaying the
detail data, depending on the article type).
When choosing the button, the
method showDetails() is called. It prepares the
adapter of the inner page to display the detail data of the requested article.
Afterwards, the method
SUBCISPAGEInfo.refreshContentOfCurrentPage is called
in order to reload the embedded page. Consequently, the article details are
shown.
See the JavaDoc documentation of class
SUBCISPAGEInfo.
| Basic | |||
| subcispageprop |
Name of adapter property representing the control on server side. The property must be of type "TABSUBPAGESInfo". View the Java API Documentation for further information. |
Optional | |
| width |
Width of the control. There are three possibilities to define the width: (A) You do not define a width at all. In this case the width of the control will either be a default width or - in case of container controls - it will follow the width that is occupied by its content. (B) Pixel sizing: just input a number value (e.g. "100"). (C) Percentage sizing: input a percantage value (e.g. "50%"). Pay attention: percentage sizing will only bring up correct results if the parent element of the control properly defines a width this control can reference. If you specify this control to have a width of 50% then the parent element (e.g. an ITR-row) may itself define a width of "100%". If the parent element does not specify a width then the rendering result may not represent what you expect. |
Optional |
100 120 140 160 180 200 50% 100% |
| height |
Height of the control. There are three possibilities to define the height: (A) You do not define a height at all. As consequence the control will be rendered with its default height. If the control is a container control (containing) other controls then the height of the control will follow the height of its content. (B) Pixel sizing: just input a number value (e.g. "20"). (C) Percentage sizing: input a percentage value (e.g. "50%"). Pay attention: percentage sizing will only bring up correct results if the parent element of the control properly defines a height this control can reference. If you specify this control to have a height of 50% then the parent element (e.g. an ITR-row) may itself define a height of "100%". If the parent element does not specify a width then the rendering result may not represent what you expect. |
Optional |
100 150 200 250 300 250 400 50% 100% |
| comment |
Comment without any effect on rendering and behaviour. The comment is shown in the layout editor's tree view. |
Optional | |
| Appearance | |||
| width | (already explained above) | ||
| height | (already explained above) | ||
| borderwidth |
Border size of control in pixels. Specify "0" not to render any border at all. |
Optional |
1 2 3 int-value |
| withownborder |
Default is false. If WITHOWNBORDER is set to true, the subcispage2 control is rendered with its own 3D lookalike border. Set BORDERWIDTH to 0 if WITHOWNBORDER is set to true. |
Optional |
true false |
| pagestyle |
CSS style definition that is directly passed into this control. With the style you can individually influence the rendering of the control. You can specify any style sheet expressions. Examples are: border: 1px solid #FF0000 background-color: #808080 You can combine expressions by appending and separating them with a semicolon. Sometimes it is useful to have a look into the generated HTML code in order to know where direct style definitions are applied. Press right mouse-button in your browser and select the "View source" or "View frame's source" function. |
Optional | |
| colspan |
Column spanning of control. If you use TR table rows then you may sometimes want to control the number of columns your control occupies. By default it is "1" - but you may want to define the control to span over more than one columns. The property only makes sense in table rows that are snychronized within one container (i.e. TR, STR table rows). It does not make sense in ITR rows, because these rows are explicitly not synched. |
Optional |
1 2 3 4 5 50 int-value |
| rowspan |
Row spanning of control. If you use TR table rows then you may sometimes want to control the number of rows your control occupies. By default it is "1" - but you may want to define the control to span over more than one columns. The property only makes sense in table rows that are snychronized within one container (i.e. TR, STR table rows). It does not make sense in ITR rows, because these rows are explicitly not synched. |
Optional |
1 2 3 4 5 50 int-value |