Securing Access Token Calls with PKCE
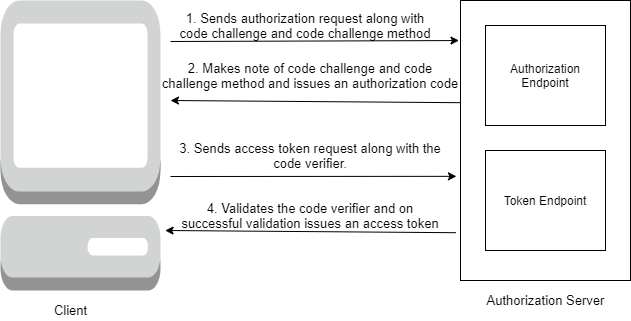
PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange) is a mechanism that prevents Authorization Code Interception attacks and makes OAuth 2.0 authorization code grant more secure for public clients. The client application should give proof to the authorization server that the authorization code belongs to the client application. Only then the authorization server issues an access token for the client application.
The PKCE flow works with these parameters:
 Code Verifier
Code Verifier. The code verifier should be a high-entropy cryptographic random string with a minimum of 43 characters and a maximum of 128 characters.
 Code Challenge
Code Challenge. The code challenge is created by SHA256 hashing the code verifier and then applying base64 URL encoding of the resulting hash. If the client cannot do the hashing and encoding transformation, it can use the code challenge method as
plain where the code challenge is same as code verifier
 Code Challenge Method
Code Challenge Method. This is an optional parameter. If the client uses SHA256 hashing the code challenge method value must be
S256. If no hashing is done, then the code challenge method value must be
plain. If the code challenge method value is not passed in the client request then plain would be considered as default value.
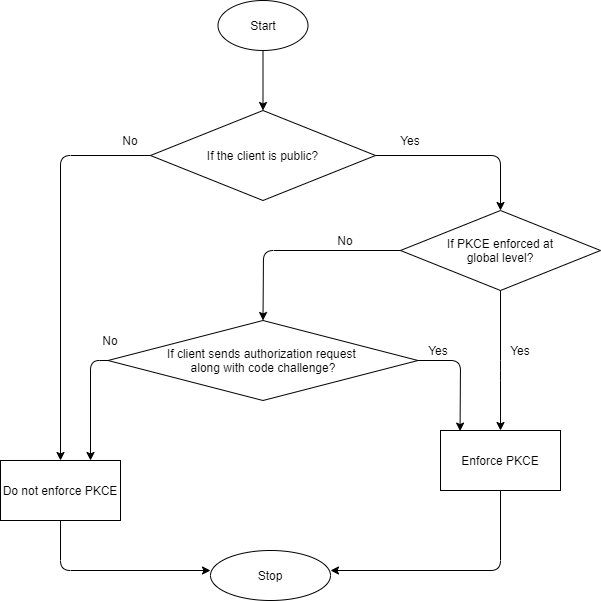
The flow chart explains the Get Access Token workflow in API Gateway using authorization code grant type with PKCE.