Configuring Reverse Invoke Setup
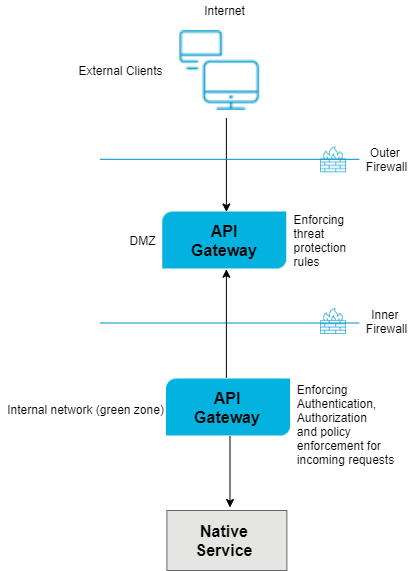
In this scenario, you can configure the threat protection rules in API Gateway server (Standard Edition) located in the DMZ. In the API Gateway instance located in the green zone, you can configure the authentication, authorization, and mediation rules prior to routing the requests to the native API.
Note:
For a HA setup in API Gateway Standard Edition in DMZ, two nodes are adequate, and Software AG recommends not to cluster the API Gateway Standard Edition. Hence, policies, threat protection rules and configurations must be created or deployed to individual nodes to keep the nodes synchronized.
The following figure describes how reverse invoke works. The client requests are sent to the API Gateway instance in DMZ. These requests are present on the registration port. The green zone API Gateway listens to these requests through the listener port, processes the request through the native service application and responds back to the API Gateway instance in DMZ. The API Gateway instance in DMZ responds to the external clients.
Important:
A connection between API Gateway Server in DMZ and the API Gateway Server in Green zone is available except when a request is being made to the API Gateway in green zone or a response is being returned from the API Gateway in green zone. In other words, DMZ API Gateway connection utilization is I/O bound. Therefore, if you expect large, simultaneous transactions, increase the number of registered connections accordingly.

To configure reverse invoke
1. Configure external and registration ports on API Gateway in DMZ.
a. Log on to API Gateway as an Administrator user.
b. Expand the menu options icon, in the title bar, and select Administration.
c. Navigate to Security > Ports.
d. Click Add ports.
e. Select API Gateway external option from the Type drop-down menu.
f. Click Add.
g. Provide the following information in the API Gateway external listener configuration to configure the External port.
 External port
External port. Specifies the port number you want to use for the external port.
Use a number that is not already in use. This is the port that clients connect to through your outer firewall.
 Alias
Alias. Specifies an alias for the port.
An alias must be between 1 and 255 characters in length and include one or more of the following: letters (a -z, A-Z), numbers (0-9), underscore (_), period (.), and hyphen (-).
 Description (optional)
Description (optional). A description of the port.
 Protocol
Protocol. Specifies the protocol to use for this port (HTTP or HTTPS).
If you select HTTPS, additional security and credential boxes appear for which you have to provide the required values.
 Bind address (optional)
Bind address (optional). Specifies the IP address to which to bind this port.
Specify a bind address if your machine has multiple IP addresses and you want the port to use this specific address. If you do not specify a bind address, API Gateway picks one for you.
 Backlog
Backlog. Specifies the number of requests that can remain in the queue for an enabled port before
API Gateway begins rejecting requests.
The default is 200. The maximum value is 65535.
 Keep alive timeout
Keep alive timeout. Specifies when to close the connection if the server has not received a request from the client within this timeout value (in milliseconds) or when to close the connection if the client has explicitly placed a close request with the server.
The default value is 20000ms.
Note:
For more information on ports, see
Ports.
h. If you want to configure m-TLS, select HTTPS in the Protocol field under API Gateway external listener configuration and select one of the following options in the Client authentication field, in the in Security configuration section.
 Request client certificate
Request client certificate. This option requests for a certificate from the client. However, even if the client does not provide a valid certificate, the connection is established.
 Require client certificate
Require client certificate. This option requests for a certificate from the client. If the client does not provide a valid certificate, the connection is not established. If you select this option, you must also configure the following fields in the
Listener specific credentials section.
 Keystore alias
Keystore alias. Select a Keystore.
 Key alias(signing)
Key alias(signing). Select a Key alias.
 Truststore alias
Truststore alias. Select Truststore.
i. Provide the required information to configure the registration port, in the API Gateway registration listener configuration section.
The important fields to be configured are
Registration port,
Alias, and
Protocol. For more information on ports, see
Ports.
j. Configure the Keystore alias, Key alias, and Truststore alias fields. in the Listener specific credentials section.
2. Click Add.
3. Click the  icon in the Enabled column next to the external and registration ports to enable them.
icon in the Enabled column next to the external and registration ports to enable them. The port is enabled and a success message appears.
4. Execute the following steps in the green zone API Gateway.
a. Create an API Gateway internal port.
b. Select HTTPS in the Protocol field.
c. In the API Gateway external server section, type the hostname of the DMZ API Gateway in the Host field.
d. Type the port number of the API Gateway registration port of DMZ API Gateway in the Port field.
e. In the Registration credentials section, provide the following information.
 Keystore alias
Keystore alias. Select a Keystore.
 Key alias(signing)
Key alias(signing). Select a Key alias.
 Truststore alias
Truststore alias. Select Truststore.
5. Configure the internal port of the API Gateway in green zone with the registration port of API Gateway in DMZ.
6. Configure load balancer URL in the green zoneAPI Gateway.
a. Expand the menu options icon, in the title bar, and select Administration.
b. Navigate to General > Load balancer.
Provide the configured external server host and port or an external load balancer URL. The API endpoints expose this port for external consumers. If you have a Load Balancer, then the requests from the Load Balancer must be directed to API Gateway's external port.
For more information on load balancers, see
Clusters and Load Balancers.
7. Create an API in the internal API Gateway Server with routing protocol and endpoint as the native API. For more information on how to create APIs, see
Creating an API. 8. You can now access the API by using the URL in the format http://externalserver:externalport/gateway/api-name/resource-path.

 icon in the Enabled column next to the external and registration ports to enable them.
icon in the Enabled column next to the external and registration ports to enable them.