The API for Context Variables
API Gateway provides an IS service that you can use to:

Set, get, declare, and remove custom context variables.

Set and get the predefined system context variables. (It is not allowed to declare or remove the predefined system context variables.)
API Gateway provides the following JAVA services, which are defined in the class ISMediatorRuntimeFacade.java:

pub.apigateway.ctxvar:getContextVariable

pub.apigateway.ctxvar:setContextVariable

pub.apigateway.ctxvar:declareContextVariable

pub.apigateway.ctxvar:removeContextVariable
pub.apigateway.ctxvar:getContextVariable
Use this JAVA service to retrieve a context variable’s value and assign it to a pipeline variable. All parameter names are case-sensitive.
Parameter | Pipeline Type | Data Type | Description | Examples |
MessageContext | in | Object ref | This object is inserted into the pipeline by API Gateway. | N/A |
varName | in | String | Context variable name (system or custom). | For system context variable, use just the variable name to get its value. For example, PROTOCOL_HEADERS. For custom context variable, use the prefix "mx:" with the variable name to get its value. For example, mx:CUSTOM_VAR |
serValue | out | Object ref | Java.io.serializable value. (Usually a string). | |
The table lists the predefined system context variables and its syntax used to get system context variables using pub.apigateway.ctxvar:getContextVariable.
System Context Variable Name | ctxVar IS Service Syntax | Set or Get Supported |
User | USER | Supports get |
Inbound HTTP method | INBOUND_HTTP_METHOD | Supports get |
Routing method | ROUTING_METHOD | Supports get |
Inbound content type | MESSAGE_TYPE | Supports get |
Inbound accept | BUILDER_TYPE | Supports get |
Inbound protocol | INBOUND_PROTOCOL | Supports get |
Inbound request URI | INBOUND_REQUEST_URI | Supports get |
Inbound IP | INBOUND_IP | Supports get |
Gateway hostname | MEDIATOR_HOSTNAME | Supports get |
Gateway IP | MEDIATOR_IP | Supports get |
Operation name | OPERATION | Supports get |
Native Endpoint | NATIVE_ENDPOINT | Supports get Note:
This variable returns native endpoint value, only after Routing policy gets executed. |
Protocol headers | PROTOCOL_HEADERS[xxx] | Supports set and get |
SOAP headers | SOAP_HEADERS[xxx] | Supports set and get |
Notes on getting and setting the PROTOCOL_HEADERS
All context variable values are typed as either string or int except for the predefined context variables, PROTOCOL_HEADERS, which is of the type IData. You can set or get value for PROTOCOL_HEADERS in one of the following ways:
 set or get the entire structure.
set or get the entire structure.To set the entire structure, you must:

Set the
varName parameter in
pub.apigateway.ctxvar:setContextVariable to
PROTOCOL_HEADERS.

Use the method
ISMediatorRuntimeFacade.setContextVariableValue().
To get the entire structure, you must:

Set the
varName parameter in
pub.apigateway.ctxvar:getContextVariable to
PROTOCOL_HEADERS.

Use the method
ISMediatorRuntimeFacade.getContextVariableValue().
If the varName is set to PROTOCOL_HEADERS, you get or set the entire IData structure containing all of the transport headers. The key is the transport header name (for example, Content-Type) and the value is a String. The IData object for PROTOCOL_HEADERS contains a set of string values where each IData string key matches the header name in the transport headers map. The set of possible keys includes the HTTP v1.1 set of headers as well as any custom key-value pairs you might have defined.
Alternatively, you can set the varName parameter to address a specific element in the array. For example, setting it to PROTOCOL_HEADERS[Content-Type] would apply to the Content-Type transport header.
 set or get a nested value.
set or get a nested value.Set a nested value in one of the following ways:

Set the
varName parameter in
pub.apigateway.ctxvar:setContextVariable to
PROTOCOL_HEADERS[arrayElement], where
[arrayElement] refers to a specific element. For example,
PROTOCOL_HEADERS[Content-Type] (to indicate the first array element in the set).

Alternatively, use the method
ISMediatorRuntimeFacade.setContextVariableValue(). Use this method only if you are writing a JAVA service and you want to access it through the JAVA source code.
Get a nested value in one of the following ways:

Set the
varName parameter in
pub.apigateway.ctxvar:getContextVariable to
PROTOCOL_HEADERS[arrayElement], where
[arrayElement] refers to a specific element. For example,
PROTOCOL_HEADERS[Content-Type] (to indicate the first array element in the set).

Alternatively, use the method
ISMediatorRuntimeFacade.getContextVariableValue(). Use this method only if you are writing a JAVA service and you want to access it through the JAVA source code.
You can set or get a nested value inside PROTOCOL_HEADERS through an additional keyName. In this case, the object reference is not an IData object. For PROTOCOL_HEADERS, the keyName must match the transport header name in a case-sensitive manner (for example, PROTOCOL_HEADERS[Content-Type] or PROTOCOL_HEADERS[Authorization]). In this case, the Serializable value will be a string.
pub.apigateway.ctxvar:setContextVariable
Use this JAVA service to set a value on a context variable. The pipeline variable containing the context variable value should be an object reference that implements java.io.Serializable. All parameter names are case-sensitive.
Parameter | Pipeline Type | Data Type | Description | Examples |
MessageContext | in | Object ref | This object is inserted into the pipeline by API Gateway. | N/A |
varName | in | String | Context variable name (predefined or custom). | PROTOCOL_HEADERS mx:CUSTOM_VAR |
serValue | in | Object ref | Java.io.serializable value. (Usually a string). | |
pub.apigateway.ctxvar:declareContextVariable
Use this JAVA service to declare a custom context variable. All custom-defined context variables must be declared in a custom namespace that is identified by using the prefix mx (for example, mx:CUSTOM_VARIABLE). All parameter names are case-sensitive.
Note:
It is not legal to use this service to declare the predefined context variables; you can only declare custom variables.
Parameter | Pipeline Type | Data Type | Description |
ctxVar | in | Object ref | The document type defining the context variable object. Use the ctxVar Document Type provided in the JAVA service pub.apigateway.ctxvar:ctxVar and map it to this input variable. Define the name (for example, mx:CUSTOM_VARIABLE), the schema_type (string or int), and isReadOnly (true or false). |
ctxVar | out | Object ref | The set Context variable document type. |
varNameQ | out | Object ref | javax.xml.namespace.QName value. The QName of the variable. |
Note the following:

After declaring the context variable, you can use the setContext variable to set a value on the context variable.

You do
not need to declare the following kinds of context variables:

The predefined context variables provided by
API Gateway. If you attempt to declare an existing predefined context variable, an error will occur.

Any custom context variable that you define in a routing rule that you create in the conditional routing step.

Any custom context variables that you explicitly declare in source code using the API will have a declaration scope of SESSION.

Any custom context variable's state that is defined during the inbound request processing steps will still be available during the outbound response processing steps.

All context variable values are typed as either
string or
int (excluding the PROTOCOL_HEADERS variables, which are of the type
IData).

Valid names should be upper case (by convention) and must be a valid JAVA Identifier. In general, use alpha-numerics, $ or _ symbols to construct these context names. Names with punctuation, whitespace or other characters will be considered invalid and will fail deployment.

All custom context variables must be declared in a custom namespace that is identified by using an
mx prefix (for example,
mx:CUSTOM_VARIABLE).

To reference a custom context variable in a flat string, you need to prepend a $ symbol to the context variable name to indicate that variable’s value should be referenced. Think of this usage as being similar to the
& address operation for C variables.
An expression that references a custom context variable might look like this:
$mx:TAXID=1234 or $mx:ORDER_SYSTEM_NAME="Pluto"
Notice that the values of the data type “int” are not enclosed in quotation marks, while the values of the data type “string” are. The quotation marks are only needed if a context variable expression (as opposed to a reference) is defined.

Referencing an undefined context variable does not result in an error.

Once a variable has been declared it cannot be declared again.
pub.apigateway.ctxvar:removeContextVariable
Use this JAVA service to remove a custom context variable from a request or response session. All parameter names are case-sensitive.
Note:
Keep the following points in mind:

It is not legal to use this service to remove any predefined context variables; you can only remove custom variables.

Attempting to remove a non-existent context variable will
not result in an error.
Parameter | Pipeline Type | Data Type | Description | Examples |
MessageContext | in | Object ref | This object is inserted into the pipeline by API Gateway. | N/A |
varName | in | String | Custom context variable name. | mx:CUSTOM_VAR |
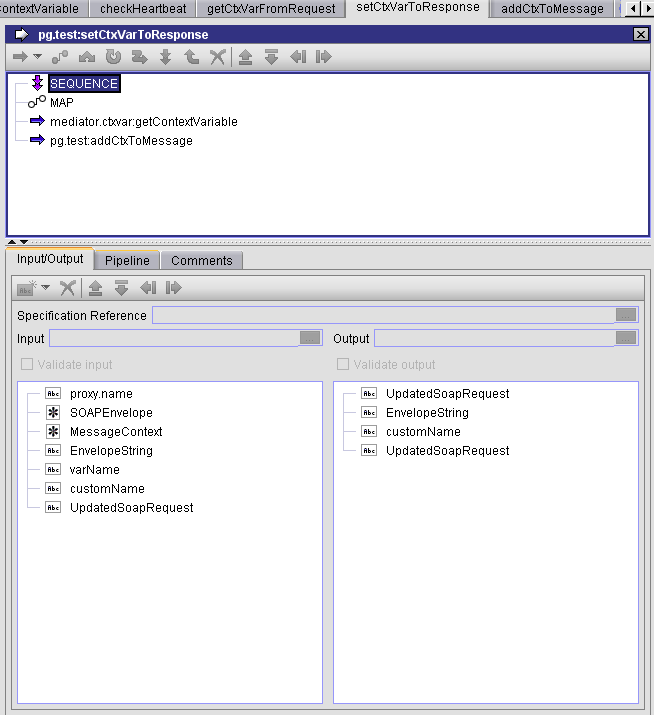
Sample Flow Service: Getting a Context Variable Value
This flow service sets the value of a custom context variable to be used in a response.
This flow service declares a pipeline variable named customName, which is set to the value mx:COMP_TEST.
This flow service will retrieve the context variable for customName and create an element for its context variable value in the response message return to the consumer.
Step 1. Declaring customName
You can define the customName variable value to be mx:COMP_TEST so you can use this variable to lookup the custom variable name that was seeded in the previous example.
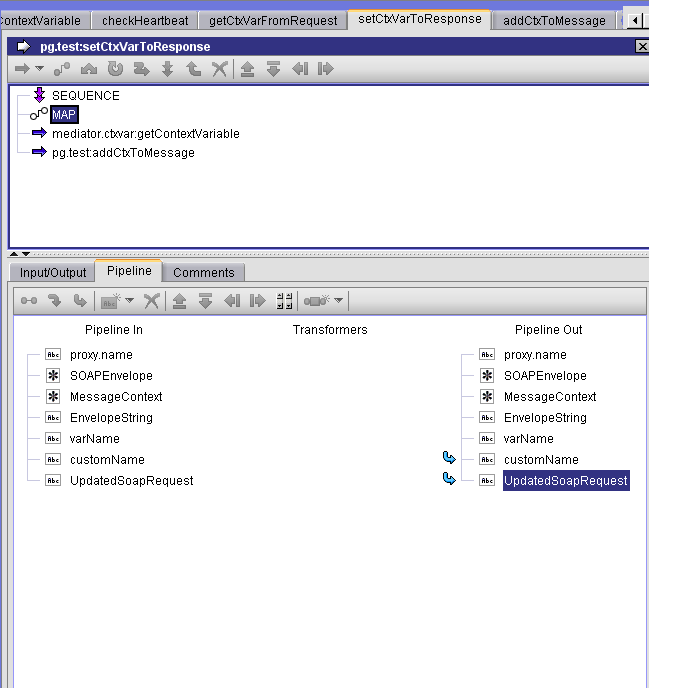
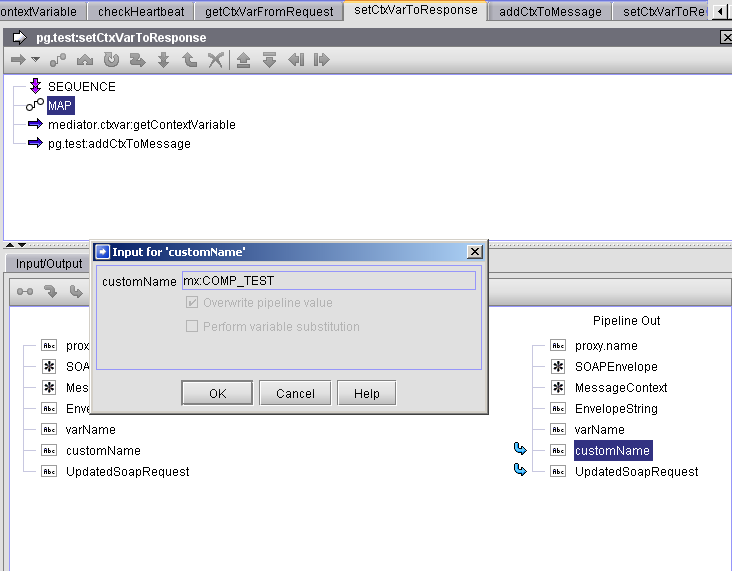
Step 2. Setting customName to mx:COMP_TEST
Clicking on the customName pipeline variable displays the name.
Step 3. Displaying the value of customName
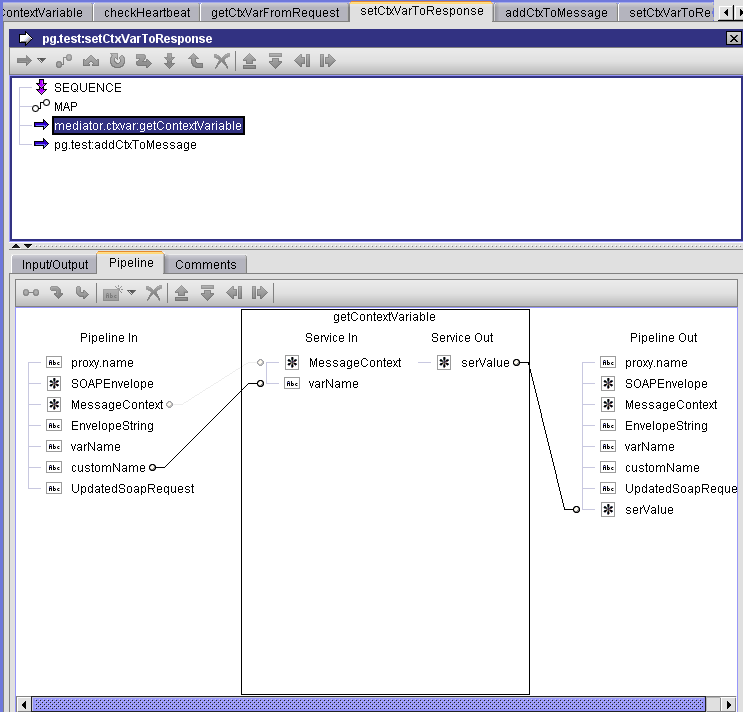
The call to pub.mediator.ctxvar:getContextVariable retrieves the value of the custom context variable from the context variable map.
Step 4. Calling meditor.ctxvar:getContextVariable
This is just a sample JAVA service that takes the context variable and creates a top-level element in the response message using the same name and value.
Step 5. Sample service using the context variable
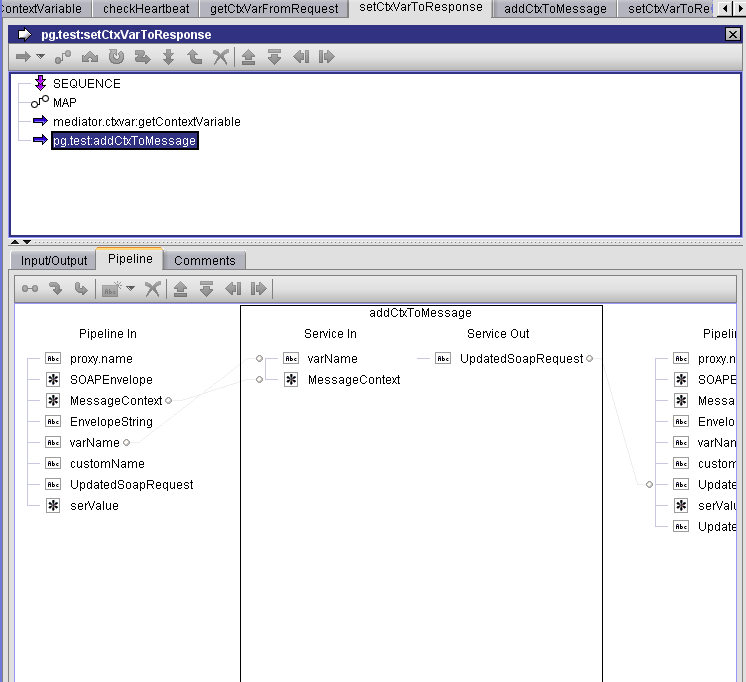
Sample Flow Service: Setting a Context Variable Value
This flow service sets the value of a custom context variable to be used in a response.
This flow service declares a pipeline variable named customName, which is set to the value mx:COMP_TEST.
This flow service retrieves the context variable for customName and create an element for its context variable value in the response message return to the consumer.
Step 1. Declaring customName
You define the customName variable value to be mx:COMP_TEST so you can use this variable to lookup the custom variable name that was seeded in the previous example.
Step 2. Setting customName to mx:COMP_TEST
Clicking on the customName pipeline variable displays the name.
Step 3. Displaying the value of customName
The call to pub.mediator.ctxvar:getContextVariable retrieves the value of the custom context variable from the context variable map.
Step 4. Calling meditor.ctxvar:getContextVariable
This is just a sample JAVA service that takes the context variable and creates a top-level element in the response message using the same name and value.
Step 5. Sample service using the context variable