Configuration Options that Affect Data Life
This topic covers managing the life of the data in each of the data-storage tiers, including the pinning features of Automatic Resource Control (ARC).
You use the options to manage data life within the data-storage tiers:
 Flush
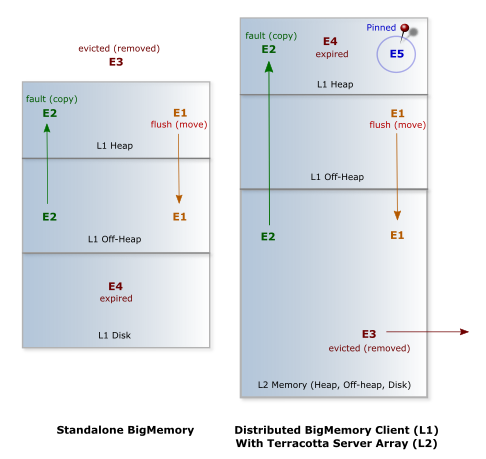
Flush – To move an entry to a lower tier. Flushing is used to free up resources while still keeping data in
BigMemory Max.
 Fault
Fault – To copy an entry from a lower tier to a higher tier. Faulting occurs when data is required at a higher tier but is not resident there. The entry is not deleted from the lower tiers after being faulted.
 Eviction
Eviction – To remove an entry from
BigMemory Max. The entry is deleted; it can only be reloaded from an outside source. Entries are evicted to free up resources.
 Expiration
Expiration – A status based on Time-To-Live and Time-To-Idle settings. To maintain performance, expired entries may not be immediately flushed or evicted.
 Pinning
Pinning – To keep data in memory indefinitely.
The following figure depicts the movement of data across the storage tiers.