Concepts and Architecture
BigMemory WAN Replication uses regional Orchestrators to manage data replication.
Region - A data center, typically geographically distinct and connected to other regions with a high-speed link. A region holds one or more Terracotta Server Arrays (TSAs), and it can support multiple Orchestrators.
Orchestrator - The process that coordinates communication among regions and replicates cache modifications to all regions. Orchestrators can manage multiple caches.
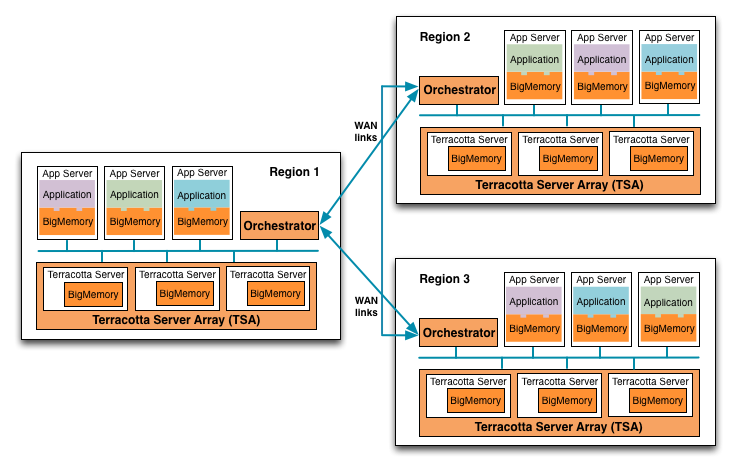
Region-Orchestrator Example
In the figure below, each application has access to BigMemory data held in its TSA. Each Orchestrator communicates with the TSA in its region, as well as with the Orchestrators in other regions, in order to allow data to become eventually consistent across all regions.
WAN Replication Topology
Master and Replica Caches
The Orchestrators manage replication through designated Master and Replica instances of each cache.
Master Cache - The cache that serves as the authoritative data set against which its Replica caches are synchronized. Each replicated cache will have one active Master at a time.
Replica Cache - A cache mirror that receives replication updates from the Master cache. A Replica cache becomes active only after it fully synchronizes with the Master cache.
Note:
Although the WAN Replication Service architecture includes facilities for queuing bursts of transactions that out-pace the WAN link's bandwidth and latency capabilities, it is important to understand that if the WAN Orchestrator falls too far behind, it will create back-pressure on clients attempting to perform transactions on Caches, leading to possibly significant impact on application performance.