RAQL Operators
Arithmetic Operators
You may use the standard arithmetic operators in RAQL expressions: + , - , * or / .
Comparison Operators
You may use the following comparison operators in Where clauses:
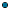 =
= or
!=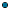 <
< or
<=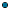 >
> or
>=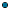 like
like: for matching text based on a pattern. Use
% to indicate zero to any number of characters. For example:
where lastname like 'A%' to find any last name starting with a capital A.
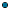 in
in: to match values against an enumerated set of values defined within brackets. For example:
where direction in ("N","NW","W")The literal values or other expressions being compared
must be the same basic datatype. In many cases, this may require that values or expressions be cast to an appropriate type for a successful comparison. See
Literal Values in Conditions or Expressions for additional information.
Text comparison with the mathematic comparison operators is not case sensitive. Text comparisons to patterns or enumerations are case sensitive.
Logical Operators
You may use the following logical operators in Where clauses:
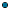 and
and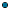 or
or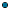 not
notOperators are not case sensitive. You can use parentheses to build complex logical expressions such as: where (service_level in ("gold","silver")) and (rating >= 2.0 or overdue < 100 ).
String Operators
You may use the || string operator to concatenate strings or the concat function.