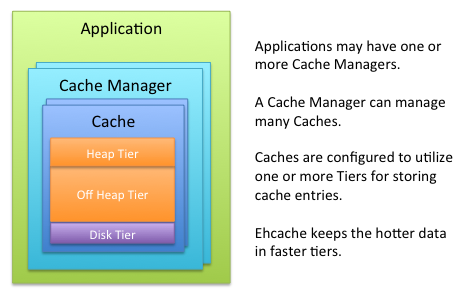
Storage Tiers
You can configure Ehcache to use various data storage areas. When a cache is configured to use more than one storage area, those areas are arranged and managed as tiers. They are organized in a hierarchy, with the lowest tier being called the authority tier and the others being part of the caching tier. The caching tier can itself be composed of more than one storage area. The hottest data is kept in the caching tier, which is typically less abundant but faster than the authority tier. All the data is kept in the authority tier, which is slower but more abundant.
Data stores supported by Ehcache include:
 On-Heap Store
On-Heap Store – Utilizes Java's on-heap RAM memory to store cache entries. This tier utilizes the same heap memory as your Java application, all of which must be scanned by the JVM garbage collector. The more heap space your JVM utilizes the more your application performance will be impacted by garbage collection pauses. This store is extremely fast, but is typically your most limited storage resource.
 Off-Heap Store
Off-Heap Store – Limited in size only by available RAM. Not subject to Java garbage collection (GC). Is quite fast, yet slower than the On-Heap Store because data must be moved to and from the JVM heap as it is stored and re-accessed.
 Disk Store
Disk Store – Utilizes a disk (file system) to store cache entries. This type of storage resource is typically very abundant but much slower than the RAM-based stores. As for all applications using disk storage, it is recommended to use a fast and dedicated disk to optimize the throughput.
 Clustered Storage
Clustered Storage – This data store is a cache on a remote server. The remote server may optionally have a failover server providing improved high availability. Since clustered storage comes with performance penalties due to such factors as network latency as well as for establishing client/server consistency, this tier, by nature, is slower than local off-heap storage.