About Working with Interfaces
Interfaces within a Universal Messaging realm server define a protocol, a network interface, and a port number. When a Universal Messaging client connects to a realm using an RNAME, the client actually connects to an interface that has been created on the Universal Messaging realm.
If a machine that is running a Universal Messaging realm has multiple physical network interfaces, with different IP addresses, you can bind specific protocols to specific ports. This way you can segment incoming network traffic to specific clients. For example, if a realm is running on a machine that has an external Internet-facing network interface, as well as an internal interface, you can create a Universal Messaging interface that uses nhp or nhps on port 80 or 443, respectively, using the external facing interface. However, if you do not want to segment network traffic for specific protocols, you can choose to bind to all known network interfaces to the specified protocol and port.
The default Universal Messaging interface is nhp. The default nhp interface enables clients to connect to it using not only the nhp protocol, but also the nsp protocol. If you do not specify a port for the default interface when you install or create a Universal Messaging server instance, the default port is 9000.
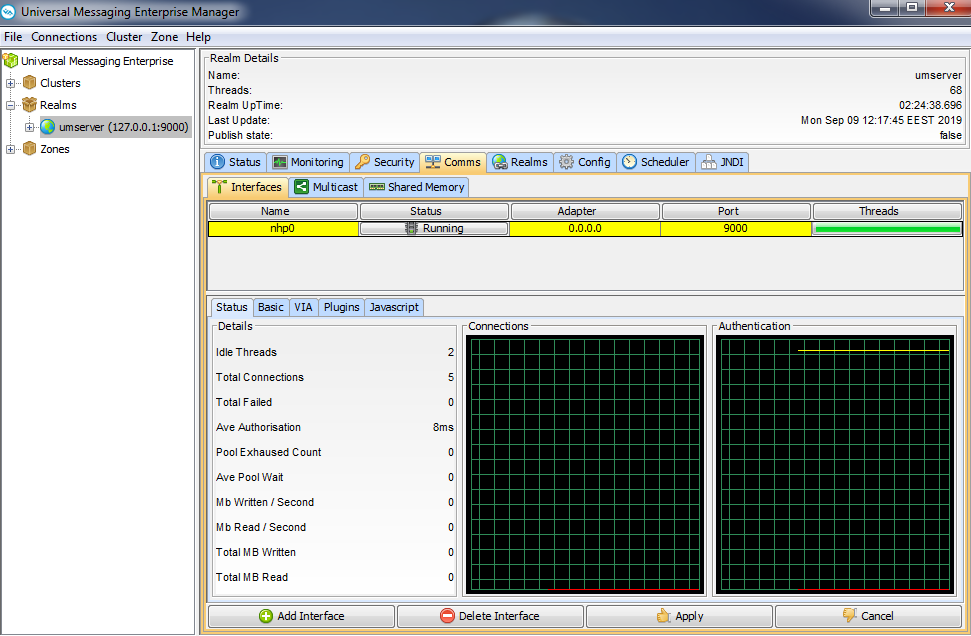
You create, configure, and manage interfaces on the Comms > Interfaces tab for a realm in the Enterprise Manager, as shown in the following image.