About OAuth 2.0
Note:
This page is not applicable if you have created your account using the Software AG Cloud sign-up page.
The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework facilitates the sharing of private resources (data or services) with a third-party client application (client). In an OAuth session, private resources are stored on a resource server and the owner of the resources, or resource owner, grants the client application permission to access them. The resource owner is typically a person; however, in some cases it could be an application. When a resource owner grants permission, the OAuth authorization server issues an access token to the client application. When the client application passes the access token to the resource server, the resource server communicates with the authorization server to validate the token and, if valid, provides access to the resources.
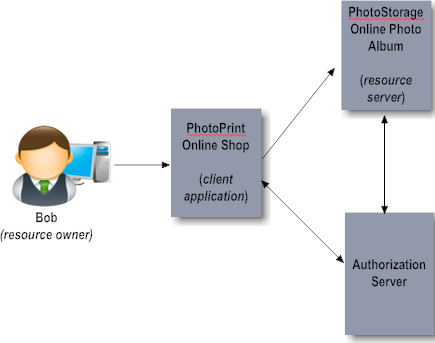
The following example illustrates the roles involved with an OAuth session. In the example, Bob is the resource owner who wants to access and print his photos stored on the PhotoStorage website (the resource server) using the PhotoPrint service (the client application). PhotoPrint supplies Bob with an application that runs on his device (phone or laptop). Bob uses that application to initiate the process. PhotoPrint sends a request to the PhotoStorage authorization server. The authorization server requests authorization from Bob and issues a token to PhotoPrint. PhotoPrint can then access Bob's photos on PhotoStorage.
Integration Cloud services can be accessed through REST APIs from any REST client. In OAuth 2.0, the client obtains an access token issued by an authorization server on approval of the resource owner. The client uses the access token to access the protected resources.
Note:
Integration Cloud acts both as a Resource server and as an Authorization server.
An in-depth description of OAuth is beyond the scope of this guide but is available elsewhere. For information about the OAuth protocol, see the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework.