This section describes the SYSUTIL utility, the new rich GUI interfaces of the SYSEXT and SYSEXV utilities and the Message Retrieval utility.
This document covers the following topics:
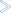
The SYSUTIL utility is used to start selected Natural tools and utilities from NaturalONE. It may also be used to start user-defined tools. The tools are executed on the server side whereby any kind of server (mainframe, UNIX, Windows) is supported.
In addition to that, it can be used to open web pages from NaturalONE.
For technical reasons, only rich GUI (Natural Ajax) and character-based tools are supported.
Tools using the dialog interface are not supported.
Tools which are implemented in NaturalONE such as SYSPROD or SYSPROF, are not provided by SYSUTIL.
Web I/O must be enabled on the Natural server. Otherwise, the output of a character-based tool cannot be displayed.
The PARSE XML statement has to be
enabled in a mainframe environment. Use the following parameter:
XML=(ON,PARSE=ON)
For further information, see the XML
parameter description in the Parameter Reference section
of the Natural for Mainframes documentation.
On non-mainframe environments, the
PARSE statement is enabled by default.
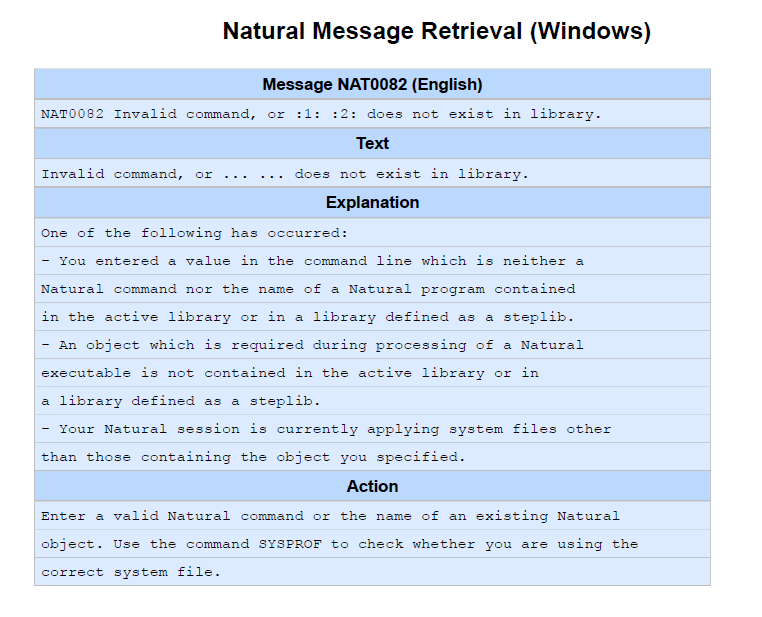
Natural Version 9.1 or higher is required on the server side to run the Natural tools and utilities from NaturalONE. Otherwise you will receive a message like
NAT0082 Invalid command, or Program SYSUTIL does not exist in library.
 To start the Natural tools and utilities
To start the Natural tools and utilities
In your workspace, select the Natural project, library or object from which you want to start the Natural tools and utilities.
Invoke the context menu and choose NaturalONE > Tools and Utilities.
Or:
Press Alt+U.
This starts the SYSUTIL utility from which you can start selected Natural tools and utilities.
The SYSUTIL utility lists Natural tools and utilities which can be executed from NaturalONE.
If Natural Security is installed in your environment, the list only displays tools you are authorized to use.
The tools can be listed alphabetically by Tool Names (default) or grouped by Categories or Keywords. By default, the list shows the tools of all categories. A specific category can be selected so that only tools belonging to this category are listed.
You can specify a search string so that only the tools containing the string in the name, title, category or a keyword are shown.
The buttons in SYSUTIL have the following meaning:
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| Exit | Exit SYSUTIL. |
| Reset | Reset all fields to their initial state. |
| Open All | Open all nodes in the tree. Only enabled if the tree is grouped by categories or keywords. |
| Close All | Close all nodes in the tree. Only enabled if the tree is grouped by categories or keywords. |
| Execute | Execute a selected tool. Works only if a tool has been selected or a command has been specified. |
The entries on the right side of SYSUTIL have the following meaning:
| Entry | Description |
|---|---|
| Library | SYSUTIL issues a LOGON to this library before it executes the command. If no library is specified, the command is executed in the library from where SYSUTIL has been started. |
| Command | The command or program to be executed. If the field contains a valid web address (URL), the corresponding web page is opened in a new window. |
| Environment | The environment from where SYSUTIL has been started. |
| Name | The name of the tool. |
| Title | The descriptive name of the tool. |
| Category | The category to which the tool belongs. |
| Keywords | Keywords associated to the tool. |
| Description | A short description of the functionality of the tool. |
 To start a specific Natural tool or utility
To start a specific Natural tool or utility
Select a tool in the SYSUTIL tree. The Library and Command fields are filled according to your selection.
Add parameters to the command as desired.
Click on Execute.
Or:
Double-click the tool entry in the SYSUTIL tree.
Or:
Select a tool in the SYSUTIL tree.
Invoke the context menu and choose Execute.
Or:
Specify a library and a command (including parameters if desired) in the corresponding fields.
Press Enter or click on Execute.
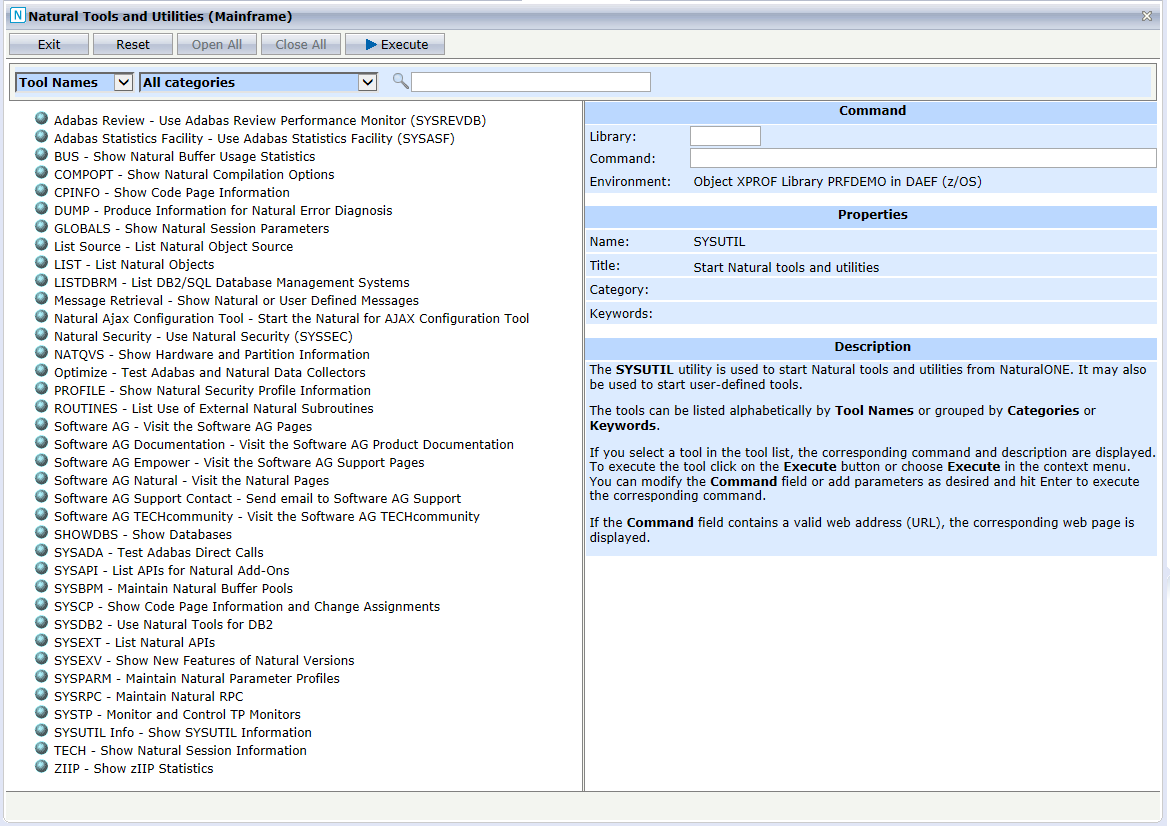
In the following example, the Natural tools and utilities are grouped by categories and the SYSEXV utility in the Example Libraries category has been selected. The entries on the right side are filled with the values of the SYSEXV utilities. The utility will be started by clicking on .
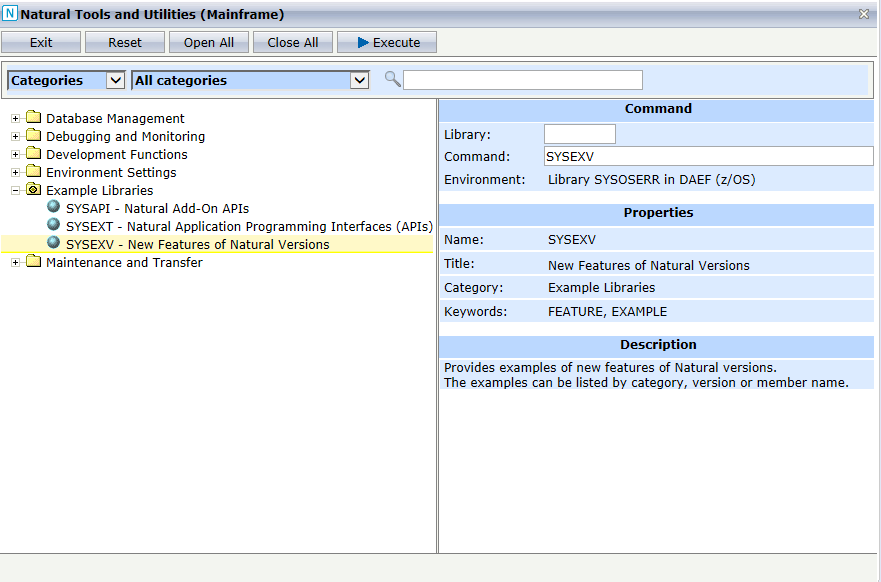
The utility SYSEXT is used to locate and test Natural Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) contained in the current system library SYSEXT.
This section describes the rich GUI interface to SYSEXT from NaturalONE. For further information regarding the SYSEXT utility, refer to the section SYSEXT Utility in the Natural documentation corresponding to your platform.
 To start the SYSEXT utility
To start the SYSEXT utility
In your workspace, select any Natural project, library or object in the environment in which you want to start the SYSEXT utility.
Invoke the context menu and choose NaturalONE > Tools and Utilities to start the SYSUTIL utility.
Select SYSEXT in the tree and click on .
The rich GUI interface of the SYSEXT utility is displayed.
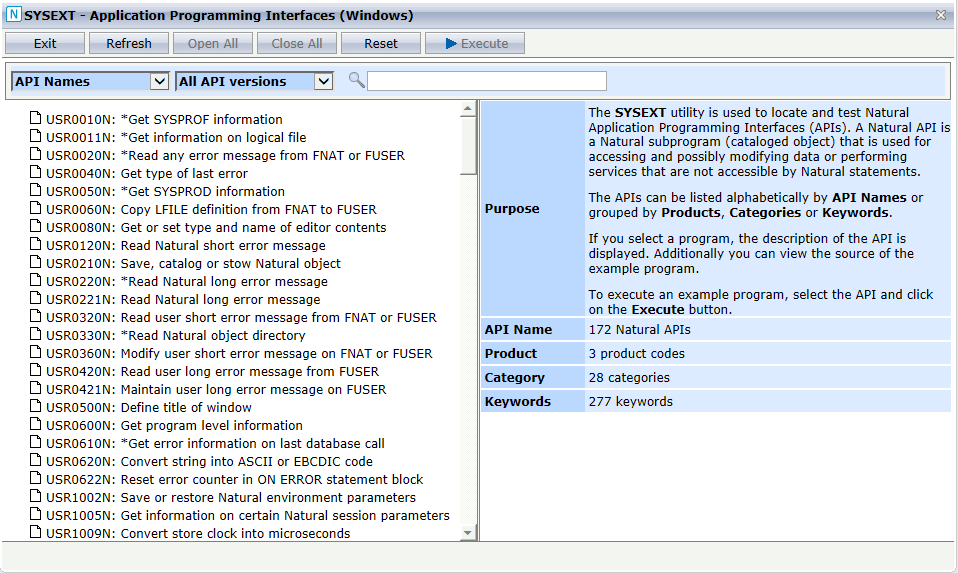
The Natural APIs can be listed alphabetically by API Names (default) or grouped by Products, Categories or Keywords. By default, the list shows all versions of the APIs whereby previous versions of an API are indicated by an asterisk (*). If you want to see only the most recent version of an API in the list, select Current API version.
You can specify a search string so that only the APIs containing the string in the name, purpose, category or a keyword are shown.
The buttons in SYSEXT have the following meaning:
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| Exit | Exit SYSEXT. |
| Refresh | Update the API information. It reads all APIs and regenerates the input files which are used to fill the tree. This is only required if API descriptions have been changed. |
| Open All | Open all nodes in the tree. Only enabled if the tree is grouped by products, categories or keywords. |
| Close All | Close all nodes in the tree. Only enabled if the tree is grouped by products, categories or keywords. |
| Reset | Reset all fields to their initial state. |
| Execute | Execute the example program related to the API. Works only if an API has been selected. |
On the right side of SYSEXT, the purpose, name, category and the
keywords of a selected API are displayed. Additionally, you can choose whether
you want to see the description of the API (member
USRnnnnT) or the source of the
corresponding example program
USRnnnnP.
 To start an example program of a Natural API
To start an example program of a Natural API
Select an API in the SYSEXT tree. The fields on the right side are filled according to your selection.
Click on .
Or:
Double-click the API entry in the SYSEXT tree.
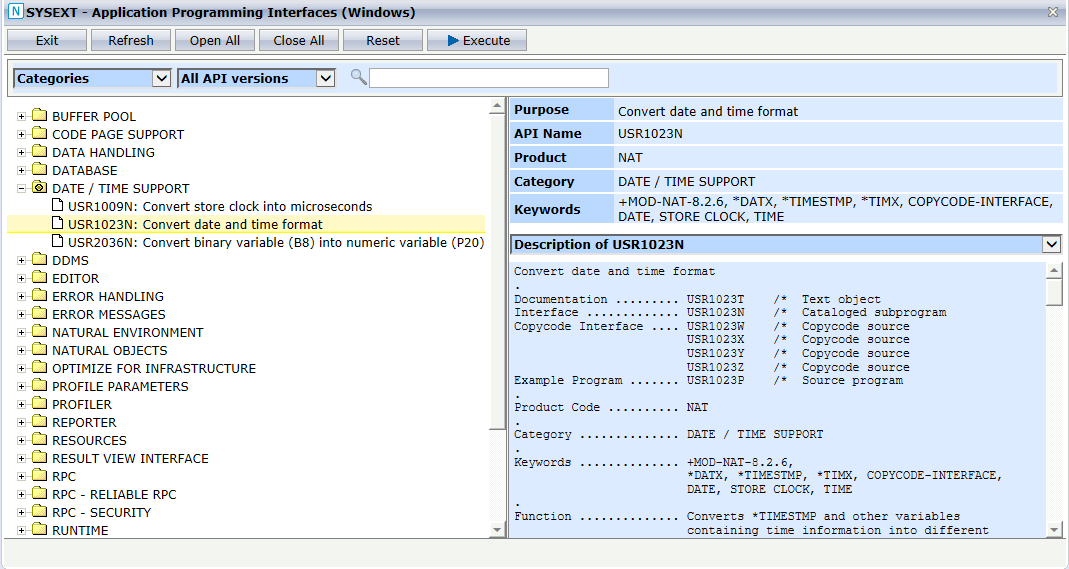
In the following example, the APIs of SYSEXT are grouped by
categories and the API USR1023N in the DATE/TIME
SUPPORT category has been selected. The entries on the right side
are filled with the values of the API USR1023N. The example
program USR1023P will be started by clicking on
.
The utility SYSEXV provides example programs that demonstrate the use of Natural features introduced in the current or a previous version of Natural.
This section describes the rich GUI interface to SYSEXV from NaturalONE. For further information regarding the SYSEXV utility, refer to the section SYSEXV Utility in the Natural documentation corresponding to your platform.
 To start the SYSEXV utility
To start the SYSEXV utility
In your workspace, select any Natural project, library or object in the environment in which you want to start the SYSEXV utility.
Invoke the context menu and choose NaturalONE > Tools and Utilities to start the SYSUTIL utility.
Select SYSEXV in the tree and click on .
The rich GUI interface of the SYSEXV utility is displayed.
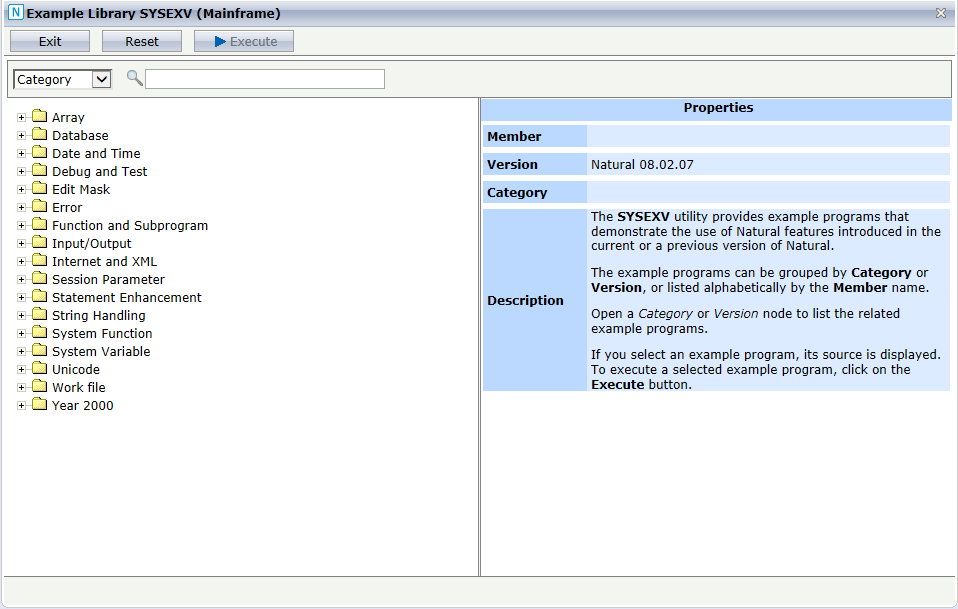
The example programs can be listed alphabetically by Member names or grouped by Category (default) or Version. You can specify a search string so that only the example programs containing the string in the member name, version, category or description are shown.
The buttons in SYSEXV have the following meaning:
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| Exit | Exit SYSEXV. |
| Reset | Reset all fields to their initial state. |
| Execute | Execute the example program. Works only if an example program has been selected. |
On the right side of SYSEXV, the member name of the example program, the version in which the Natural feature was introduced, the category and the description of the Natural feature are displayed. Additionally the source of the example program is provided.
 To start an example program
To start an example program
Select an example program in the SYSEXV tree. The fields on the right side are filled according to your selection.
Click on .
Or:
Double-click the example program entry in the SYSEXV
tree.
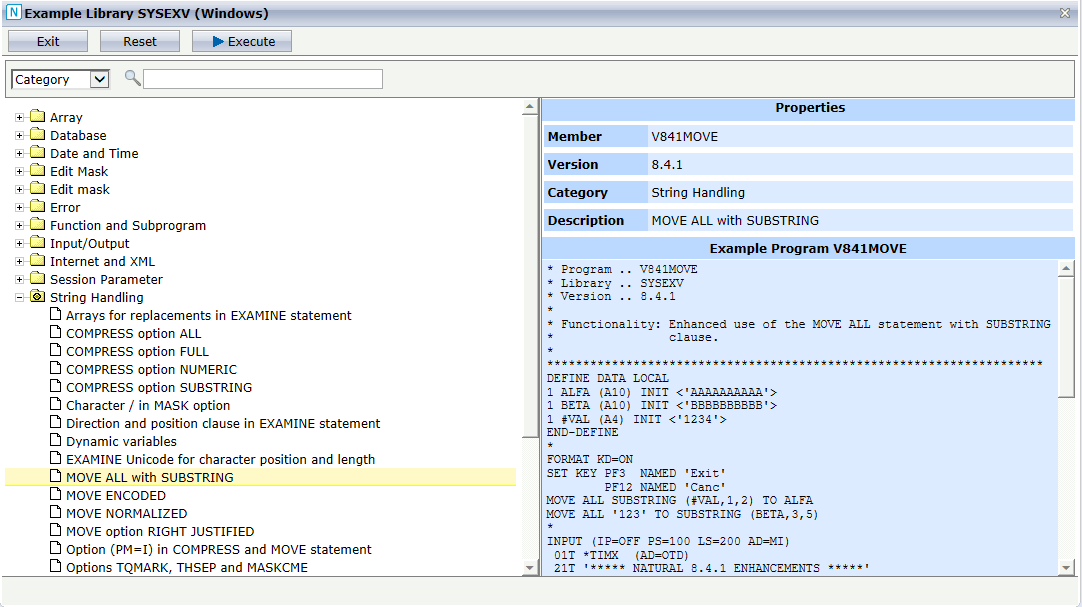
In the following example, the example programs of SYSEXV are
grouped by categories and the example program for the MOVE ALL with
SUBSTRING feature in the String Handling
category has been selected. The entries on the right side are filled with the
values of the example program V841MOVE. The example program will
be started by clicking on .
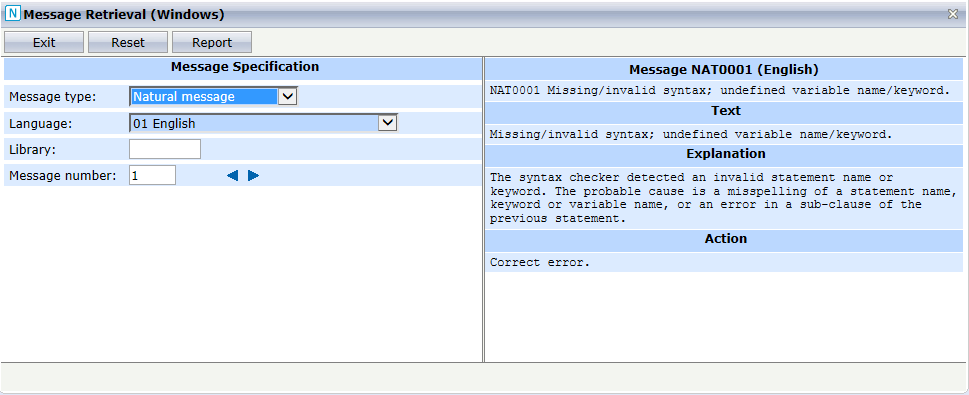
The SYSUTIL Message Retrieval function is used to read Natural or user defined messages.
 To start the Message Retrieval
To start the Message Retrieval
In your workspace, select any Natural project, library or object for which you want to start the message retrieval. If you have selected a library or an object in a library, this library is taken as default library for user defined messages.
Invoke the context menu and choose NaturalONE > Tools and Utilities to start the SYSUTIL utility.
Select Message Retrieval in the tree.
Add parameters to the command as desired.
Click on .
The Message Retrieval is displayed.
The SYSUTIL Message Retrieval function offers the following parameters:
SYSUTIL -MSG [nnnn [library]]
Where nnnn is the message number and library is the library containing the user defined message.
Alternatively, you can start the SYSUTIL Message Retrieval with the following command:
? [nnnn [library]]
If the message number and the library are specified, the user
defined message nnnn from library
library is displayed. If only the message number is
specified, the Natural message nnnn is displayed. If
no parameter is given, the Natural message NAT0001 is shown
initially.
The buttons in Message Retrieval have the following meaning:
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| Exit | Exit Message Retrieval. |
| Reset | Reset all fields to their initial state. |
| Report | A preview of the message is generated. It can be used for printing the message or converting it into a PDF member. |
The entries on the left side of the Message Retrieval have the following meaning:
| Entry | Description |
|---|---|
| Message type | Select the message type: Natural message or User defined message. If you view Natural messages, the Library field is cleared. If you view user defined messages, the Library field is filled with the previously used user library or initially, with the library from which you have started the Natural tools and utilities. |
| Language | Choose the language of the message. |
| Library | If you clear this field, Natural messages are displayed. Enter a library name to view the user messages of the given library. |
| Message number | The number of the message to be displayed. Click on the left or right arrow to show the previous or next message. |
On the right side of the Message Retrieval, the short and long text of the message is displayed.
The following example shows the PDF output of the Natural message 82.
The SYSUTIL utility can be extended to also list user defined tools in the tree.
 To extend the Natural tools and utilities
To extend the Natural tools and utilities
Create an XML member according to the SYSUTIL standards.
Name it either TOOL-*.XML or
USER-uid.XML where the asterisk
(*) stands for any character combination and
uid for a user ID.
Save the XML member in the Resource folder of the SYSUTIL library.
TOOL-*.XML contains customer specific tools. It is
visible to all who share the same FNAT system file.
USER-uid.XML contains user
specific tools. It is only visible to the user with the *INIT-USER
user ID uid.
Notes:
SAG-*.XML contains Software AG tools. Do not
modify these members.
EXAMPLE.XML in the library SYSUTIL
contains an example XML. You may use it as template for creating your own XML
members.
The following shows the standard layout of a SYSUTIL XML member:
<?xml version='1.0' ?>
<SYSUTIL VERSION='version' USAGE='usage'>
<COMMENT>comment</COMMENT>
<TOOL>
<NAME>name</NAME>
<TITLE>title</TITLE>
<LIBRARY>library</LIBRARY>
<COMMAND>command</COMMAND>
<CLEARSCREEN>clear-screen</CLEARSCREEN>
<CATEGORY>category</CATEGORY>
<KEYWORDS>keywords</KEYWORDS>
<DESCRIPTION>description</DESCRIPTION>
<MACHINE-CLASS>machine-class:filter</MACHINE-CLASS>
</TOOL>
<TOOL>
...
</TOOL>
</SYSUTIL>
The entries in the XML member have the following meaning:
| Tag Value | Description | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
version |
The version of the XML member. The entry is not interpreted by SYSUTIL. | ||||||||
usage
|
A short internal description of the XML member. The entry is not interpreted by SYSUTIL. | ||||||||
comment |
More detailed internal description of the XML member. The tag is not interpreted by SYSUTIL. | ||||||||
name |
The name of the tool. It is used as main index in the list of tools. Maximum size: 32 characters. | ||||||||
title |
A descriptive title of the tool. It is used as supplement to the tool name in the list of tools. Maximum size: 61 characters. | ||||||||
library |
SYSUTIL issues a Default: If started on a project level: SYSTEM Otherwise: Current library |
||||||||
command |
The command, program or URL to be executed. Parameters may be added separated by blanks. The following special values can be used in the command:
|
||||||||
clear-screen |
Whether SYSUTIL clears the screen before command
execution. This may be set to Possible values: Default: |
||||||||
category |
The category to which the tool belongs. If appropriate, use an existing category of SYSUTIL. | ||||||||
keywords |
Keywords associated to the tool. The keywords are written in upper case and separated by commas. If appropriate, use existing keywords of SYSUTIL. | ||||||||
description |
The long description of the tool in HTML format. To avoid that special characters of HTML are interpreted by XML, replace the following characters:
Alternatively, you can save the description in HTML format (without replacements) in a UTF-8 resource in the SYSUTIL library. Start the DESCRIPTION value with "HTML:" followed by the name of the HTML resource. For example: HTML:MyDesc.htm |
||||||||
machine-class:filter |
|
The following example shows the example XML member
TOOL-Admin.XML for SYSUTIL. If you save it in the SYSUTIL resource
folder, the ReadCust application will be added to the list of
tools. The one-letter filter code (here: S) in the
MACHINE-CLASS tag has the effect that the ReadCust application is
only shown in the list of tools if the user is allowed by Natural Security to
execute the application.
<?xml version='1.0' ?>
<SYSUTIL VERSION='1.0' USAGE='SYSUTIL entry for READCUST'>
<COMMENT>
Customer data administration
</COMMENT>
<TOOL>
<NAME>ReadCust</NAME>
<TITLE>Read customer data</TITLE>
<LIBRARY>CUSTLIB</LIBRARY>
<COMMAND>READCUST</COMMAND>
<CLEARSCREEN>FALSE</CLEARSCREEN>
<CATEGORY>Administration</CATEGORY>
<KEYWORDS>DATABASE,READ,CUSTOMER</KEYWORDS>
<DESCRIPTION>Read all <strong>customer</strong> data.</DESCRIPTION>
<MACHINE-CLASS>A:S</MACHINE-CLASS>
</TOOL>
</SYSUTIL>
If Natural Tools and Utilities has been extended to call a user defined tool, it is a desired behavior that after the user tool has finished, control is given back to SYSUTIL. Therefore, SYSUTIL places itself on the Natural stack including all settings so that it is restarted automatically when the user defined tool ends. All selections and field contents of SYSUTIL are restored to the state it was in before the user defined tool had been called.
If the user defined tool releases the Natural stack with a
RELEASE STACK command by any reason, the approach
described above will not work. In this case, the tool may issue the statement
STACK TOP COMMAND 'RETURN'. This will restart
SYSUTIL, but all selections and field contents will be set to initial state.
The information regarding the library and object selection will also be lost.