This document covers the following topics:
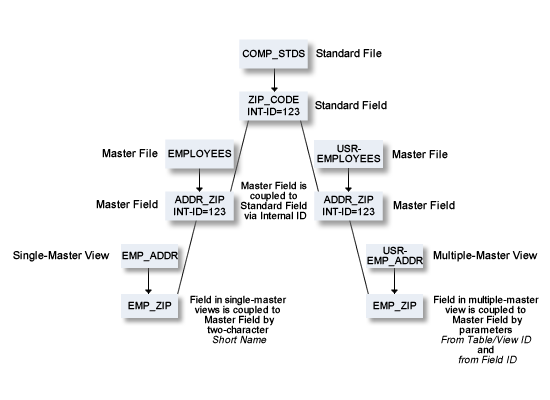
Predict rippling options can be used to define a standard, hierarchical data structure and to ensure consistent use of this structure throughout an organization: Whenever field definitions on higher levels are changed, all data definitions on lower levels (including views/userviews) are automatically updated.
This option determines whether attribute changes in standard fields are rippled to connected fields. See also Check against standard in the section Field.
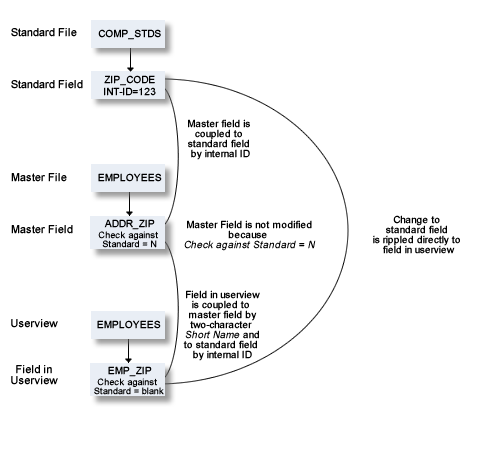
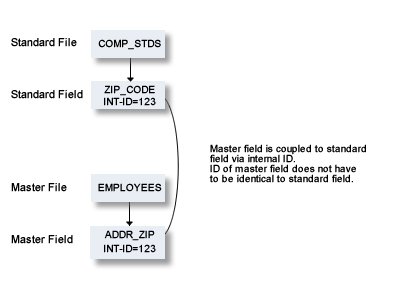
Standard fields and connected fields are coupled internally by means of Internal ID.
The coupling remains intact even if the connected field is subsequently renamed.
To couple fields select the Field List tab and select a field.
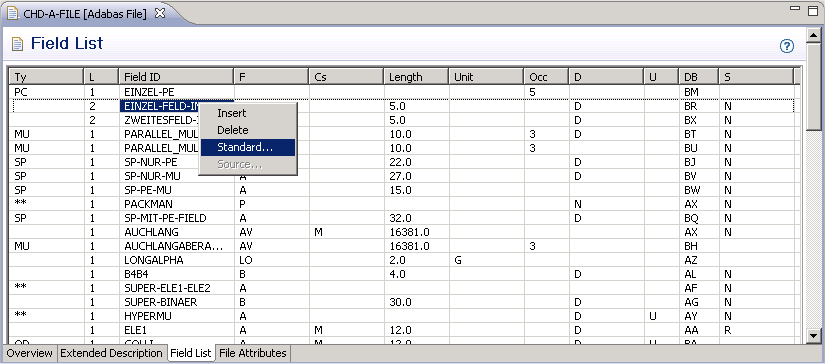
Choose the button and select a related standard file and field in the resulting window.
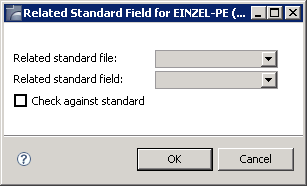
The following attributes of a standard field can be rippled to coupled fields at lower levels.
Field length
Field format
Field type
Suppression option
Uniqueness option
Descriptor type (see below)
Character set
Timestamp, timezone and precision
Inline length
If an attribute is not defined in a standard field (which means the attribute is blank if it is alphabetic, or zero if it is numeric), no rippling takes place for this attribute and the lower-level object can be modified without restriction. It is therefore possible to have some field attributes defined centrally and others modifiable without restriction at lower levels. See also Changing Coupled fields.
Note:
If one of the attributes above is changed and this change is not
compatible with the coupled field, the attribute Check against standard of the
field is set to N. For example: If you change a field type to HY
(hyperdescriptor, this change is not rippled to coupled fields in DB2 files and
the attribute Check against standard of the coupled fields is set to N.
The attribute Descriptor type of a standard field can have the following values:
| D | Disallowed. The descriptor type of coupled fields must be blank. All non-blank descriptor types in coupled fields are set to blank. |
| F | Force. The descriptor type of coupled fields may not be blank. If a coupled field has a non-blank descriptor type, no rippling is performed. If a coupled field has descriptor type blank, the descriptor type is set to N and a message is given. |
| blank | Undefined. The descriptor type of coupled fields can be any value, including blank. No checks are performed, no rippling takes place. |
When the verification list of a standard field is edited, corresponding changes are automatically made in the verification list of every field derived from the standard field. The following rules apply:
Every verification contained in the verification list of a standard field must also be contained in the verification list of a field coupled to that standard field. However, the sequence of verifications in the lists can differ.
If a verification is removed from the verification list of a standard field, the verification is automatically removed from the verification lists of all coupled fields.
If a verification is added to the verification list of a standard field (at any position), the verification is automatically added to the end of the verification list of all coupled fields.
If the parameter Check against standard is set to N in connected fields, the checks listed above are not performed.
The following rules apply when changing fields at lower levels:
Attributes not defined in a standard field can be modified in coupled fields.
Attributes that have been defined in standard fields cannot be modified in coupled fields.
If an attribute of a coupled field that is defined in the standard field has to be changed, the fields must be uncoupled. See below.
Fields can be temporarily or permanently uncoupled from the standard field with the parameter Check against standard.
Temporarily
From the Fieldlist tab
choose the button. In the upcoming window empty
the box Check against Standard. The field is
uncoupled temporarily from the standard field from which it was derived. The
coupling can be reactivated by filling the box
Check against standard.
Permanently
From the Fieldlist tab
choose the button. In the upcoming window
remove the names of the standard file and field. The field is
uncoupled permanently from the standard field from which it was derived. The
coupling cannot be reactivated with the parameter Check against standard. To
recouple a field, you have to enter the names of the
standard file and field.
The following rules apply:
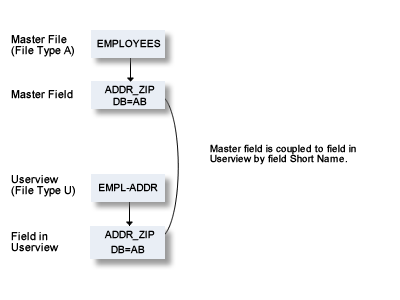
Changes to master fields are rippled to fields in userviews that were derived from master files. If the master field is coupled to a standard field, changes to the standard field are rippled to the coupled master field and to the derived field in the userview.
Changes to fields in userviews are rejected if they are not compatible with the master field.
For example: if a field in a userview is derived from a master field of type T (time), the field in the userview can only be changed to format P with length 13.
All other changes are rejected.
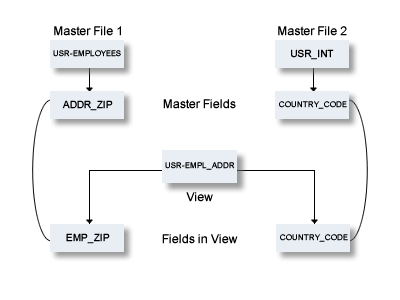
The coupling between master files and views/userviews depends on whether the view is derived from a single master file or from one or several master files.
Userviews are derived from one of the following master files:
Adabas file
Physical and logical VSAM files
IMS Segments
Entire System Server files
Master fields and fields of Userviews are coupled by field short name (column DB in field maintenance screens).
The following table indicates the valid combinations of view types and master file types:
| Type of View | Type of Master File |
|---|---|
| AT | A |
| B | A(SQL) AT, B |
| BV | BT, BV |
| E, IV | D, E, IV |
| J | I |
| JV | JT, JV |
| K | I |
| L | V |
| OV | OT, OV |
| Q | P |
| R | L |
| U | A |
| W | V |
| XV | XT, XV |
| YV | YT, YV |
For views which can be derived from several master files, the coupling is established by parameters from Table/View ID and from Field ID in the field List of the file documenting the view. This applies to the following master file types:
Adabas Files (with SQL usage set to Y)
Adabas Cluster Tables
Adabas D Table
DB2 Table
Informix Table
Ingres Table
Oracle Table
Sybase Table
If fields in a master file are modified, views and userviews coupled to these fields are changed accordingly. The following rules apply for this rippling:
The following attributes are always rippled:
short name (if applicable)
Field type
suppression / null value option
uniqueness option
character set
null default option
The following attributes are rippled if the attribute values in the userview and the master field were identical before the master field was modified:
Field ID
length, format (both must be identical)
max. occ.
gr. structure
justify
header / edit mask
Field/View name name synonym
The abstract of a field is rippled according to the setting of the following parameter in the Profile SYSTEM
| Ripple abstract |
|
When a verification list of a master field is edited, corresponding changes are automatically made in the verification list of fields in the view/userview derived from the master file. The following rules apply:
The verification list of a field in a userview does not have to contain all the verifications that are contained in the list of the master file field from which the userview field has been derived.
If a verification is removed from the verification list of a master field, the verification is automatically removed from the verification list of coupled fields.
If a verification is added to the verification list of a master field, it is automatically added to the verification list of coupled fields.