This document covers the following topics:
There are two methods of documenting Adabas tables:
Files of Type A (SQL)
If an Adabas table corresponds exactly to a base table in
Adabas SQL Server, it can be documented as a file of type A (SQL). The Adabas
file must not contain groups structures or multiple value fields. Rotated
fields are not supported with this method. This method is retained for reasons
of compatibility with earlier Predict versions.
Files of Type AT
Tables can also be documented with files of type AT (Adabas cluster
table). Files of this type can be understood as userviews to an Adabas file.
See Adabas Cluster
Table.
Adabas SQL views are documented with files of type B. See Adabas SQL View.
The following naming conventions apply to files documenting Adabas SQL Server tables and views (files of type AT, B).
If the Predict parameter General Defaults > Miscellaneous > Upper/lower case / Object ID is set to L, the following attributes are stored in upper and lower case as entered:
File ID (object IDs containing lower case letters are not recommended)
Derived field expressions
SQL verifications
Check expressions
Constraint names
See also section Defaults in the Predict Administration documentation.
Table/View names for Adabas SQL Server objects can have up to 32 characters.
See overview of permitted characters in the section Naming Conventions.
The identifier of a table or view must be given in qualified form: the schema identifier, a delimiter and the table/view name. A hyphen is used as a delimiter (not a period as in SQL). An example: SYSSAG-SYSCOLUMNS. Hyphens in names are treated as follows:
When a table/view is generated from a Predict file object, the hyphen is transformed into a period (.).
Because hyphens are used as delimiters, only one hyphen can occur in the SQL identifier. Column names must not contain a hyphen.
The hyphen can be used as a minus sign or negative sign in the field expression or the subselect clause and must then be preceded by a blank.
Note:
Parameters not listed below are described in other sections of this
documentation: Parameters common to all object types, for example Keys, are
described under Global
Attributes. Parameters common to all file types, for
example Literal name, are described under
Common File
Attributes. See also
Common
Parameters for SQL File Types.
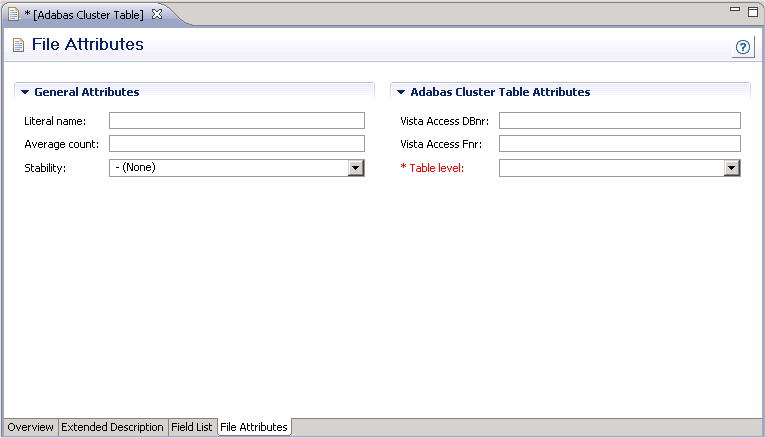
| Parameters | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table level |
|
||||||||
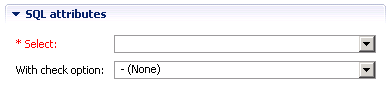
Note:
Parameters common to all object types,
for example Keys, are described under Global Attributes.
Parameters common to all file types, for example Literal name, are described
under Common File
Attributes. See also
Common
Parameters for SQL File Types.