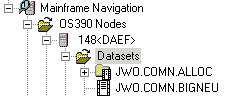
In the object workspace, the z/OS datasets are shown when you expand the Datasets folder of a z/OS node. Example:
This document covers the following topics:
Before displaying z/OS datasets, you can define a filter so that only those datasets are shown which correspond to your filter criteria.
 To define a filter
To define a filter
In the object workspace, select the Datasets folder in the appropriate node.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
Or:
Press F3.
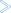
The following dialog box appears:
Enter the filter criteria.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Dataset name | Enter the datasets that are to be shown. For example, when you specify "ABC*", only the dataset names starting with these characters will be shown. |
| Volume |
If you do not specify a volume, the dataset list is created from the catalog. If you do specify a volume, the dataset list is created from the VTOC of that volume. |
| Password | Enter the system password if dataset is protected. |
Choose the button.
The number of objects shown in the list view window depends on whether or not a filter has been defined for the datasets (see Filtering z/OS Datasets).
 To list z/OS datasets
To list z/OS datasets
In the object workspace, select the Datasets folder in the appropriate node.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
Or:
Press F8.
The list view window appears.
The type of information contained in the list view window depends on whether or not filter criteria for Volume have been defined (see Filtering z/OS Datasets).
The following topics are covered below:
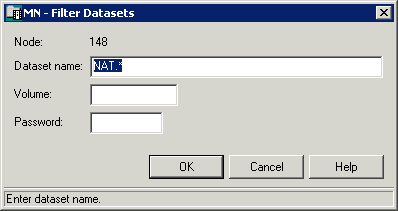
When a volume has not been specified with the command, the dataset list is created from the catalog. Example:
Since no volume was specified, the list of datasets appears as shown above with the following columns:
| Column | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Dataset Name | Name of the dataset. | |
| Volume | Volume serial number. | |
| Series | Device series. | |
| Class | Device class. Possible values: | |
| COMM | Communications. | |
| CTCA | Channel-to-channel adapter. | |
| DASD | Direct access. | |
| DISP | Display station. | |
| NA | Not applicable. | |
| TAPE | Tape. | |
| UREC | Unit record. | |
| Type | Dataset type, for example: NONVSAM, CLUSTER, DATA, GDG BASE. | |
When a volume has been specified with the command, the datasets contained in the VTOC of the specified volume are shown. Example:
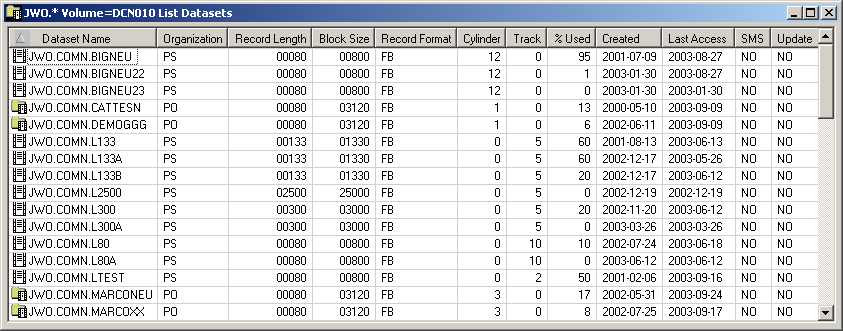
Since a volume was specified, the list of datasets appears as shown above with the following columns:
| Column | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Dataset Name | Name of the dataset. | |
| Organization | Dataset organization, for example: | |
| DA | Direct access. | |
| PO | Partitioned dataset (PDS). | |
| POE | Partitioned dataset (PDSE). | |
| PS | Sequential dataset. | |
| Record Length | Logical record length in bytes. | |
| Block Size | Block size in bytes. | |
| Record Format | Record format, for example: | |
| F | Fixed length record. | |
| FB | Fixed blocked record. | |
| FBA | Fixed blocked record, ANSI control characters. | |
| U | Unformatted record. | |
| V | Variable record. | |
| VB | Variable blocked record. | |
| Cylinder | Size of dataset in cylinders. | |
| Track | Size of dataset in tracks. | |
| %Used | Percentage of dataset used. | |
| Created | Dataset creation date. | |
| Last Access | Date of last access. | |
| SMS | Is this an SMS-controlled device/unit (YES, NO)? | |
| Update | Has the file been updated since the last backup (YES, NO)? | |
Mainframe Navigation internally maintains a list of the 100 datasets most recently accessed by the user. This list is stored at the end of a session and is read when Mainframe Navigation is started.
The following topics are covered below:
All commands that are available for datasets can also be invoked from the list of recent files.
 To list recently-used z/OS datasets
To list recently-used z/OS datasets
In the object workspace, select the Datasets folder in the appropriate node.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
The list view window containing recently-used datasets appears in the content pane. Example:
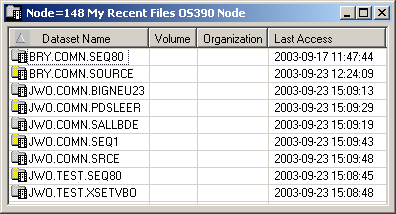
The list view window contains the following columns:
| Column | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Dataset Name | Name of the dataset. | |
| Volume | Volume serial number. | |
| Organization | For example: PO (PDS), PS (sequential dataset), DA (direct access). | |
| Last Access | Date (YYYY-MM-DD) and time the dataset was last accessed. | |
You can remove a dataset from the list of recent files. This does not delete the dataset on the server.
 To remove a z/OS dataset from the list of recent files
To remove a z/OS dataset from the list of recent files
In the list of recent files, select the dataset to be removed.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
You can synchronize the list of recent files with the data on the server. List entries which no longer exist on the server (for example, because they have been renamed or deleted) are deleted from the list of recent files.
 To synchronize the list of recent files for z/OS
datasets
To synchronize the list of recent files for z/OS
datasets
In the object workspace, select the Datasets folder in the appropriate node.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
A dialog box appears, asking to confirm the synchronize function for the selected object.
Choose the button to synchronize the list of recent files.
You can add a z/OS dataset to a catalog.
 To catalog a z/OS dataset
To catalog a z/OS dataset
In the object workspace, select an uncataloged dataset in the Volumes folder of the appropriate node.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
The dataset is cataloged. It will appear in the Datasets folder (depending on your filter criteria).
You can remove a z/OS dataset from a catalog.
 To uncatalog a z/OS dataset
To uncatalog a z/OS dataset
In the object workspace, select a cataloged dataset either in the Volumes or Datasets folder of the appropriate node.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
A dialog box appears, asking to confirm the uncatalog function for the selected object.
Choose the button to uncatalog the dataset.
The selected dataset is uncataloged and removed from the Datasets folder.
You can compress a partitioned z/OS dataset (PDS).
 To compress a z/OS dataset
To compress a z/OS dataset
In the object workspace, select a partitioned dataset either in the Datasets or Volumes folder of the appropriate node.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
A dialog box appears, asking to confirm the compress function for the selected object.
Choose the button to compress the dataset.
This command is generally issued for an existing dataset. The allocation information for the existing item is displayed and you can overwrite the name and modify the specifications for the new item.
 To allocate a z/OS dataset
To allocate a z/OS dataset
In the object workspace, select a dataset either in the Datasets or Volumes folder of the appropriate node.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
The following window appears in the content pane:
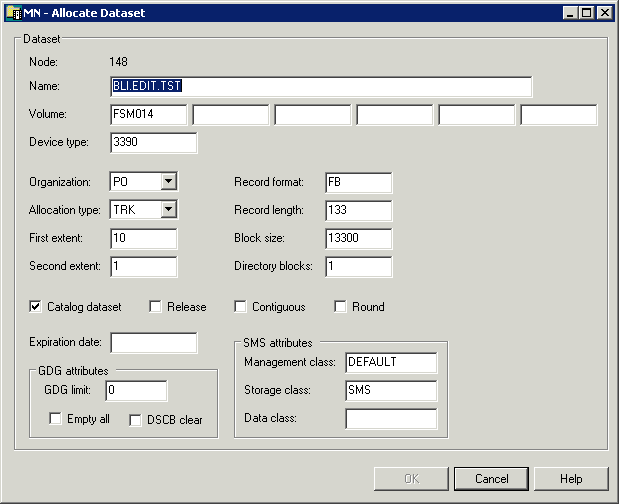
Enter a new name for the dataset and enter or change other options as described in the table below.
| Option | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Node | Node containing the dataset. | |
| Name | Dataset name. | |
| Volume | Serial number of the volume on which the dataset is to be allocated. You can specify up to 5 volumes for multi-volume datasets. | |
| Device type | If you do not specify a volume, specify the generic identifier from which a volume is to be selected (for example, 3380). | |
| Organization | For example: PO (PDS), PS (sequential dataset), DA (direct access). | |
| Allocation type | Space type for dataset. Possible values: | |
| BLK | Blocks | |
| CYL | Cylinders | |
| TRK | Tracks | |
| First extent | Initial quantity to be allocated. | |
| Second extent | Additional quantity to be allocated if dataset fills. | |
| Record format | For example: | |
| FB | Fixed block | |
| VB | Variable block | |
| FBA | Fixed block, ANSI control characters | |
| Record length | Given in bytes. | |
| Block size | Given in bytes. | |
| Directory blocks | Must be specified for PO-type datasets. | |
| Catalog dataset | Activate this check box to automatically catalog the dataset when it is allocated. | |
| Release | Activate this check box to release allocated space if it is not used by the dataset. | |
| Contiguous | Activate this check box if tracks or cylinders must be adjacent. | |
| Round | Activate this check box to automatically round up space to the nearest cylinder if tracks or blocks are specified as space units. | |
| Expiration date | Date when the dataset expires. Until this date is reached, each attempt to update or delete the dataset causes a console message, requiring an operator reply. | |
| GDG attributes | GDG limit | A value in this field identifies the file to be allocated as GDG. The value specifies the maximum number of generation datasets that can be associated with the GDG being defined. |
| Empty all | Activate this check box to uncatalog all generation datasets when the GDG limit is reached. If you do not activate this check box, only the oldest generation dataset is uncataloged. | |
| DSCB clear | Activate this check box to delete the dataset's DSCB from the VTOC; the GDS no longer exists. If you do not activate this check box, the DSCB is not deleted from the VTOC and the dataset can be processed as any non-VSAM dataset. | |
| SMS attributes | These attributes are available only if SMS is installed. | |
| Management class | The management class to be used to obtain the management-related data for SMS (migration, backup and retention criteria) to allocate the dataset. | |
| Storage class | The storage class to be used to obtain the storage-related data for dataset allocation. | |
| Data class | The data class to be used to obtain the data-related information (SPACE, LRECL, etc.) for dataset allocation. | |
Choose the button.
A dialog box appears, informing you that the dataset was successfully allocated.
Choose the button to allocate another dataset.
Or:
Choose the button to finish
allocation.
You can display information about a z/OS dataset. Different types of information are shown for sequential and partitioned datasets and for generation data groups (GDGs).
 To display the properties of a z/OS dataset
To display the properties of a z/OS dataset
In the object workspace, select a dataset in the Datasets folder.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
Or:
Press ALT+ENTER.
A properties dialog box appears.
The following topics are covered below:
The properties dialog box for a sequential or partitioned dataset looks as follows:
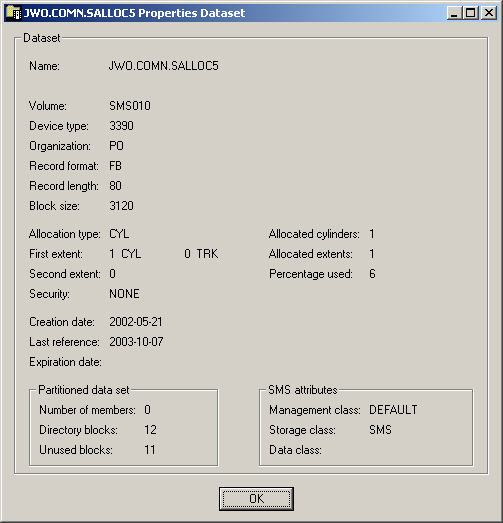
The following information is shown in this dialog box:
| Option | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the dataset. | |
| Volume | Serial number of the volume on which the dataset is allocated. | |
| Device type | If a volume is not specified, this is the generic identifier from which a volume is to be selected (e.g. 3380). | |
| Organization | For example: | |
| PO | PDS | |
| PS | Sequential dataset | |
| DA | Direct access | |
| Record format | For example: | |
| FB | Fixed block | |
| VB | Variable block | |
| FBA | Fixed block, ANSI control characters | |
| Record length | Logical record length in bytes. | |
| Block size | Block size in bytes. | |
| Allocation type | Space type for dataset. Possible values: | |
| BLK | Blocks | |
| CYL | Cylinders | |
| TRK | Tracks | |
| First extent | Initial quantity allocated. | |
| Second extent | Additional quantity to be allocated if dataset fills. | |
| Security | Security status. Possible values: | |
| NONE | Not password-protected. | |
| READ | Password-protected for read and write operations. | |
| WRITE | Password-protected for write operations. | |
| Allocated cylinders/tracks | Number of cylinders or tracks allocated. | |
| Allocated extents | Number of extents, 1 to 16. | |
| Percentage used | Percentage of dataset used. | |
| Creation date | Dataset creation date in format YYYY-MM-DD. | |
| Last reference | Date of last access in format YYYY-MM-DD. | |
| Expiration date | Date when the dataset expires in format YYYY-MM-DD. Until this date is reached, each attempt to update or delete the dataset causes a console message, requiring an operator reply. | |
| Partitioned dataset | These fields appear only if the dataset is partitioned. | |
| Number of members | Number of members in the dataset. | |
| Directory blocks | Number of directory blocks. | |
| Unused blocks | Number of unused directory blocks. | |
| SMS attributes | These fields appear only if SMS attributes have been defined for the dataset during allocation. | |
| Management class | The management class used to obtain the management-related data for SMS (migration, backup and retention criteria) to allocate the dataset. | |
| Storage class | The storage class used to obtain the storage-related data for dataset allocation. | |
| Data class | The data class used to obtain the data-related information (SPACE, LRECL, etc.) for dataset allocation. | |
The properties dialog box for a generation data group looks as follows:
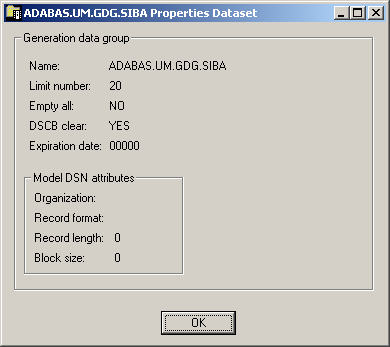
The following information is shown in this dialog box:
| Option | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the dataset. | ||
| Limit number | The maximum number of generation datasets that can be associated with the GDG being defined. | ||
| Empty all | When the maximum number of generation datasets is reached: | ||
| YES | All generation datasets are uncataloged. | ||
| NO | Only the oldest generation dataset is uncataloged. | ||
| DSCB clear | When the generation dataset is uncataloged (due to the command or Empty all value): | ||
| YES | The dataset's DSCB is deleted from the VTOC and the generation dataset is deleted. | ||
| NO | The dataset's DSCB is not deleted from the VTOC. The DSCB is left in the VTOC and the dataset can be processed as any non-VSAM dataset. | ||
| Expiration date | Date the dataset expires. Until this date is reached, each attempt to update or delete the dataset causes a console message, requiring an operator reply. | ||
| Model DSN attributes | Organization | For example: PO (PDS), PS (sequential dataset), DA (direct access). | |
| Record format | For example: | ||
| FB | Fixed block | ||
| VB | Variable block | ||
| FBA | Fixed block, ANSI control characters | ||
| Record length | Logical record length in bytes. | ||
| Block size | Block size in bytes. | ||