This document covers the following topics:
For general information on how to manage objects (for example, how to add or copy an object), see the Object Description documentation.
The table below contains a list of all valid database types.
| Code | Database Type |
|---|---|
| A | Adabas |
| B | Adabas D handler |
| C | Conceptual |
| D | DB2 |
| E | Gen. SQL handler |
| H | Other handler |
| I | IMS |
| J | Ingres handler |
| M | RMS handler |
| O | Oracle handler |
| P | Entire System Server |
| Q | Adabas SQL handler |
| R | rdb handler |
| S | SQL Server |
| T | Target node |
| V | VSAM handler |
| X | Informix handler |
| Y | Sybase handler |
When you add a database, you first have to specify the database type in the Type dialog box.
When you choose the button, a database type-specific window appears. The database type is indicated in the title bar.
The following sample window shows the parameters which apply to most types of databases.
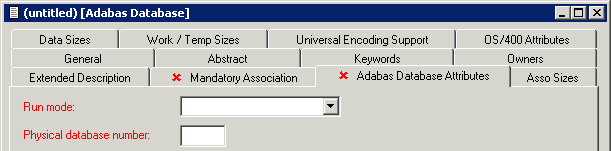
| Attributes | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belongs to VM |
This attribute can be found on the Mandatory Association tab. Predict virtual machine object documenting the hardware and operating system environment of the database. See also Defining the Distribution of Data in Predict in the section Vista in the Predict and Other Systems documentation. |
||||||||||
| Run mode |
|
||||||||||
| Physical database number |
|
||||||||||