An application can be documented with a Predict object of type System. See System Types for a list of possible system types.
In the predefined Predict metastructure, a system can have passive and active associations of the following types:
| Valid passive associations: |
"Contained in LS" |
| Valid active associations: |
"Uses PR concept." (default active
association) |
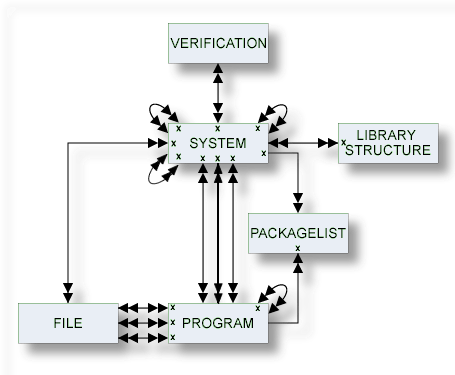
This document covers the following topics:
The System Maintenance menu is called with
function code M and object code SY in a Predict main menu or the command
MAINTAIN SYSTEM.
13:51:33 ***** P R E D I C T ***** 2007-05-31
Plan 0 - (SY) System Maintenance - Profile HNO
Function Function
A Add a system D Display system
C Copy system L Link children
M Modify system S Select system from a list
N Rename system
P Purge system
Function .........
System ID ........ Attributes........*
Copy ID .......... System of type....*
Library .......... User system Fnr
User system DBnr ...
Restrictions ....* Profile HNO,used Association.......*
Command ===>
Enter-PF1---PF2---PF3---PF4---PF5---PF6---PF7---PF8---PF9---PF10--PF11--PF12---
Help Next Stop Last LnkEl Flip Print Impl AdmFi SelFi Prof Main
|
Note:
Parameters not listed here are described under
Global
Attributes.
| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Function | Standard functions are described in the section Maintenance in the Predict Reference documentation. Functions Purge system and Rename system are described under System-Specific Maintenance. |
| System of type | For the Select function: a system type can be
specified as a selection criterion. For the Add and Copy functions: the system type can be specified here. This type will be passed to the add System or copy System screen. See System Types below for a list of valid values. |
| Library, User system Fnr/DBnr | For the select function: Implementation pointer values can be used to restrict the scope of objects to be processed. Only those Predict system objects will be processed that document libraries meeting the specified Library/Fnr/DBnr parameters. |
The table below contains a list of all valid system types.
| Code | System Type |
|---|---|
| A | Application Library |
| B | Base Application |
| C | Conceptual. Used to outline the preliminary description of an application in the design phase. |
| G | 3GL Application |
| O | Compound Application |
| P | DB2 plan. Used to document a DB2 application. |
The screen is displayed for the Add a System function. The Copy and Modify screens are similar.
13:54:46 ***** P R E D I C T ***** 2007-05-31
- Add a System -
System ID ....... HNO-SY
Type ...........* C Conceptual
Keys .. Zoom: N
Implementation pointer
Library ............
User system Fnr ....
User system DBnr ...
DB2 Plan name ........
Profile
Name ...............
Fnr ................
DBnr ...............
Port .................
Server name .......... Zoom: N
Development platform *
Abstract Zoom: N
Additional attributes ..* N Associations ..* N
|
Note:
Parameters not listed here are described under
Global
Attributes.
| Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System ID | The ID of the Predict system object. A read-only field. | ||||||
| Type | System type. Enter asterisk to display valid values or see list in the section System Types above. | ||||||
| Implementation pointer |
|
||||||
| DB2 plan name | Unique DB2 plan name. Only applicable to DB2 plans (systems of type P). | ||||||
| Profile |
|
||||||
| Port | The port number. | ||||||
| Server name | The name of the server. | ||||||
| Development platform | The development platform. Enter one of the following
values:
|
||||||
Systems documented with Predict objects of type System can be identified with three parameters: library, file number and database number. The three possible combinations of these parameters are shown below.
| Library | Y | Y | Y |
| File number | Y | Y | |
| Database number | Y |
The following rules apply to this function:
A system of type A (Application Library) cannot be deleted if it is linked to one or more systems via association "Has library SY".
A system of type G (3GL application) cannot be deleted if XRef data exist.
If you confirm the function with
DELETE, the following objects are deleted:
the system object
all links to child objects
all links from parent objects
If you confirm with SCRATCH, the following
objects are deleted additionally:
Programs linked to the system via association "Belongs to SY" (programs that are linked to packagelists via "Contained in PG" are not deleted)
all links to/from objects that are deleted together with the system
XRef data for the system (including DBRMs and system programs)
XRef data for scratched programs (parameter Language = Ada, BAL, COBOL, FORTRAN, PL/I, Static SQL, System Program).
Use this function to change the ID and/or type of a system object. The following restriction applies:
You cannot change the type of a system of type 3GL application for which XRef data exists.
You cannot change the type of a system of type A (Application Library) if it is linked to one or more systems via association "Has library SY".
All system-specific retrieval parameters are described in the section System Maintenance Menu.
The retrieval function Systems with Children (with association "Uses PR concept") evaluates only documentation data. If you require information on an implemented system, use the active retrieval function Systems containing programs.
13:40:59 ***** P R E D I C T ***** 2007-05-31
- List System - Page: 1
Cnt System ID Type Library Fnr DBnr
1 ADABAS C
2 ARH-LO C
3 * ARH-SYS A ARH
4 ARH-SYS-P P
|
| Meaning of Columns | |
|---|---|
| System ID | ID of the system object. If the output option Mark implementation is set to Y, implemented objects are marked with an asterisk. "Implemented" in this case means that XRef data exists for at least one program contained in a library documented by the system object. |
| Type | The type of system. See list of valid types and codes under System Types. |
| Library, Fnr, DBnr | Information on where a system is implemented: Library, file number and database number of the user system file. |
The output options valid for this object type are identical to those for object type Dataspace. See Output Options for Dataspace Retrieval.