This document covers the following topics:
Every time a control needs a static text definition (the name of a button or the name of a label), there are always two possibilities to define this text:
Specify a name directly.
Specify a text ID. This is a literal replaced with a string that is determined inside the multi language management at runtime.
Most controls that allow dynamic sizing offer the following properties:
colspan - number of columns occupied by
the control.
rowspan - number of rows occupied by the
control.
width - width.
height - height.
These properties influence the way how controls are placed into container rows.
Controls are put into table columns. If the column is wider or higher than the control itself, then you can explicitly control the vertical and horizontal alignment of the control inside the columns.
Most controls offer two properties:
valign
Specifies the vertical alignment. Valid values are
"top", "middle",
"bottom". "middle" is the
default value.
align
Specifies the horizontal alignment. Valid values are
"left", "center",
"right". The default value depends on the control.
For example, labels are aligned "left" by default,
the default for radio buttons is "center".
Pay attention: valign and
align only affect the position of the control
inside the column in which it is positioned if the column is larger than the
control. If the column is exactly as wide and high as the control itself, which
is the typical case, then they do not have any visual effects - and also need
not be defined.
align/valign
do not affect the control's internal alignment.
Most controls provide properties to specify the binding to the adapter processing. There is a naming convention, which is:
The names of the properties which specify the binding to an adapter parameter end with "prop".
The names of the properties which specify the binding to an event end with "method".
The type of the adapter parameter which is referenced by a control depends on the control itself:
Most controls directly bind to scalar adapter parameters.
More complex controls bind to an array of group structures.
The type of adapter parameter is described with each control.
All controls that incorporate textual information - such as labels, buttons or fields - offer the possibility to influence directly the style that is used for displaying the information.
The normal style is derived from the definition inside a cascading style definition file (file layout.css inside the html/general directory of the server). Overwrite or enhance this style information for your controls by passing the style information inside the corresponding style properties.
The properties specifying the style information end with the suffix
"style", e.g. there is a property
labelstyle for the label tag. The value of the
property can be any kind of a valid HTML style specification. If you want to
change the display style of a label to be large and blue, define the label in
the following way:
<label name="Test" width="150" labelstyle="font-size: 24pt; color: #0000FF"> </label>
It is possible to influence the visibility of all input controls (FIELD, BUTTON, etc.) by adapter parameters.
For some of these controls there is a property
visibleprop, specifying an adapter
parameter that returns "true"
or "false". By this, you can control whether you
want to display the control within the client or not.
Input controls support a property
statusprop and a property
displayprop. Using the corresponding adapter
parameters, you can dynamically control the display
status of the input control. The adapter parameter for the
statusprop can contain the
following values:
INVISIBLE
ERROR
ERROR_NO_FOCUS
FOCUS
FOCUS_NO_SELECT
The adapter parameter for the displayprop specifies
whether the control is display-only (TRUE) or whether it can be edited (FALSE).
The adapter parameter can contain the values
"TRUE" and "FALSE".
The combination of these two parameter values dynamically defines how the controls are rendered at runtime. The following table defines the rendering of the control for the different combinations:
displayprop |
statusprop |
Control Status |
|---|---|---|
| FALSE (default) | EDIT (deprecated) 1 | EDIT |
| FALSE (default) | INVISIBLE | INVISIBLE |
| FALSE (default) | ERROR | ERROR |
| FALSE (default) | ERROR_NO_FOCUS | ERROR_NO_FOCUS |
| FALSE (default) | FOCUS | FOCUS |
| FALSE (default) | FOCUS_NO_SELECT | FOCUS_NO_SELECT |
| TRUE | DISPLAY (deprecated) 1 | DISPLAY |
| TRUE | INVISIBLE | INVISIBLE |
| TRUE | ERROR | ERROR_DISPLAY |
| TRUE | ERROR_NO_FOCUS | ERROR_DISPLAY |
| TRUE | FOCUS | DISPLAY |
| TRUE | FOCUS_NO_SELECT | DISPLAY |
1 For statusprop, the above-mentioned
deprecated values are still supported to ensure compatibility with older
versions. In case you use these deprecated values for statusprop,
the values for displayprop are ignored.
The difference in behavior between "FOCUS" and "FOCUS_NO_SELECT" affects only the FIELD and TEXT controls. For these controls, FOCUS set the focus and selects the complete text inside the control. "FOCUS_NO_SELECT" sets the focus to the control, but does not select the text. For all other controls, "FOCUS_NO_SELECT" behaves like "FOCUS".
For all other controls - and for more complex manipulations of what is visible and not - use the possibility to be able to control the visibility of rows (ITR, TR) or containers (ROWAREA, ROWTABLE0): these controls provide for a visibility parameter and consequently can be switched on and off.
There is an extended management of what the control status
"INVISIBLE" means. Most input controls (FIELD,
CHECKBOX, etc.) supporting a statusprop or a
visibleprop also support a property
invisiblemode. The allowed values of
invisiblemode are:
invisible
The corresponding control is completely removed. The horizontal space
it occupied before is taken out.
cleared
The corrresponding control is not visible but still occupies its
horizontal space.
disabled
The corresponding control is displayed with a disabled state. This
state is only allowed with a certain number of controls (e.g. button and
icon).
Sometimes you want to control the keyboard focus inside a page. Here are the internal rules how a page finds out where to put the focus on.
The default reaction is - if a page is displayed for the first time - to put the focus on the first input control (FIELD, CHECKBOX, RADIOBUTTON, etc.) that is available inside a page. After that, you can navigate through the input controls - and the focus is kept stable when interacting with the server.
With statusprop - as mentioned in the
previous section - you can interrupt this default reaction; there are two
possibilities:
If an input control is set to status "ERROR", it requests the focus automatically. The purpose is to guide the user automatically to those fields that are not correctly entered.
If an input control is set to status "FOCUS", it is editable - just as normal - and also requests the focus.
If several input controls are requesting the focus at the same time, the focus is put on the first corresponding input control.
Sometimes you want to change the focus management behavior
of the framework for specific server round trips. For TABPAGE controls, you
sometimes want the framework not only to set the focus to the first
focus-requesting input control but also to open the corresponding tab. For some
events, you sometimes do not want the framework to automatically set the focus
to the first focus-requesting control. The
focusmgtprop property of the NATPAGE control
allows you to control the focus management for single server round trips.
Depending on the executed event, the application can define different focus
management modes for corresponding server round trips. For more information,
see the description of the focusmgtprop property
of the NATPAGE control.
Most input controls (FIELD, CHECKBOX, RADIOBUTTON, COMBOFIX, etc.)
support a property named flush. This property
controls whether data input from a user causes an immediate synchronisation
with the server or whether data input from a user is stored internally within
the client and is synchronized with the next flushing event (e.g. when choosing
a button).
There are three different values that can be specified with the
flush property:
"" (blank)
The data is not synchroized after leaving the control. This is the
default.
server
The data is synchronized with the server immediately when the data has
been entered, i.e. when the user has left the corresponding input field.
screen
The data is synchronized within the controls of the screen. This means
- if you have two fields displaying the same property - you can synchronize the
fields immediately, without interacting with the server.
Tip:
On the one hand, it is useful to flush information in a very fine
granular way; you can react on wrong entered data immediately - on the other
hand, you have to remember that each flush causes network traffic. The screen's
data is sent to the server side processing and the screen waits for the
response of the server. During this time, the page is blocked for input and the
user sees an hour glass popping up in the left top corner of the screen.
By default, the tab sequence of the controls of a page is defined by the
order of the controls inside the page's XML layout definition. Using the
property tabindex, this order can be overridden
and the order of the tab index can be explicitly defined.
The following example shows a page with three fields and one button with an explicitly defined tab sequence:
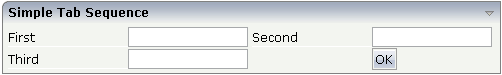
The XML layout definition is:
<rowarea name="Simple Tab Sequence">
<itr takefullwidth="true">
<coltable0 width="50%">
<itr>
<label name="First" width="120">
</label>
<field valueprop="first" width="120" tabindex="1">
</field>
</itr>
<itr>
<label name="Third" width="120">
</label>
<field valueprop="third" width="120" tabindex="3">
</field>
</itr>
</coltable0>
<coltable0 width="50%">
<itr>
<label name="Second" width="120">
</label>
<field valueprop="second" width="120" tabindex="2">
</field>
</itr>
<itr>
<hdist width="120">
</hdist>
<button name="OK" method="onOK" tabindex="4">
</button>
</itr>
</coltable0>
</itr>
</rowarea>
According to the sequence of controls inside the layout definition, the default tab sequence would be: field First, field Third, field Second and button .
Due to explicitly defining the tabindex
property for the fields and the button, the tab sequence is now correct: field
First, field Second, field
Third and button .
Pay attention:
Once having started to explicitly set the tab index in a page, you must consequently continue with all controls of the page. Adding new controls without tab index, is internally interpreted as if these controls were defined with tab index "0".
Equal tab indices in controls are allowed. In this case, the sequence of the controls inside the layout definition defines the tab sequence among the controls with an equal index.
Moving controls from one location to the other within a page typically means that you have to adapt the tab sequence accordingly.
The tab index usually is a positive integer value. You may define tab index "-1" for excluding certain controls from the tab sequence at all. In this case, the corresponding controls may only be reached by mouse clicking.
Conclusion:
In typical pages, you do not have to take care of the tab sequence at all because the default (tab sequence by order of controls in page layout) is adequate to the user's experience.
Only use the explicit definition of the tab sequence if really it is required - the effort for maintaing each tab index with each control should not be underestimated.
Tooltips can be applied to many controls. If the user hovers with the mouse cursor over a control for some seconds, a small yellow box appears showing some more detailed explanation.
The corresponding controls offer two properties:
title
Here you can specify a hard-coded text that is used as the
tooltip.
titletextid
Here you specify a text ID that is passed to the multi language
management..
This section describes how to apply images that are contained in binary variables on the Natural server to your page layout. The images can be applied statically and dynamically.
Many controls provide properties for loading images. In the corresponding image properties, you usually specify an absolute or relative URL such as "../myproject/images/myicon.gif". For images which are contained in binary variables on the Natural server, however, you must use a different URL value such as "nat:myimage1". Example:
<itr> <icon image="nat:myimage1"> </icon> </itr>
The prefix "nat:" indicates that the image is contained in a binary variable on the Natural server. "myimage1" is the name that your Natural application uses for this image. There is no need to download or copy the image manually from the Natural server to the application server or web container. This is done automatically by the Natural for Ajax framework.
You simply add an NJX:OBJECTS control to your page layout and provide the image data in the corresponding Natural data fields as shown below:
<natpage>
<njx:objects>
</njx:objects>
...
<pagebody>
...
<itr>
<icon image="nat:myimage1">
</icon>
</itr>
For information on how to load the image into the data structure of the NJX:OBJECTS control, see the description of the NJX:OBJECTS control.
Dynamic images are specified in the same way as static images. You also add an NJX:OBJECTS control to your page layout. This time, you specify the images that are contained in a binary variable on the Natural server in the corresponding dynamic image properties of the control as shown below:
<natpage>
<njx:objects>
</njx:objects>
...
<pagebody>
...
<itr>
<imageout valueprop="myimageprop">
</imageout>
</itr>
This allows your Natural program to apply images which are contained in a binary variable on the Natural server and images which reside in the web application layer alternatively to the same dynamic image property at runtime ("myimageprop" in the above example).
For information on how to load the image into the data structure of the NJX:OBJECTS control, see the description of the NJX:OBJECTS control.
This section describes how to embed, download and upload documents that are contained in binary variables on the Natural server to your page layout.
As with images, you add an NJX:OBJECTS control to your page layout and load the document into the corresponding data structure of the NJX:OBJECTS control. For further information, see the description of the NJX:OBJECTS control.
To embed a document into your page layout, you add a
SUBPAGE control to your page. In the
valueprop property of the SUBPAGE control, you
have to specify the corresponding document URL dynamically at runtime. If you
want to force downloading instead of opening the document, add the parameter
DOWNLOAD=TRUE to the URL (for example,
"nat:mydoc.pdf?DOWNLOAD=TRUE").
Via the NJX:DOCUMENTLINK control, you can integrate hyperlinks to documents. When clicking on a hyperlink, the corresponding document is opened in a pop-up dialog.
As an alternative to the NJX:DOCUMENTLINK control, you can use the
predefined event showDocumentForXXX in all controls
which support a method property. XXX is the name of a property you
can choose. For XXX, a corresponding Natural field will
automatically be generated in your Natural adapter. To show a document, when
the showDocumentForXXX event is triggered, the Natural
program must apply a valid document URL to the XXX field. This URL
can refer to documents transported in the data structure of the NJX:OBJECTS
control. It can also be a normal browser URL for a document which is accessible
from within the web application.
Via the NJX:NJXFILEDOWNLOAD control, you can
integrate hyperlinks which are directly executed by the browser. To force
downloading the document, add the parameter DOWNLOAD=TRUE to the
URL (for example,
"nat:mydoc.pdf?DOWNLOAD=TRUE").
See also the naturaldocument example in the njxdemos project.
Via the NJX:NJXFILEUPLOAD2 control you can upload documents from the client to the NJX:OBJECTS data structure. You can also upload dynamically generated PDF documents to the NJX:OBJECTS data structure by triggering corresponding built-in events in the REPORT control.