This document contains special considerations that apply when running Natural in batch mode. It covers the following topics:
Natural distinguishes between two processing modes:
interactive mode (via the Natural Main Menu)
batch mode
The main difference between these two modes is that in interactive mode, the commands and data are input by the user by means of the keyboard and the output is displayed on a screen. In batch mode, input is read from a file and output is written to a file - without user interaction.
When Natural is run as a batch job, no interaction between Natural and the person who submitted the batch job is necessary. The batch job consists of programs that are executed sequentially and that receive sequential input data.
Batch mode is useful for mass data processing on a regular basis.
Batch mode is activated with the parameter
BATCHMODE.
 To start a Natural session in batch mode
To start a Natural session in batch mode
Start Natural with the dynamic parameter
BATCHMODE as shown below:
natural BATCHMODE
The above call (where only the
BATCHMODE parameter is specified) assumes that the
required input and output channels have already been defined in the
Configuration Utility. For information on the input and output channels, see
Using Natural in Batch
Mode later in this section). For information on the
batch-mode-relevant profile parameters in the parameter file, see
Batch
Mode in the Configuration
Utility documentation.
It is also possible to add the required input and output channels as dynamic parameters to the above call. This is illustrated in Sample Session for Batch Mode later in this section. Any input and output channels that are specified as dynamic parameters with the above call override the channel definitions in the parameter file.
Check the file which has been defined as the output channel. At its end, this file should contain the message that your session has terminated normally.
A Natural session in batch mode is terminated when one of the following is encountered during the session:
the system command FIN in the
batch input file, or
a TERMINATE statement in a
Natural program which is being executed.
Note:
When an end-of-input condition occurs in the batch input file,
the batch session is also terminated. In this case, the file which has been
defined as the output channel contains a message which indicates an unexpected
end.
To start a Natural
session in batch mode you have to specify the dynamic parameter
BATCHMODE. In addition, input and output channels have
to be defined as described below.
Important:
The input channels CMSYNIN and/or
CMOBJIN and the output channel
CMPRINT are always required for batch mode.
The following topics are covered below:
The following parameters are available for batch mode:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
CMSYNIN |
Defines the batch input file which
contains the Natural commands and (optionally) data to be read by
INPUT statements during
execution of Natural programs.
|
CMOBJIN |
Defines the batch input file which
contains the data to be read by INPUT statements. This data can
alternatively be placed in the file defined with the parameter
CMSYNIN, immediately following the relevant
RUN or
EXECUTE
command.
|
CMPRINT |
Defines the batch output file for the
output resulting from DISPLAY,
PRINT and
WRITE statements in a
Natural program.
|
CMPRTnn |
Defines an output file for additional
reports referenced by any Natural program executed during the session.
nn is a two-digit decimal number in the range from
01 to 31 which corresponds to the report number used in a
DISPLAY,
PRINT or
WRITE statement.
|
CMWRKnn |
Defines a work file referenced by any
Natural program executed during the session. nn is a
two-digit decimal number in the range from 01 to 32 which corresponds to the
number used in a READ WORK
FILE or WRITE WORK
FILE statement.
|
NATLOG |
Used to log messages that could not
be written to the batch output file defined with the parameter
CMPRINT. It is recommended to enable
NATLOG in batch mode.
|
The following parameters are used to specify the code pages in which the input files are encoded and in which the output file shall be encoded.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
CPSYNIN |
Specifies the code page in which the
batch input file for commands is encoded. This file is defined with the
parameter CMSYNIN.
|
CPOBJIN |
Specifies the code page in which the
batch input file for data is encoded. This file is defined with the parameter
CMOBJIN.
|
CPPRINT |
Specifies the code page in which the
batch output file shall be encoded. This file is defined with the parameter
CMPRINT.
|
Encoding for CMSYNIN and
CMOBJIN:
If a code page is specified for one of the input files
CMSYNIN or CMOBJIN, it is assumed
that the data in the input file is encoded using this code page.
If no code page is specified for one of the input files
CMSYNIN or CMOBJIN, it is assumed
that the data in the input file is encoded using the default code page
specified in the Natural parameter CP.
If no code page is specified in the Natural parameter
CP, it is assumed that the data in the input file is
encoded using the current system code page.
Encoding for CMPRINT:
If a code page is specified for the output file
CMPRINT, the output data will be encoded using this code
page.
If no code page is specified for the output file
CMPRINT, the output data will be encoded using the
default code page specified in the Natural parameter
CP.
If no code page is specified in the Natural parameter
CP, the output data will be encoded using the current
system code page.
If the encoding/decoding fails (for instance if a character is
written to CMPRINT that is not contained in the code
page used to encode the file), the batch job terminates with a startup error 42
(batch mode driver error) that specifies the file on which the
encoding/decoding error occurred.
Note that it is possible in particular to specify UTF-8 as code page in each of these parameters. This allows for reading and writing Unicode data encoded in UTF-8.
This example demonstrates how to start Natural in batch mode. A
simple Natural program is executed and data items are taken from the batch
input file. After the items are processed with the INPUT
statement, a DISPLAY statement follows, which writes the data to
the batch output file. Then, Natural terminates.
This example uses the program RECCONT which is stored
in the library SYSEXBAT.
Note:
See the text A-README in the library
SYSEXBAT for information on the objects that are stored in this
library.
The sample session is invoked with the following call:
natural BATCHMODE CMSYNIN=cmd.txt CMOBJIN=data.txt CMPRINT=out.txt NATLOG=ALL
Note:
This call assumes that all files can be found in the current
directory and that the output is written to this directory. If the files are
located in different directories or if the output is to be written to a
different directory, you have to specify the path.
The parameters in the above call are described below:
BATCHMODEThe parameter
BATCHMODEenables batch mode and sets the value of the system variable*DEVICEtoBATCH.CMSYNIN=cmd.txtThe batch input file cmd.txt is a text file which is stored in your file system. The content of this file is shown below. It contains Natural system commands for logging on to the library
SYSEXBAT, executing the Natural programRECCONT, and terminating the Natural session.LOGON SYSEXBAT EXECUTE RECCONT FINThe Natural program
RECCONThas the following content:DEFINE DATA LOCAL 1 #firstname (A10) 1 #lastname (A10) END-DEFINE INPUT (IP=OFF AD=M) #firstname #lastname DISPLAY #firstname #lastname ENDCMOBJIN=data.txtThe
INPUTstatement in the programRECCONTuses the data which is defined in the batch input file data.txt. This is a text file which is stored in your file system. The content of this file is shown below.Ben % SmithNote:
The percent character (%) indicates that the information continues in the next line.CMPRINT=out.txtThe
DISPLAYstatement in the programRECCONTwrites the data to the batch output file out.txt which is created in your file system. The content of this file is shown below:NEXT LOGON SYSEXBAT Logon accepted to library SYSEXBAT. NEXT EXECUTE RECCONT DATA Ben % DATA Smith Page 1 25.04.05 13:39:09 #FIRSTNAME #LASTNAME ---------- ---------- Ben Smith NEXT FIN NAT9995 Natural session terminated normally.NATLOG=ALLWhen you invoke the sample session with the above call, a log file is created with contains all types of messages (which also includes the names of the batch input and outfile files). The log file is normally created in Natural's temporary directory which is defined in the local configuration file. See also the description of the
NATLOGparameter.
The image below illustrates the different ways in which Natural reads input and writes output in batch mode.
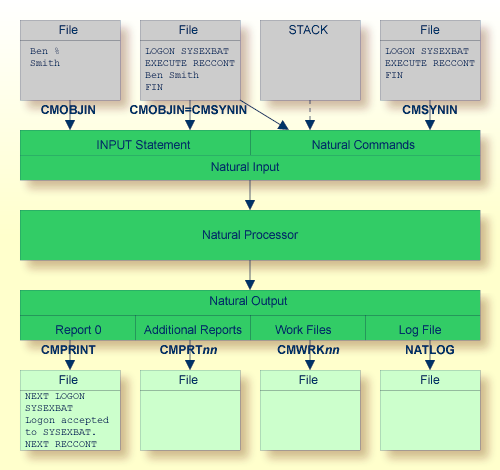
As shown in the above graphic, you can proceed in one of the following ways:
CMOBJIN and
CMSYNIN
Different files are used for batch input. One file contains
the Natural commands and the other file contains the data:
natural BATCHMODE CMSYNIN=cmd.txt CMOBJIN=data.txt CMPRINT=out.txt
CMSYNIN
One file is used for batch input. It contains both the Natural
commands and data:
natural BATCHMODE CMSYNIN=data.txt CMOBJIN=data.txt CMPRINT=out.txt
Note:
Even though only one batch input file is used, both
parameters CMSYNIN and CMOBJIN
have to be specified. Both parameters must refer to the same file.
CMOBJIN and
STACK
One file is used for batch input. It contains the data. The
Natural commands are specified with the profile parameter
STACK:
natural BATCHMODE CMOBJIN=data.txt STACK="(LOGON SYSEXBAT; RECCONT;FIN)"
The system variable *DEVICE
indicates whether Natural is running in batch mode or interactive mode.
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| Batch mode | *DEVICE
contains the value BATCH. This value is set by the parameter
BATCHMODE.
|
| Interactive mode | *DEVICE
contains a value other than BATCH. In most cases, it contains the
value VIDEO.
|
Example:
IF *DEVICE = "BATCH" THEN WRITE 'This is the background task' ELSE WRITE 'This is the interactive session' END-IF
When Natural is running in batch mode, some features are not available or are disabled:
Interactive input or output is not possible.
Only data for an INPUT statement can be processed.
The terminal database SAGtermcap is not
supported. Therefore, the terminal capability TCS which is used for a different
character set is not supported. To use a different character set, use
environment variable NATTCHARSET instead.
No colors and video attributes are written to the batch output
file defined by CMPRINT.
Filler characters are not displayed within an
INPUT statement.
Certain Natural system commands are not executable in batch mode, and are ignored. In the System Commands documentation, a corresponding note is provided for each system command to which this restriction applies.
In addition to the batch mode as described above, you can also simulate batch mode. However, it is recommended to use batch mode instead of batch mode simulation. Batch mode has the following advantages over batch mode simulation:
Easy data input with support of keyword delimiter mode.
Configurable and formatted output processing.
Extended error handling.
Faster startup and shutdown.
Faster program execution.
If the input channel is redirected to a file, Natural does not read the input commands and data from the keyboard but from this file. You have to specify the data in exactly the same way as you would do on the terminal. For example, for two input fields you have to fill up the first field with trailing blanks to position to the second field. No keyword delimiter mode is supported. To use keyword delimiter mode, use batch mode instead of batch mode simulation.
If the output channel is redirected to a file, Natural writes any output that would appear on the screen to this file. Control sequences are also written to the file, which makes the file unreadable. To get a formatted output, use batch mode instead of batch mode simulation.
Use the dynamic parameter BATCH when starting
Natural, to set the system variable *DEVICE
to the value BATCH. This value can be checked within a Natural
program.
natural BATCH < input-file-name
Natural then receives all input operations from this input file (an example of this input file is provided below).
natural BATCH < input-file-name > output-file-name
If you want to keep Natural reports only and hide all other output
(write output to the null device), set the profile parameter
MAINPR to
a valid printer number and assign an executable file to the corresponding
logical printer (device) in the parameter file, then specify:
natural BATCH < input-file-name > /dev/null
Any Natural reports are written to the executable file, whereas any screen output is suppressed. An input file must be specified even if Natural does not expect any input at all. In this case, also the null device may be used.
dlist program *^M fin^M
The input file for batch mode simulation must contain the same keystrokes that you would make in an interactive session.
The following keystrokes are used in the above sample input file:
| d | Opens the Direct Command window. |
| list program * | Executes the Natural system command which is used to list all programs. |
| ^M | Stands for the key combination CTRL+M (carriage return). Simulates the ENTER key. |
| fin | Executes the Natural system command which is used to terminate the Natural session. |
| ^M | Stands for the key combination CTRL+M (carriage return). Simulates the ENTER key. |