The DBLOG utility logs each Adabas command, DL/I or SYNC/ROLB call, SQL statement or VSAM call after it has been processed by the database system. Logging starts when you activate DBLOG and execute or run a Natural program.
This section covers the following topics:
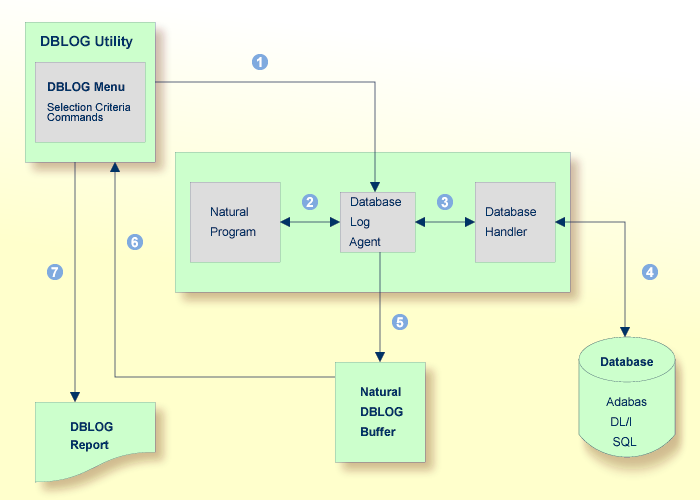
The following graphic illustrates the process flow when database calls are being logged from a Natural program with the DBLOG utility:
|
|
The logging of database calls (Adabas commands, DL/I and
SYNC/ROLB calls, SQL statements or VSAM calls) is activated by using the
corresponding DBLOG Menu function or the Natural system
command |
|
|
A Natural program issues a statement that initiates a database
call, for example, FIND or
READ.
|
|
|
The database log agent forwards the database call to the database handler. |
|
|
The database handler adapts the database call to the particular database (Adabas, DL/I, SQL or VSAM), retrieves the data requested by the database call and returns this data to the database log agent. |
|
|
The database log agent records in the Natural DBLOG buffer the data returned by the database handler and forwards this data to the Natural program. |
|
|
The report function of the DBLOG utility reads the data
recorded in the Natural DBLOG buffer and selects records according to the
selection criteria specified in the DBLOG Menu in
|
|
|
From the data records selected, the report function of the DBLOG utility generates a report that can be displayed, written to a work file or used for batch processing. |
The data logged by the DBLOG utility is recorded in the Natural DBLOG
buffer. The initial and maximum sizes of the buffer are determined by the
DSIZE
profile parameter described in the Parameter Reference
documentation.
If there is not enough space to hold the data in the DBLOG buffer,
Natural increases the DBLOG buffer size appropriately (possibly several times)
until the maximum size specified with the DSIZE profile
parameter is reached. After the maximum is reached, only the most recent log
data is held in the Natural DBLOG buffer.
If the DBLOG buffer size cannot be further increased due to lack of
storage, Natural issues a NAT7545 message that indicates
insufficient space for the DBLOG buffer. All data logged prior to this
lack-of-storage situation will be kept in the Natural DBLOG buffer and can be
displayed by using the TEST DBLOG command.
DBLOG can be used online or in batch mode. DL/I and SYNC/ROLB calls can be logged under CICS, under IMS TM or in batch mode. For further information on batch-mode processing, refer to Natural in Batch Mode described in the Operations documentation.
The logs recorded are displayed on the DBLOG Trace screen.
The DBLOG utility provides default settings for data recording. When
using the DBLOG Menu, you can specify selection criteria
for the commands, calls or statements to be logged and the information
displayed. The DBLOG Menu also provides functions for
activating or deactivating logging. You can also use the Natural system command
TEST DBLOG to control DBLOG execution.
The fields of the DBLOG
Trace screen, the DBLOG Menu and the Natural
system command TEST
DBLOG are explained in the relevant sections of the
DBLOG documentation.
The commands used to activate or deactivate DBLOG with the default DBLOG utility settings are described in the following section. See also TEST DBLOG Command for additional information.
 To activate or deactivate DBLOG for Adabas
To activate or deactivate DBLOG for Adabas
Enter the following Natural system command (toggle command):
TEST DBLOG
Oder:
Enter the following to activate:
TEST DBLOG ON
or
TEST DBLOG START
Enter the following to deactivate:
TEST DBLOG OFF
Oder:
In the DBLOG Menu, enter function code
B (to activate) or function code E (to
deactivate).
 To activate or deactivate DBLOG for DL/I
To activate or deactivate DBLOG for DL/I
Enter the following Natural system command (toggle command):
TEST DBLOG D
Oder:
Enter the following to activate:
TEST DBLOG D ON
or
TEST DBLOG D START
Enter the following to deactivate:
TEST DBLOG D OFF
Oder:
In the DBLOG Menu, enter function code
B (to activate) or function code E (to
deactivate).
 To activate or deactivate DBLOG for SQL
To activate or deactivate DBLOG for SQL
Enter the following Natural system command (toggle command):
TEST DBLOG Q
Oder:
Enter the following to activate:
TEST DBLOG Q ON
or
TEST DBLOG Q START
Enter the following to deactivate:
TEST DBLOG Q OFF
Oder:
In the DBLOG Menu, enter function code
B (to activate) or function code E (to
deactivate).
 To activate or deactivate DBLOG for VSAM
To activate or deactivate DBLOG for VSAM
Enter the following Natural system command (toggle command):
TEST DBLOG V
Oder:
Enter the following to activate:
TEST DBLOG V ON
or
TEST DBLOG V START
Enter the following to deactivate:
TEST DBLOG OFF
Oder:
In the DBLOG Menu, enter function code
B (to activate) or function code E (to
deactivate).
The following are example instructions for logging Adabas commands, DL/I calls, SQL statements or VSAM calls with selection criteria specified in the DBLOG Menu.
 To perform DBLOG with selection criteria
To perform DBLOG with selection criteria
Invoke the DBLOG Menu by entering one of the following Natural system commands:
For Adabas:
TEST DBLOG MENU
For DL/I:
TEST DBLOG D MENU
For SQL:
TEST DBLOG Q MENU
For VSAM:
TEST DBLOG V MENU
The DBLOG Menu appears.
In the DBLOG Menu, specify logging restrictions
and activate logging: complete the input fields and enter function code
B.
The message DBLOG started now is
displayed.
Execute a Natural program which contains Adabas commands, DL/I calls, SQL statements or VSAM calls.
Invoke the DBLOG Trace screen and deactivate logging by entering one of the following Natural system commands:
For Adabas:
TEST DBLOG
For DL/I:
TEST DBLOG D
For SQL:
TEST DBLOG Q
For VSAM:
TEST DBLOG V
or
TEST DBLOG V SHOW
The DBLOG Trace screen appears.
Clear the Natural DBLOG buffer and deactivate logging by entering one of the following Natural system commands:
For Adabas:
TEST DBLOG OFF
For DL/I:
TEST DBLOG D OFF
For SQL:
TEST DBLOG Q OFF
For VSAM:
TEST DBLOG V OFF
DBLOG terminates and the NEXT prompt appears.
See also the section TEST DBLOG Command for additional information.