This Dokument covers the following topics about Natural Advanced Facilities:
Natural Advanced Facilities consists of NATSPOOL, the
spooling and report management system. NATSPOOL manages Natural
program output, thus enabling the output (that is, a report) to be directed to
a physical printer. NATSPOOL also supports the Natural hardcopy
facility.
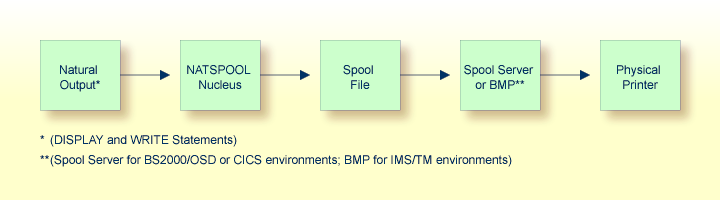
All reports are stored in the spool file. A report may be directed to the physical printer in one of the following ways:
automatically at the end of the program which generated the report; or
by using the corresponding NATSPOOL functions.
In BS2000 and IMS TM environments, the spool file must be an Adabas file. In CICS environments, it may be an Adabas file or a VSAM file (Natural for VSAM must be installed in this case).
This section explains the most important terms used in this documentation.
| Allocation Table | Describes an output destination and a form which can be assigned to a logical printer. The allocation table specifies the allocated physical printer(s) and optional parameters which are used to spool reports. |
| Application | Describes a library which can be used from the
NATSPOOL application.
|
| Calendar | Defines non-working and working days of a year. The calendar is used to compute the retention date for reports. A calendar can be assigned to logical printers. |
| Cluster | A group of logical printers. |
| Header Page | A user-designed page which can be assigned to an allocation. The reports spooled for this allocation will start with this page. |
| Logical Printer | Describes the characteristics of reports. The logical printer
is referenced as (rep) in a WRITE or
DISPLAY statement contained in a Natural program.
rep can be a value from 1 to
31.
|
| Message Header | Specific control sequences which are inserted at the beginning of each data block sent to a physical printer in a BS2000 environment (for example, to invoke a hardcopy function for printers connected to a terminal). |
| NTCC Table | Describes the replacements for user-defined and standard attributes. The replacements are used to rework report data for printer-dependent spool output. |
| Physical Printer | The alphanumeric name of a printer and the technical
information which is used to build up a connection and to spool the reports.
In a BS2000 environment, this is the station name defined in the network (PDN, TCP/IP) or the name of an RSO device. In a CICS environment, this is the TCT name. In an IMS TM environment, this is the LTERM name. |
| Queue | All reports created for the same allocation (Destination/Form). |
| Report | Natural program output identified by a job number. |
| Spool File | The physical file for all reports and objects. The database ID
and file number must be specified either in the Natural parameter module or
dynamically by using the Natural profile parameter
FSPOOL.
|
| User Profile | A set of logical printers to be used during a Natural session.
A user profile may be specified either in the Natural parameter module or
dynamically, by using the Natural profile parameter
NAFUPF.
If Natural Security is installed, the user profile can be specified for a library or user entry. |
The following illustration shows the logical connections between
NATSPOOL objects.
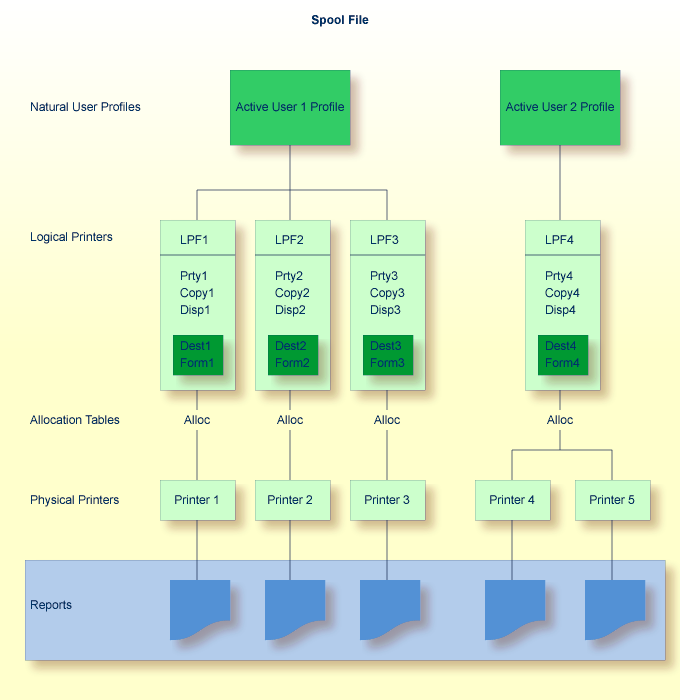
A maximum of 31 logical printers and one logical printer for hardcopy may be defined for one user.
A maximum of 16 physical printers may be allocated to each logical printer. In the above diagram, a total of 48 printers may be allocated to User 1, and a total of 16 printers to User 2.
Each logical printer requires 2 KB of storage, which is allocated at
Natural initialization. Natural executes a 2 KB GETMAIN
(REQM) command for each printer (n)
where
NTPRINT (1-n), AM=NAF
If the thread size (CICS), the roll-slot size (IMS TM) or the
MAXSIZE (openUTM) is not large enough, a Natural error
message is issued and Natural is not initialized.
The BUS (buffer usage
statistics) command can be used to obtain information on the sizes of the
buffers allocated by Natural Advanced Facilities. The following information is
provided:
PRINTnn
which contains the buffer for printer nn.
A WRITE (1) statement issued by User 1 causes the report
to be printed on Printer 1, a WRITE (2) statement causes the
report to be printed on Printer 2, and a WRITE (3) statement
causes the report to be printed on Printer 3.
A WRITE (1) statement issued by User 2 causes the report
to be printed on either Printer 4 or Printer 5, depending on which printer is
in FREE status. If both printers are in FREE status,
the first printer in the allocation table is used (for example, Printer 4 in
the above diagram).
 To start NATSPOOL
To start NATSPOOL
Enter the Natural system command
SYSPOOL.
The Natural Spool Administration menu appears with
the cursor positioned in the Command line.
Time 11:25:12 *** Natural Spool Administration *** Date 2002-10-22
User SAG M e n u File 7/411
Administration Information
10 Reports/Queues 20 Cross-Reference
11 Devices 21 Statistics
12 Abstracts 22 Look at Spool File
13 Applications 23 CALLNAT Handling
14 Change Spool File
Maintenance Control Functions
30 Spool File Properties 40 Check Spool File
31 Objects 41 Logging Data
32 Mass Update 42 Create Test Reports
33 Hardcopy Allocations 43 Delete Reports by Date
34 Transfer Objects
Enter function, mark with cursor, or press a PF-key.
Command ===>
Enter-PF1---PF2---PF3---PF4---PF5---PF6---PF7---PF8---PF9---PF10--PF11--PF12---
Help Exit Repor Devic Flip Abstr Appli Cross Stati Look Canc |
The individual NATSPOOL functions are described in detail
in individual sections of this documentation.
 To invoke a function, proceed in any of the following ways
To invoke a function, proceed in any of the following ways
Enter a command (and
object type) in the Command line.
Oder:
enter a number in the
Command line.
Oder:
select a function with the cursor.
Oder:
press the PF
key assigned to a function.
To invoke a function, enter a command (and object type) in the Command line.
For example, to display the device status (Function 11), enter
DISPLAY DEVICE in the Command line.
To display a list of available commands, enter an asterisk (*) or a
question mark (?) in the Command line. To display a list of all
available object types for a specific command, mark this command in the list
with any character.
On a selection screen or window, each function is prefixed by a number.
To invoke a function, enter the number of this function in the Command
line. For example, to invoke the function Layout of Spool
File, enter 30 in the Command line. The
Layout of Spool File window will then appear.
In the Layout of Spool File window, each function
is prefixed by a number and can also be invoked by entering the corresponding
number. For example, to invoke the function Display Last
Modification, enter 8 in the Command line of this
window.
If you know the number of a function which is listed in a window, you
can also directly invoke this function. To do so, concatenate the individual
numbers with a period in between. For example, to invoke the above mentioned
function Display Last Modification directly, enter
30.8 in the Command line.
To select a function with the cursor, place the cursor on the number of a function and press Enter.
Most functions are assigned to PF keys.
The PF-key lines at the bottom of the screen indicate which function is assigned to which PF key. To invoke a function, simply press the PF key assigned to this function.
For example, on the NATSPOOL menu, the function
Reports/Queues is assigned to PF4.
The following PF-key assignments apply for most NATSPOOL
screens:
| Key | Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| PF1 | Help | Invoke the online help facility. |
| PF2 | Menu | Invoke the NATSPOOL menu.
|
| PF3 | Exit | Leave the current function and apply all modifications made. |
| PF6 | Flip | Switch to display of keys PF13 to PF24 and back. |
| PF12 | Cancel | Leave the NATSPOOL application.
|
| PF13 | %H | Hardcopy function. |