The SYSCP utility is used to obtain information on code pages available in the current Natural Windows environment.
This helps avoid problems that can occur when a code page is not defined in Natural or when source objects are converted to an incorrect code page or Unicode format.
For detailed information on how Natural supports Unicode and code pages and Unicode-specific items, see the descriptions and presentations in the SYSEXV Utility and Related Topics below.
The SYSCP Utility - Code Page Information documentation covers the following topics:
Unicode and Code Page Support: Natural documentation
Unicode: Unicode Consortium at web site at http://www.unicode.org/
ICU: International Components for Unicode at web site http://site.icu-project.org/
ICU: Converter Explorer documentation at web site http://demo.icu-project.org/icu-bin/convexp
Instructions for invoking and terminating the SYSCP utility are provided in the following section.
 To invoke the SYSCP utility
To invoke the SYSCP utility
Enter the following system command:
SYSCP
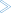
A SYSCP Utility - All Code Pages window similar to the example below appears:
This window is opened by the function, which is executed by default when you invoke the SYSCP utility.
All SYSCP utility functions are provided in the menu. They are explained in the remainder of this documentation.
The menu provides online help information about the SYSCP utility.
 To terminate SYSCP
To terminate SYSCP
Choose the standard Windows close function.
Or:
From the menu, choose
.
This function opens the SYSCP Utility - All Code Pages window, which provides a list of all code pages available in your current Natural Windows environment. The list is sorted in ascending order by code page name.
The columns contained in the window and the options provided for each code page listed are described in the following section:
The columns contained in the list of code pages are described in the following section:
This column lists the IANA name of the code page.
The IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) name is the
standard and unambiguous name of the code page. The IANA name is used by
Natural as the default code page name (see the CP profile parameter
described in the Parameter Reference documentation) for
conversions to and from Unicode. The IANA name is returned by the
*CODEPAGE
system variable (see the System Variables
documentation).
If no IANA name is specified, the internal ICU name is listed
instead. This is indicated by ICU Name:, which is used as a prefix
for all ICU names.
You can use the option of the context menu to display all code page names specified for a code page.
This column displays a three-letter code, which represents the attributes of the code page: see the Show Attributes option of the context menu for details.
This column indicates the code units (minimum and maximum numbers of bytes) assigned to the code points.
For the code page selected, you can use the context menu to obtain further information on the code page or to test code-point assignments of characters.
 To open the context menu
To open the context menu
From the code page list, select the code page required.
Click the right mouse button.
Or:
Press SHIFT+F10.
The context menu appears.
The options provided in the context menu are described in the following section:
This option can be used to display the attributes of the code page selected. Attributes are character sets and languages supported by the code page. Attributes and codes that represent each attribute are listed in the following table:
| Code | Attribute |
|---|---|
A |
ASCII character set. |
E |
EBCDIC character set. |
D |
Double-byte or multi-byte character set for languages such as Japanese and Chinese. |
S |
Single-byte character set. |
R |
Right-to-left direction. |
L |
Left-to-right direction for bi-directional languages such as Arabic and Hebrew. |
This option can be used to display all names that can be specified for the code page selected:
IANA name
If not specified, this field is blank.
ICU name
Alias names
One or more alternate names used for the code page.
You can test code-point conversion from a selected code page to
the default code page (value of *CODEPAGE)
defined with the CP profile
parameter:
from an alphanumeric character string to Unicode code points and vice versa, or
from hexadecimal values to Unicode code points and vice versa.
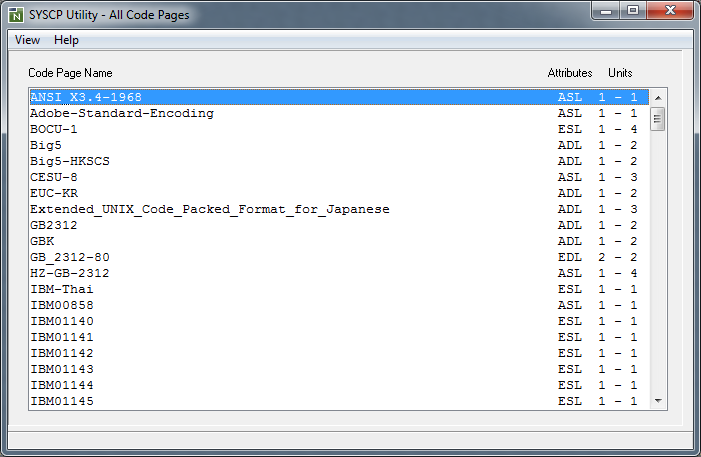
The test conversion dialog box of a code page (here:
windows-1250) shown in the example below contains the following
information:
the code page name,
the byte units (minimum and maximum numbers of bytes) assigned to the code points,
an alphanumeric character string and its equivalent hexadecimal values and
the corresponding Unicode code points.
 To convert a character or code point
To convert a character or code point
Enter a literal string in the Alphanumeric box.
Or:
Enter hexadecimal values in one or more
Hexadecimal boxes.
Or:
Enter Unicode code points in one or more
Unicode boxes.
The boxes not used for input are deactivated.
Choose or press ENTER.
The value entered in one of the boxes is converted to its equivalent code points or literal string.
Choose OK to close the Test Conversion dialog box.
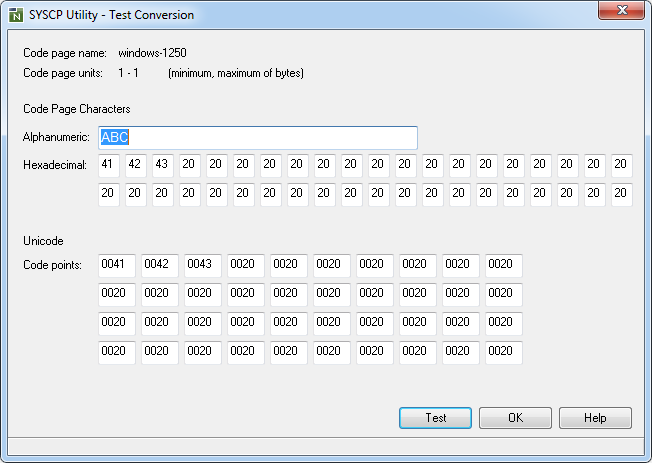
This function is used to display the Unicode properties for a
Unicode character or a Unicode code point as shown in the example of the letter
A below:
The function can also be used to view the code point assigned to a character.
 To display the code-point assignment and Unicode
properties
To display the code-point assignment and Unicode
properties
In the Unicode character box, enter the character whose code point and properties you want to view.
Or:
In the Unicode code point box, enter
the code point whose character and properties you want to view.
Choose or press ENTER.
The value entered in one of the boxes is converted to its equivalent character or code point whose Unicode properties are displayed in the window.
A Unicode property shown in boldface letters denote that this property applies to the character such as Alphabetic in the example above.
For explanations of the Unicode character properties displayed in the window, refer to Unicode Consortium's documentation Unicode Character Database at web site http://www.unicode.org/Public/4.1.0/ucd/UCD.html.
This function provides information on the current ICU and Unicode versions.