Data defined in a global data area (GDA) can be shared by multiple programs, external subroutines and helproutines.
Any modification of a data element value in a global data area affects all Natural objects that reference this global data area. Therefore, if you change the source of a global data area, you have to stow all previously created Natural objects that reference this global data area once more. The sequence in which objects are stowed is important. You must first stow the global data area and then the program. If you stow the program first and then the global data area, the program cannot be stowed because new elements in the global data area cannot be found.
You will now create a global data area which will be shared by your program and an external subroutine that you will create later. As the basis for your global data area, you will use some of the information from the local data area you have just created.
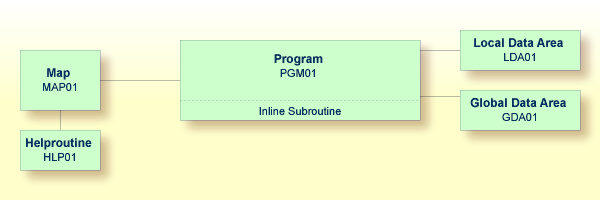
When you have completed the exercises below, your sample application will consist of the following modules:
This document contains the following exercises:
You can create a new data area from an existing data area by editing it
and saving it under a different name and with a different type. The original
data area remains unchanged, and the new data area can be edited. Since the
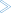
fields #NAME-START and #NAME-END are not required in
the global data area, you will remove them.
Note:
It is also possible to create a global data area by
choosing from the
menu.
 To create the global data area
To create the global data area
Return to your local data area.
From the menu, choose .
The Save As dialog box appears.
Specify "GDA01" as the name for the global data area.
Make sure that the library is selected which also contains your program (that is: the TUTORIAL node).
From the Type drop-down list box, choose Global.
Choose the button.
The new name and type are now shown in the title bar of the editor window. In the library workspace, the new global data area is shown in the Global Data Areas node.
Press CTRL and select the following fields:
#NAME-START
#NAME-END
From the context menu, choose .
Or:
Press DEL.
The global data area should now look as follows:
Stow the global data area.
The global data area can now be found by your program and by the external subroutine that you will define later.
Close the editor window for the global data area.
The fields contained in the global data area are no longer required in
the local data area. Therefore, you will now remove all fields except
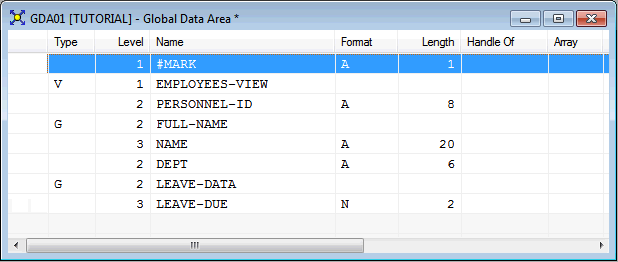
#NAME-START and #NAME-END from the local data
area.
 To remove the fields
To remove the fields
In the library workspace, select the local data area
LDA01, and from the context menu, choose
Or:
In the library workspace, double-click the local data area
LDA01.
In the resulting data area editor,
select all fields except #NAME-START and
#NAME-END.
From the context menu, choose .
Or:
Press DEL.
Stow the modified local data area.
The local data area should now look as follows:
Once a global data area has been stowed, it can be referenced by a Natural program.
You will now change the DEFINE DATA statement in your
program so that it also uses the global data area that you have just
defined.
Leave the data area editor open in the background.
 To use the global data area in your program
To use the global data area in your program
Return to the program editor.
Insert the following in the line above LOCAL USING
LDA01:
GLOBAL USING GDA01
A global data area must always be defined before a local data area. Otherwise, an error occurs.
Your program should now look as follows:
DEFINE DATA
GLOBAL USING GDA01
LOCAL USING LDA01
END-DEFINE
*
RP1. REPEAT
*
INPUT USING MAP 'MAP01'
*
IF #NAME-START = '.' THEN
ESCAPE BOTTOM (RP1.)
END-IF
*
IF #NAME-END = ' ' THEN
MOVE #NAME-START TO #NAME-END
END-IF
*
RD1. READ EMPLOYEES-VIEW BY NAME
STARTING FROM #NAME-START
ENDING AT #NAME-END
*
IF LEAVE-DUE >= 20 THEN
PERFORM MARK-SPECIAL-EMPLOYEES
ELSE
RESET #MARK
END-IF
*
DISPLAY NAME 3X DEPT 3X LEAVE-DUE 3X '>=20' #MARK
*
END-READ
*
IF *COUNTER (RD1.) = 0 THEN
REINPUT 'No employees meet your criteria.'
END-IF
*
END-REPEAT
*
DEFINE SUBROUTINE MARK-SPECIAL-EMPLOYEES
MOVE '*' TO #MARK
END-SUBROUTINE
*
END
Run the program.
To confirm that the results are the same as before (when the
DEFINE DATA statement did not reference a global data area), enter
"JONES" as the starting name and press
ENTER.
Press ESC to close the output window.
Stow the program.
You can now proceed with the next exercises: External Subroutines.