You can generate single or multiple stub subprograms (interface objects)
in either online or batch mode by using the Stub
Mass Generation function or the command SYSRPC
SGMASS. Either method will invoke a window that
indicates the send and receive lengths required by the specified
subprogram(s).
Using the command or function, field attributes will be generated as described in Specifying Parameters in the section Generating Single Stubs with Parameter Specification.
You generate stub subprograms from subprograms.
This section contains information on:
This section provides instructions for generating single or multiple stub subprograms (interface objects) by using the Stub Mass Generation function.
![]() To perform the Stub Mass Generation function
To perform the Stub Mass Generation function
In the SYSRPC - Remote Procedure Call window, from the Tools menu, choose Stub Mass Generation.
Or:
In the SYSRPC - Remote Procedure Call window,
press CTRL+F6.
An SYSRPC - Input for Stub Mass Generation dialog box similar to the example below appears:
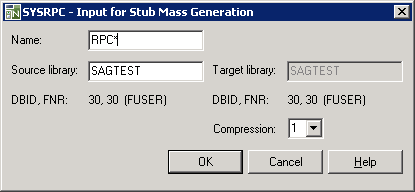
In the Name text box, enter the name of the stub subprogram to be generated or specify a range of names. The text box is preset to asterisk (*), indicating all subprograms. For valid entries, see Name in Name Specification and Compression.
The name(s) of the stub subprogram must be identical to the name(s)
of the remote CALLNAT program(s).
Important:
If you do not specify a name, with few exceptions (see
below), all subprograms in the current library will be converted to stub
subprograms.
If required, in the Source library text box, enter the name of the library that contains the subprogram(s) from which you want to generate the stub subprogram(s). The text box is preset to the name of the current library.
Target library is a read-only text box that contains the name of the current library into which the stub subprograms are generated.
DBID, FNR are non-modifiable text boxes that
display the database ID (DBID), the file number (FNR) and the type of Natural
file (FNAT = system, FUSER = user) for the source and
target libraries entered.
From the Compression drop-down list box, select compression type 0, 1 or 2 (default is 1); see Using Compression described in Operating a Natural RPC Environment in the Natural Remote Procedure Call (RPC) documentation.
Choose OK.
The SYSRPC - Stub Generation in Library window appears for the library specified (here: SAGTEST) with the tabbed pages Summary and Details.
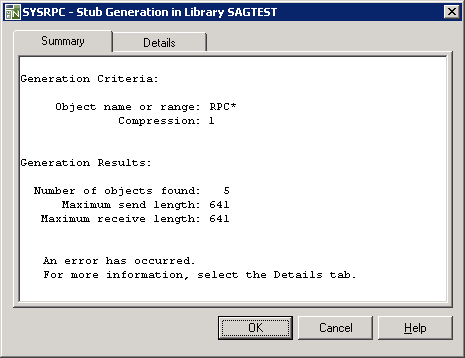
The Summary page contains a report that indicates the send and receive length requirements of the subprograms (objects) selected as shown in the following example:
The report is organized in two sections, which contain the following information:
Generation Criteria:
The criteria based on which the stub subprograms were generated: a
single object name or a range of names (here: RPC*) and the
compression (here: 1).
Generation Results:
The number of objects selected for the stub generation.
The maximum buffer sizes all generated stub subprograms require for sending and receiving data from the client.
If the stub generation fails, a message at the bottom of the page indicates this error.
The Details page contains a list of all generated stub subprograms similar to the example shown below:
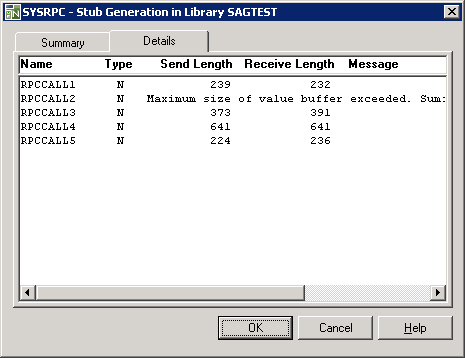
The list is sorted in alphabetical order of object names (Name column) and contains information on the following:
the type of object from which the stub subprogram was generated
(here: N for subprogram) in the Type column,
the buffer sizes each object requires for sending (Send Length) and receiving (Receive Length) data from the client,
and a possible comment on each stub generation in the Message column.
If the stub generation fails, an error message is displayed next to
the objects affected (here: RPCCALL2).
You can enter the command SYSRPC
SGMASS in the Command line for generating stub subprograms
(interface objects) online.
The report produced by the command corresponds to the report described for the Stub Mass Generation function.
The syntax that applies to SYSRPC SGMASS is
illustrated in the diagram below:
SYSRPC SGMASS
[name]
[compression]
|
The syntactical items name and compression are explained in the section Name Specification and Compression.
You can specify the objects (subprograms) to be selected for stub generation and the type of compression to be used:
You can specify an object name or a range of names. The specification of an object name or a range of names is optional.
| Warning: If you do not specify an object name or a range of names, with few exceptions (see below), all subprograms in the current library will be converted to stub subprograms. |
Valid name specifications are described below where value is any combination of one or more alphanumeric characters:
| Input | Objects Selected |
|---|---|
| * |
All subprograms. This is the default setting. |
| value | A subprogram with a name equal to value. |
| value* |
All subprograms with names that start with value. |
| value | All subprograms with names less than or equal to value. |
| value | All subprograms with names greater than or equal to value. |
In the Natural system library SYSRPC, SYSRPC
SGMASS exempts from stub generation all subprograms with names
that start with any of the following prefixes: RDS, RPC, NAT, NAD or NSC.
In user libraries, SYSRPC SGMASS exempts
from stub generation the subprogram NATCLTGS.
You can specify any of the following compression types: 0,
1, 2. The specification of compression is optional.
The default type used for stub generation is 1.
See also Using Compression described in Operating a Natural RPC Environment in the Natural Remote Procedure Call (RPC) documentation.