The utility SYSEXT is used to locate and test Natural Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) contained in the current system library SYSEXT either in a local Windows environment or in a remote environment located on a Windows, a UNIX, an OpenVMS or a mainframe platform.
A Natural API is a Natural subprogram (cataloged object) that is used for accessing and possibly modifying data or performing services that are not accessible by Natural statements. Natural APIs refer to Natural, a subcomponent or a subproduct.
The SYSEXT Utility - Natural Application Programming Interfaces documentation covers the following topics:
Application Programming Interfaces - Natural Security documentation
SYSAPI - APIs of Natural Add-on Products - Utilities documentation
Natural Functions - System Functions documentation
The Enable Plug-ins option must be selected. This option is selected by default. For details, see Workspace Options in the section Setting the Options in the Using Natural Studio documentation.
For each Natural API, the utility SYSEXT provides a functional description, one example program and API-specific keywords.
The following diagram is an overview of the Natural objects and major features SYSEXT provides:
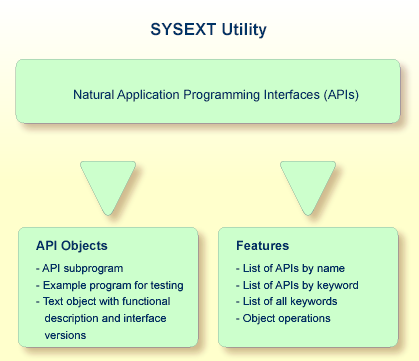
The types of Natural object typically provided for each Natural API are listed in the following section. Additional objects that might exist for a particular API are not covered.
All API-related objects are contained in the library SYSEXT on the system file FNAT.
In the following table, nnnn denotes the 4-digit number to identify the API as well as the corresponding example program and text object.
| Object Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| USRnnnnN | The API subprogram (cataloged object) that performs the designated function. |
| USRnnnnP |
An example program (source object) that can be used to test the effect of the API. The example program invokes the corresponding subprogram USRnnnnN. |
| USRnnnnT |
A text object that contains a description of the corresponding API. The description comprises purpose, function and calling conventions of the API and relevant keywords, category and interface versions. |
Caution:
Do not modify the source objects EXT-XML1 and
EXT-XML2. They are required for configuring the SYSEXT utility and intended for
Software AG internal use only.
This section provides instructions for invoking and terminating the SYSEXT utility.
![]() To invoke SYSEXT
To invoke SYSEXT
Enter the following system command:
SYSEXT
Or:
From the menu, select
.
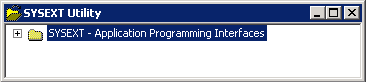
When invoking SYSEXT, the plug-in for the utility SYSEXT is activated and the SYSEXT utility window appears with the root node SYSEXT - Application Programming Interfaces as shown in the example below:
![]() To restart SYSEXT
To restart SYSEXT
If you want to restart SYSEXT during the current Natural session, as an alternative to the start methods mentioned above, from the toolbar, choose the following icon:
![]()
This icon appears after initially invoking SYSEXT, when the plug-in for the utility SYSEXT is activated.
![]() To terminate SYSEXT
To terminate SYSEXT
Choose the standard Windows close function.
This section describes the nodes and items contained in the tree view of the SYSEXT utility window.
If you expand all tree nodes, the tree looks similar to the example below:
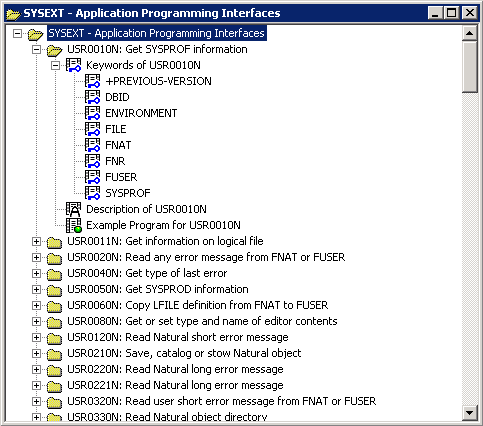
Each Natural API is represented by an API node that contains the example program, description and keywords that relate to this API. The API node name consists of the name of the API subprogram (USRnnnnN) and a brief description of its functional purpose. The nodes are sorted by API names.
The following items are provided in an API node:
| Item | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Keywords | All keywords relevant to the API. See also the functions Select Keyword and List All Keywords in Performing SYSEXT Utility Functions. |
| Description | A text object (USRnnnnT) that contains a description of the API. The description comprises purpose, function and calling conventions of the API and keywords relevant to the API. |
| Example Program | An example program (source object USRnnnnP) of how to invoke the API. |
The SYSEXT utility functions can be used to perform operations on API-specific text objects (descriptions) and example programs or find APIs relevant to a current task by specifying a keyword.
Object operations include functions such as List, Open and Execute, which correspond to the standard functions available when maintaining or executing a Natural object of the type text or program. These functions can be performed by using the context menu associated with each object. For details of these functions, refer to the relevant sections in the Using Natural Studio documentation.
The section below covers the following topics:
This function is used to list APIs by keyword.
![]() To list APIs by keyword
To list APIs by keyword
Select the root node SYSEXT - Application Programming Interfaces, open the context menu and choose or press SHIFT+K.
The Select Keyword window appears.
From the drop-down list box, select a keyword as shown in the example below:
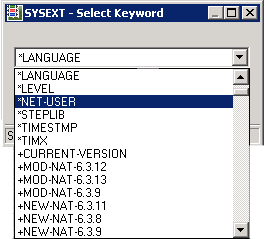
Choose the button.
The root node SYSEXT - Application Programming Interfaces with Keyword appears for the selected keyword.
The nodes of all APIs to which the specified keyword applies are
displayed as shown in the example of keyword *LANGUAGE below:

If desired, to return to the display of all API nodes (default
setting), in the Select Keyword window, select the
asterisk (*).
This function is used to list all keywords for the APIs available in the current system environment.
![]() To list all API keywords
To list all API keywords
Select the root node SYSEXT - Application Programming Interfaces, open the context menu and choose or press SHIFT+A.
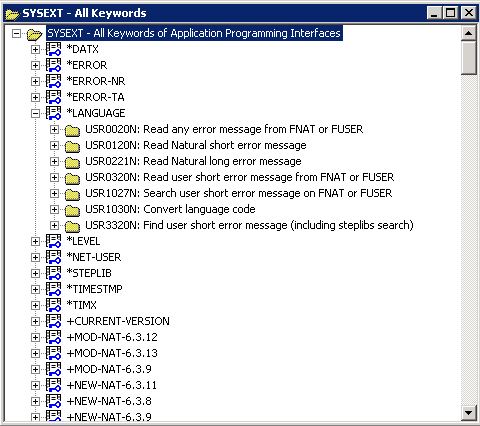
The All Keyword window appears as an additional window with the root node SYSEXT - All Keywords of Application Programming Interfaces.
A list of all keywords is displayed as shown in the example below:
This function updates API information in the tree view using the data from the objects contained in the current library SYSEXT. The refresh is only required if an API description or a keyword was modified or if a text object was removed.
Note:
Do not modify the source objects EXT-XML1 and EXT-XML2.
They are required for configuring the SYSEXT utility and intended for Software
AG internal use only.
![]() To refresh API information
To refresh API information
Select the root node SYSEXT - Application Programming Interfaces, open the context menu and choose or press SHIFT+R.
A Refresh window appears.
If you access a remote environment on a mainframe, you must specify
the parameter SORT in the map environment settings as
indicated below:
SORT=(WRKSIZE=50)
For details on mapping a server, see
Accessing a Remote Development
Environment in the documentation Remote
Development Using SPoD. For details on SORT,
refer to the Parameter Reference of Natural for
Mainframes.
Choose the button to confirm the refresh or choose to abort the operation.
Interface versions can be seen as a collection of APIs with (almost) the same functionality but with differently extended parameter specifications. Thus, they cover a development cycle to be kept explicit for sake of compatibility (of later versions with earlier versions).
If an API has interface versions, they are displayed in the
corresponding text object USRnnnnT. Interface
versions are ordered within a list according to the version they belong to. The
rightmost element belongs to the current version. This status is expressed by
the reserved keyword +CURRENT-VERSION. All other elements belong
to a previous version and are marked with the reserved keyword
+PREVIOUS-VERSION. APIs without interface versions are called
unique.
APIs with interface versions are displayed intensified on the menu.
Reserved keywords refer to meta information on APIs, for example the
Natural version in which an API has been added. Reserved keywords always start
with a plus sign (+). See the table below for a description:
| Reserved Keyword | Description |
|---|---|
| +CURRENT-VERSION | The current version of an API with interface versions (see Interface Versions). |
| +PREVIOUS-VERSION | A previous version of an API with interface versions (see Interface Versions). |
| +NEW-PROD-version | An API that has been added to a specific product
in a specific version. For example, +NEW-NAT-6.3.11 refers to an
API that has been added to the product Natural in version
6.3.11.
|
| +MOD-PROD-version | An API that belongs to a specific product and has
been modified in a specific version. For example, +MOD-NAT-6.3.12
refers to an API that belongs to product Natural and has been modified in
version 6.3.12.
|
If you want to use a Natural API contained in the system library SYSEXT, perform one of the following steps:
Define the system library SYSEXT in the system file FNAT as a steplib library for the user library that contains the Natural objects that use this API. Thus, no API-specific actions are required when upgrading your Natural version.
Copy the required API to the system library SYSTEM in the system file FNAT. Thus, you only need to check a single library for APIs when upgrading your Natural version.
Copy the required API to the system library SYSTEM in the system file FUSER (not recommended).
Copy the required API to the user library (or one of its steplibs) in the system file FUSER which contains the Natural objects that use this API (not recommended).
An API can only be used in the Natural version with which it is delivered. It is strongly recommended to store the APIs only in the FNAT system file. This will ensure that the right version is always executed.
![]() To make use of an interface
To make use of an interface
In the calling program, use the DEFINE DATA statement to
specify the parameters listed in the text object
USRnnnnT of that API. In the example
program USRnnnnP, the parameters are
defined within the DEFINE DATA
LOCAL statement. Alternatively, you can specify the
parameters outside the calling program in a separate LDA (Local Data Area) or
PDA (Parameter Data Area), with a DEFINE DATA LOCAL USING
statement referencing that data area.
Enter the following statement:
CALLNAT 'USRnnnnN' parameters
For further information, see the CALLNAT statement in the Statements documentation.
Note:
Non-standard usage is always documented in the respective text
object USRnnnnT.
The following table gives an overview of available APIs and their function.
Notes:
PRD are listed and documented
separately in the section Application Programming Interface
in the administration part of the Predict
documentation.
| Interface | Description | Product |
|---|---|---|
| USR0010N | Get SYSPROF information | NAT |
| USR0011N | Get information on logical file | NAT |
| USR0020N | Read any error message from FNAT or FUSER | NAT |
| USR0040N | Get type of last error | NAT |
| USR0050N | Get SYSPROD information | NAT |
| USR0060N | Copy LFILE definition from FNAT to FUSER | NAT |
| USR0080N | Get or set type and name of editor contents | NAT |
| USR0120N | Read Natural short error message | NAT |
| USR0210N | Save, catalog or stow Natural object | NAT |
| USR0220N | Read Natural long error message | NAT |
| USR0221N | Read Natural long error message | NAT |
| USR0320N | Read user short error message from FNAT or FUSER | NAT |
| USR0330N | Read Natural object directory | NAT |
| USR0360N | Modify user short error message on FNAT or FUSER | NAT |
| USR0420N | Read user long error message from FUSER | NAT |
| USR0421N | Maintain user long error message on FUSER | NAT |
| USR0500N | Define title of window | NAT |
| USR0600N | Get program level information | NAT |
| USR0610N | Get error information on last database call | NAT |
| USR0620N | Convert string into ASCII or EBCDIC code | NAT |
| USR0622N | Reset error counter in ON ERROR statement block | NAT |
| USR1002N | Save or restore Natural environment parameters | NAT |
| USR1005N | Get information on certain Natural session parameters | NAT |
| USR1009N | Convert system variable *TIMESTMP into numeric variable | NAT |
| USR1011N | Check name for wildcard or asterisk notation | NAT |
| USR1012N | Get dynamic error message parts from the last error | NAT |
| USR1013N | Display current character set | NAT |
| USR1016N | Get error level for error in nested copycodes | NAT |
| USR1020N | Add user short error message to FUSER | NAT |
| USR1021N | Check name for wildcard or asterisk notation | NAT |
| USR1022N | Get type of database | NAT |
| USR1023N | Convert date and time format | NAT |
| USR1025N | Maintain definition of multiple steplibs | NAT |
| USR1026N | Get information on RETURN data | NAT |
| USR1027N | Search user short error message on FNAT or FUSER | NAT |
| USR1028N | Convert bits and bytes | NAT |
| USR1029N | Get type of Natural object | NAT |
| USR1030N | Convert language code | NAT |
| USR1031N | Check Natural object name | NAT |
| USR1032N | List cataloged Natural objects with type | NAT |
| USR1033N | Find DBID and FNR of a cataloged DDM | NAT |
| USR1034N | Get NTTF file table with translated DBID and FNR | NAT |
| USR1035N | Maintain objects using the Software AG editor engine | NAT |
| USR1036N | Maintain user profile of the Software AG editor | NAT |
| USR1038N | Get platform-specific information | NAT |
| USR1039N | Modify the clipboard | NAT |
| USR1040N | Get or set profile parameter UDB | NAT |
| USR1041N | Install error transaction program (*ERROR-TA) | NAT |
| USR1042N | Get or set value of UPDATE command | NAT |
| USR1043N | Perform Adabas direct calls | NAT |
| USR1048N | Modify PF-key labels | NAT |
| USR1050N | Get or set work file name | NAT |
| USR1052N | Send a command to the operating system | NAT |
| USR1053N | Get the value of an environment variable | NAT |
| USR1054N | List libraries | NAT |
| USR1055N | List objects in a library | NAT |
| USR1056N | List DDMs on the FDIC file or in a library | NAT |
| USR1057N | Read a Natural source code into an array | NAT |
| USR1058N | Read a DDM source code into an array | NAT |
| USR1059N | Initialize the Natural Reporter interface | NAT |
| USR1060N | Terminate the Natural Reporter interface | NAT |
| USR1061N | Open an existing report layout | NAT |
| USR1062N | Close a report | NAT |
| USR1063N | Select printer to print a report | NAT |
| USR1064N | Print a report | NAT |
| USR1065N | Preview a report | NAT |
| USR1066N | Enable or disable the Natural message 'Executing ...' | NAT |
| USR1067N | Check Natural library name | NAT |
| USR1068N | Maintain the number of DBMS calls, MAXCL and MADIO parameters | NAT |
| USR1069N | Get or set a printer configuration | NAT |
| USR1071N | Set credentials for RPC server | RPC |
| USR1072N | Get command ID of a retain set | NAT |
| USR2001N | Get information on last error | NAT |
| USR2004N | Get information on logical file | NAT |
| USR2005N | Read internal file translation table | NAT |
| USR2006N | Get information from error message collector | NAT |
| USR2007N | Get or set data for RPC default server | RPC |
| USR2009N | Get dynamic error message parts from the last error | NAT |
| USR2010N | Get error information on last database call | NAT |
| USR2011N | Get or set work file name | NAT |
| USR2012N | Get system variable *NET-USER | NAT |
| USR2013N | Get SYSPROF information | NAT |
| USR2014N | Maintain objects using the Software AG editor engine | NAT |
| USR2018N | Read Natural object directory | NAT |
| USR2019N | Read or save Natural source code from/to the source area | NAT |
| USR2023N | Get type of database | NAT |
| USR2026N | Get TECH information | NAT |
| USR2027N | Define wait interval for current session | NAT |
| USR2030N | Get dynamic error message parts from the last error | NAT |
| USR2031N | Get SYSPROD information | NAT |
| USR2032N | Support commit for CLOSE CONVERSATION | RPC |
| USR2035N | Get or set parameters for SSL support | RPC |
| USR2036N | Convert system variable *TIMESTMP into numeric variable | NAT |
| USR2071N | Support EntireX Security on client side | RPC |
| USR2072N | Support EntireX Security on server side | RPC |
| USR2073N | Ping or terminate an RPC server | RPC |
| USR2074N | Set new password for Natural Security user in RPC context | RPC |
| USR2075N | Terminate EntireX Broker service | RPC |
| USR2076N | Get or set RPC TIMEOUT value | RPC |
| USR3013N | Get SYSPROF information | NAT |
| USR3025N | Maintain definition of multiple steplibs | NAT |
| USR3320N | Find user short error message (including steplibs search) | NAT |
| USR4003N | Get Natural stack information | NAT |
| USR4004N | Get dynamic Natural profile parameters at session start | NAT |
| USR4005N | Read all current PF-key settings | NAT |
| USR4007N | Get or set profile parameter SYNERR | NAT |
| USR4008N | Set library for RPC execution | RPC |
| USR4009N | Set parameters for EntireX | RPC |
| USR4010N | Get runtime settings of RPC server | RPC |
| USR4011N | Create A20 hash value for variable input | NAT |
| USR4012N | Set application error on RPC server | RPC |
| USR4025N | Maintain definition of multiple steplibs in Natural Security | NAT |
| USR4201N | Maintain data area sources | NAT |
| USR4206N | List objects in a library | NAT |
| USR4208N | Read or write a Natural resource | NAT |
| USR4209N | Get short name of subroutine | NAT |
| USR4210N | Perform base64 conversion of alphanumeric and binary bytes | NAT |
| USR4212N | Analyze data area | NAT |
| USR4215N | Get list of resources in a Natural library | NAT |
| USR4217N | Send data to Optimize for Infrastructure | NAT |
| USR4218N | Get information on Natural Development Server | NDV |
| USR4220N | Perform base64 conversion of alphanumeric and binary bytes | NAT |
| USR5001N | Turn results window on/off | NAT |
| USR5002N | Maintain bitmaps and icons for a tab | NAT |
| USR5003N | Maintain context menus for a tab | NAT |
| USR5004N | Maintain general layout of a tab | NAT |
| USR5005N | Get or set active tab of results window | NAT |
| USR5006N | Define UpdateCommandHandler and CommandHandler for tab | NAT |
| USR5007N | Maintain checked and enabled state for a context menu item | NAT |
| USR5008N | Maintain columns of a tab | NAT |
| USR5009N | Get number of columns or rows of a tab | NAT |
| USR5010N | Maintain default column width and specific column width | NAT |
| USR5011N | Maintain rows of a tab | NAT |
| USR5012N | Get or set data of a tab | NAT |
| USR5013N | Maintain checked state of row(s) | NAT |
| USR5014N | Maintain selected row(s) | NAT |
| USR5015N | Get or set row of focus; scroll row into visible area | NAT |
| USR5016N | Get or set data for UpdateCommandHandler and CommandHandler | NAT |
| USR5017N | Copy selected row(s) to clipboard | NAT |
| USR6001N | Call external XSLT processor | NAT |
| USR6002N | Get the current values of internal counters | NAT |
| USR6003N | Maintain type/name/library of program editor active window | NAT |
| USR6004N | Access the program editor active window | NAT |
| USR6005N | Get information on program editor active window | NAT |
| USR6006N | Get path to system file | NAT |
| USR6007N | Get information on last error in Tamino database | NAT |
| USR6008N | Get data of object in source area | NAT |
| USR6009N | Maintain Natural buffer pool | NAT |
| USR6201N | Write source to Natural Development Server | NDV |
| USR6202N | Get or set value of an environment variable | NAT |
| USR6203N | Maintain a resource in a Natural library | NAT |
| USR6204N | Set profile parameter PROGRAM | NAT |
| USR6303N | Get Natural stack information | NAT |
| USR6304N | Get or set reliable state for RPC execution | RPC |
| USR6305N | Commit or rollback reliable RPC messages | RPC |
| USR6306N | Get status of UOWs of current EntireX Broker user | RPC |
| USR6307N | Get or set Request Document timeout value (RQTOUT) | NAT |
| USR6308N | Retrieve system files defined in Natconf.cfg | NAT |