This document covers following topics:
The Natural Web I/O Interface client uses the Java Logging API. In case of problems with the Natural Web I/O Interface client, you can enable logging and thus write the logging information to an output file. This should only be done when requested by Software AG support.
You configure logging using the configuration tool.
Note:
Some logging information is also written to the console, regardless
of the settings in the configuration file. The console shows the information
which is normally provided by the logging levels SEVERE,
WARNING and INFO.
The name of the configuration file is natlogger.xml. The path to this file depends on the application server.
JBoss Application Server
<application-server-install-dir>server/default/deploy/naturalunicode.rar/log
Sun Java System Application Server
<application-server-install-dir>/domains/domain1/applications/j2ee-modules/naturalunicode/log
On Sun Java System Application Server, the logging information is written to the normal server log. That is because Sun Java System Application Server uses the same Java Logging API as the Natural Web I/O Interface client. You can thus use a powerful Sun Java System Application Server tool, the Log Viewer, for analyzing the log. The Log Viewer is started from the web-based Admin Console; for further information, see the documentation of the Sun Java System Application Server.
We recommend that you disable the file handler in the configuration file natlogger.xml. Thus, you avoid that the logging information is written to two different log files (that is, the normal server log and the output file defined in natlogger.xml).
JBoss Application Server uses a different logging API (log4j). In this case, we recommend that you enable the file handler in the configuration file natlogger.xml.
The content of the configuration file natlogger.xml is managed using the Logging Configuration page of the configuration tool.
![]() To invoke the Logging Configuration page
To invoke the Logging Configuration page
In the frame on the left, choose the Logging Configuration link.
The Logging Configuration page appears in the right frame. Example:
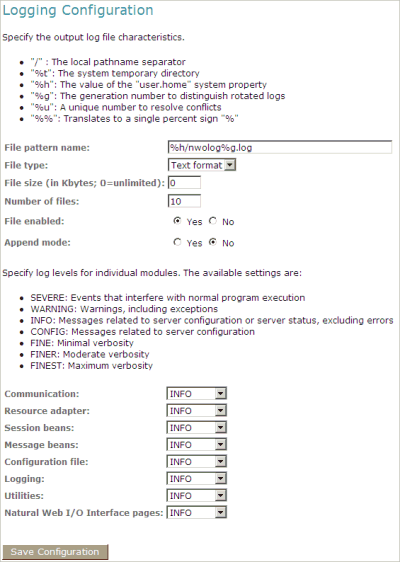
Specify the characteristics of the output file as described below in the section Overview of Options for the Output File.
Specify the log levels for individual modules by selecting the log level from the corresponding drop-down list box.
A brief description for each log level is provided on the Logging Configuration page.
Choose the button to write the modifications to the configuration file.
Caution:
When you do not choose the button but log out instead or leave the configuration
tool by entering another URL, your modifications are not written to the
configuration file.
The following options are provided for specifying the characteristics of the output file:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| File pattern name | The pattern for generating the output file name.
Default: "%h/nwolog%g.log".
The default value means that an output file with the name nwolog<number>.log will be created in the home directory of the user who has started the application server. For detailed information on how to specify the pattern, see the Java API documentation. |
| File type | The format of the output file. Select one of the
following entries from the drop-down list box:
The corresponding formatter class is then used. |
| File size | The maximum number of bytes that is to be written to an output file. Zero (0) means that there is no limit. Default: "0". |
| Number of files | The number of output files to be used. This value must be at least "1". Default: "10". |
| File enabled | If set to Yes (default), the file handler is enabled. If set to No, the file handler is disabled. |
| Append mode | If set to Yes, the logging information is appended to the existing output file. If set to No (default), the logging information is written to a new output file. |