This section covers the following topics:
With Natural SQL Gateway, a Natural user residing on z/OS can access data in an SQL database residing either on a UNIX or a Windows system.
In general, there is no difference between using Natural with an SQL database and using it with Adabas, VSAM or DL/I. Natural SQL Gateway allows Natural programs to access SQL data, using the same Natural DML statements that are available for Adabas, VSAM, and DL/I.
Therefore, programs written for SQL tables can also be used to access Adabas, VSAM, or DL/I databases. Moreover, some additional Natural SQL statements are available.
Natural SQL Gateway is comprised of the following parts:
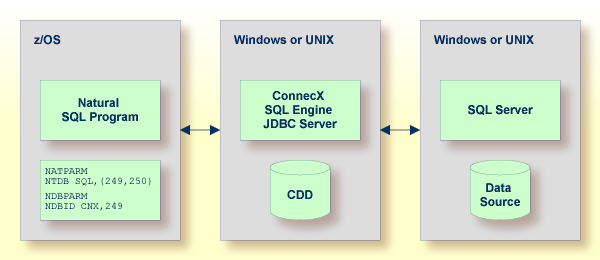
The ConnecX client part resides on the z/OS platform and communicates with the JDBC Server from a batch or TSO address space .
The Natural SQL Gateway client part resides on the z/OS platform linked to Natural in a TP environment.
The client part of Natural SQL Gateway is currently supported for CICS and Com-plete.
The Natural SQL Gateway server runs the Natural SQL Gateway Client in a batch address space.
The ConnecX SQL Engine JDBC server resides either on a Windows or a Unix platform which accesses the SQL database system residing elsewhere.
The ConnecX SQL Engine JDBC server utilises a data dictionary (CDD) in order to access the SQL database. The CDD describes the structures of tables and databases being accessed. The CDD provides a Windows based administration tool for easy maintenance of the metadata contained in the CDD. In addition, a Windows based query tool named InfoNaut is offered. InfoNaut allows developing SQL syntax, saving queries and query results in different formats.
For further information, see the ConnecX SQL Engine documentation.
The z/OS section in the figure above differs depending on whether the SQL program runs in Batch/TSO or within a TP environment.
The following figure shows the constellation under Batch/TSO.

The ConnecX Client (namely API3GL) is directly linked to
the Natural SQL program.
The following figure shows the constellation if the SQL program runs within a TP environment.
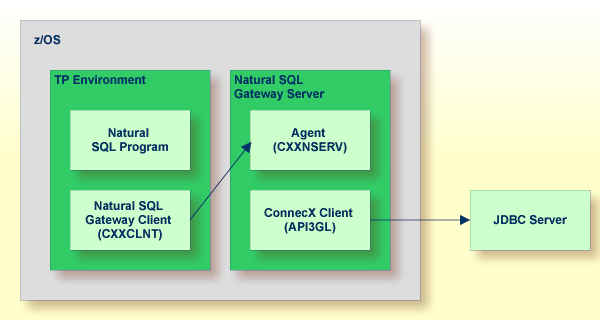
Since the ConnecX Client is not capable to run in a TP environment, it is moved into the Natural SQL Gateway server process, which runs in a batch environment. The Natural SQL Gateway Client and the Natural SQL Gateway server are responsible for transmitting the SQL requests from the Natural program to the JDBC server and the results backward.
The following table provides an overview of important terms used in the Natural SQL Gateway documentation:
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| NSB | This is the product code of Natural SQL Gateway, often used as short name in this documentation. |
| NSERV | Short for Natural SQL Gateway server. |
| File Server | The term "file server" refers to the Natural file server. |
| DB2 | DB2 refers to the family of IBM's licensed programs for relational database management. |
![]() To be able to access an SQL table with a Natural program via Natural
SQL Gateway
To be able to access an SQL table with a Natural program via Natural
SQL Gateway
A connection to the ConnecX SQL Engine JDBC server has to be established and a ConnecX SQL Engine data dictionary (CDD) has to be deployed.
The CDD has to contain the definition of the SQL table to be accessed
If the table does not yet exists on the SQL database system this
could be accomplished by a CREATE TABLE statement.
If the table is already existing this could be accomplished by
importing the table definition from the SQL catalogue into the CDD by the
ConnecX SQL Engine data dictionary manager. Keep in mind that the import
function of the data dictionary manager creates the table definition with the
qualifier name dbo. This is usually undesired and could be easily
reverted back to the original qualifier by usage of the change owner tool of
the data dictionary manager.
A DDM describing the SQL table has to be created with the Natural
utility SYSDDM.
The DBID of the DDM has to be defined as database type SQL via
NTDB macro in the NATPARM module.
The DBID of the DDM has to be defined as database type CNX via
NDBID macro in the NDBPARM module. The SQL
table to be accessed has to be defined in the CDD, see also the
ConnecX SQL Engine Data Dictionary documentation.
Once you have defined a DDM for an SQL table, you can access the data stored in this table by using a Natural program.
The Natural SQL Gateway translates the statements of a Natural program into SQL statements.
Natural SQL Gateway automatically provides for the preparation and execution of each statement in dynamic mode. Static execution is currently not supported. A statement is only prepared once (if possible) and can then be executed several times. For this purpose, Natural internally maintains a table of all prepared statements (see Statement Table in Internal Handling of Dynamic Statements).
Almost the full range of possibilities offered by the Natural programming language can be used for the development of Natural applications which access SQL tables. For a number of Natural DML statements, however, there are certain restrictions and differences as far as their use with SQL is concerned; see Natural DML Statements as described in Statements and System Variables. In the Natural Statements documentation, you can find notes on Natural usage with SQL attached to the descriptions of the statements concerned.
As there is no SQL equivalent to Adabas ISNs (Internal Sequence Numbers), any Natural features which use ISNs are not available when accessing SQL tables with Natural.
For SQL databases, in addition to the Natural DML statements, Natural provides SQL Statements as described in Statements and System Variables. In the Natural Statements documentation you can find a detailed description of these statements.
The message number ranges of Natural system messages related to Natural SQL Gateway are 3275 - 3286, 3700-3749, and 7386-7395.