This part of the Natural UTM Interface documentation covers the following topics:
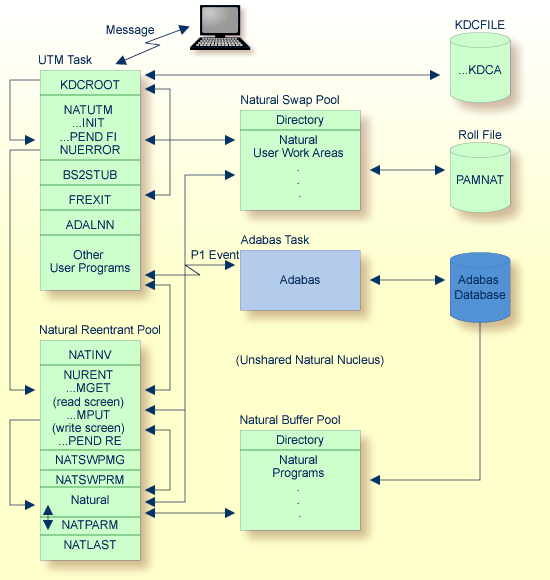
The Natural UTM Interface consists of the macros NATUTM,
BS2STUB and NURENT and of several utility programs,
which enable special requirements to be accommodated.
The macro NATUTM is used to generate the front-end part
of the Natural UTM Interface to suit the particular application based on
appropriate operand definitions for the parameters. The default values of the
parameters are chosen so that, in general, they can be used without alteration
for an initial generation.
The front-end part is present once per UTM task and consists principally of the following components:
KDCROOT of UTM,
assembled macro NATUTM,
assembled macro BS2STUB,
format exit module FREXIT,
Adabas interface module.
The reentrant part of the Natural UTM Interface is generated by
assembling the macro NURENT. This is linked with the reentrant
part of the Natural UTM application. If a shared Natural nucleus is to be used,
the generated NURENT module must be linked to the front-end
part.
The reentrant part of the Natural UTM application consists of the following components:
NATINV (address module) (must be included as the first
module),
Natural nucleus,
Natural buffer pool manager,
NURENT (CSECT name of the assembled macro
NURENT),
NATSWPMG (Natural swap pool manager),
Natural parameter module,
NATLAST (end definition) (must be included as the last
module).
The reentrant part of the Natural UTM Interface is only present once in a Natural UTM application (reentrant) if it is loaded into class 4 storage or into a common memory pool in class 6 storage. The latter is recommended.
A further possibility is to link the reentrant part with the non-reentrant front-end part of the Natural UTM application.
The Natural and UTM macro libraries are required when assembling
NATUTM, NURENT and all utility programs.
Natural uses its own formatting routines when sending messages to the
VDU (UTM format type "minus"). Messages are processed by the
format exit module FREXIT (transfer from logical to physical I/O
domain and vice versa, producing RESTART and LOGOFF
messages, etc.).
The module FREXIT must be linked with the front-end part
of the Natural UTM application and it must be defined as the format exit module
when generating KDCROOT or KDCDEF.
PROGRAM FREXIT,COMP=ASSEMB EXIT PROGRAM=FREXIT,USAGE=FORMAT
The program FREXIT supports the format name
-END for the LOGOFF message. See the description of
the parameter LOFFMAP of the macro
NATUTM. No more UTM administration commands (KDCINF,
KDCSHUT N, etc.) can be entered after the format name
-END has been used and the LOGOFF message has been
output. The LOGOFF message is output in formatted mode; however,
UTM expects administration commands in line mode and therefore any input
results in a syntax error. After this error message has been received, all
valid administration commands can be input with the administration ID. The
messages for asynchronous messages, RESTART and
LOGOFF can be changed to suit specific requirements by changing
the appropriate text constants in the program FREXIT.
The program FREXIT has a user exit INPTEX
that can be satisfied by the utility program INPTEX. See the
descriptions of the programs NATDUE and
INPTEX in
the section Utility
Programs.
Another user exit in program FREXIT is
TRMIOEX, which can be used for input/output message control.
The macro FREXIT contains the following parameters:
AMSG=ASAP
|
If there are any "free-running" (asynchronous)
messages, a further dialogue with Natural is only possible if these messages
have previously been read with the command
KDCOUT.
|
AMSG=WAIT
|
(Default) A further dialogue with Natural is possible even if
any "free-running" messages have not yet been read with the
command KDCOUT.
|
KDCDISP=YES
|
(Default) KDCDISP is supported by a
restart message with an automatic ENTER. The last screen output
will be refreshed.
|
KDCDISP=NO
|
KDCDISP is supported by a restart
message with a following refresh screen.
|
If you want to change a default operand of macro FREXIT,
you must reassemble FREXIT.
The following topics are covered:
Natural requires a common area into which Natural programs can be read from the Adabas database and where they are also executed. This common memory pool is the Natural buffer pool.
You use the parameters of macro ADDON (which assembles
module BS2STUB) either to define a local Natural buffer pool, or
to define the connection to a global Natural buffer pool. For more information,
see ADDON
Macro in the Natural Operations
documentation.
You use the parameters of module CMPSTART to define a
global Natural buffer pool. For more information on this module, see
CMPSTART
Program in the Natural Operations
documentation.
To display statistical information about the buffer pool, use the Natural utility SYSBPM; see the Natural Utilities documentation.
A Natural user work area is required for each online Natural user. This user work area must be in the computer's main store whenever the user initiates any form of dialogue transaction. To reduce the frequency with which the user work area is rolled out to the swap file and rolled in again, it is possible to set up a Natural Swap Pool. For details on the swap pool, please refer to Natural Swap Pool in the Natural Operations documentation.
You use the parameters of macro ADDON (which assembles
the module BS2STUB) either to define a local Natural swap pool, or
to define the connection to a global Natural swap pool. For more information,
see ADDON
Macro in the Natural Operations
documentation.
You use the parameters of module CMPSTART to define a
global Natural swap pool. For more information, see
CMPSTART
Program in the Natural Operations
documentation.
The reentrant part of the Natural UTM application can be loaded in
class 4 storage or linked with the front-end part of the Natural UTM
application. Alternatively, it can be loaded in a common memory pool in class 6
storage. This last method is recommended. The amount of storage required in the
common memory pool depends upon the size of the linked reentrant part of the
Natural UTM application; this can be read from the linker listing. The
parameter NUCNAME of macro
NATUTM is used if Natural is to be loaded into a common memory
pool in class 6 storage. This parameter specifies the name of the linked,
reentrant Natural nucleus. This is also the name of the Natural load pool. See
also Parameters of Macro
NATUTM.
You use the parameters of macro ADDON (which assembles
module BS2STUB) either to define a local Natural load pool, or to
define the connection to a global Natural load pool (shared Natural nucleus).
For more information, see ADDON
Macro in the Natural Operations
documentation.
You use the parameters of module CMPSTART to define a
global Natural load pool (shared Natural nucleus). For more information, see
CMPSTART
Program in the Natural Operations
documentation.
The Natural Monitor utility requires a common memory pool for data storage. This common memory pool is allocated when the Monitor utility is activated, and released when the Monitor utility is deactivated.
You use the parameters of macro ADDON (which assembles
module BS2STUB) either to define a local Natural monitor pool, or
to define the connection to a global Natural monitor pool. For more
information, see ADDON
Macro in the Natural Operations
documentation.
You use the parameters of module CMPSTART to define a
global Natural monitor pool. For more information, see
CMPSTART
Program in the Natural Operations
documentation.
For details on the Monitor utility, see SYSTP Utility in the Natural Utilities documentation.
For each UTM task a storage area with a size of
MAXSIZE
is generated. This area contains the Natural user area in decompressed
form.
The Natural user work area can be written out either asynchronously ("write without wait") or synchronously ("write with wait").
If the asynchronous option is used (this is the default option), a
write buffer having the size of defined operand for parameter
ROLLTSZ is
generated for each UTM task. Using this technique, the compressed user work
area is copied from the swap pool into the write buffer, the asynchronous write
is started and processing can continue immediately. This option gives better
performance, but at the cost of increased storage.
If roll-outs are to be performed synchronously, the parameter
ROLLACC must
have the value UPAM-SY. In this case, it is not necessary to
allocate a write buffer. Processing is suspended until the user work area has
successfully been written to the swap file.
A storage area of MAXSIZE
is allocated for each asynchronous transaction in a Natural UTM application
(Natural user work area for this transaction). It is released at the end of the
transaction. The Natural swap pool is not used to store the user work area
associated with asynchronous transactions. Every Natural program that runs
asynchronously must end with a TERMINATE statement; that is,
the UTM DC transaction is ended with PEND 'FI(NISH)'. This applies
to asynchronous transactions both within an application and between two Natural
UTM applications; see also
Asynchronous
Transaction Processing.
A PAM file is required for swapping the Natural user work areas.
Writing to and reading from this file is done by physical chained PAM-I/O.
However, this is only possible as long as the swap file does not cross an
extent boundary. This can be checked using
SPCCNTRL.
The LINK name of the
Natural swap file is PAMNAT. The size of the roll file can be
computed as follows:
NP=([(MS+4+31)/32]*32*NT+4)/2
where:
| NP | Size of dataset in PAM pages |
| MS | Parameter ROLLTSZ in Kbytes, rounded
up to next even number
|
| NT | Number of terminals online |
ROLLTSZ = 80 KBytes (per
user), number of terminals online = 40
Size of dataset = ( [ ( 80 + 4 + 31 ) / 32 ] * 32 * 40 + 4 ) / 2
= ( [ 115 / 32 ] * 32 * 40 + 4 ) / 2
= ( [ 3.59375 ] * 32 * 40 + 4 ) / 2
= ( 3 * 32 * 40 + 4 ) / 2
= 3844 / 2
= 1922 PAM pages
FILE statement:
/FILE NATUTM.SWAPFILE,LINK=PAMNAT,SPACE=(1922,96)
When a local swap pool is used, each Natural UTM application requires its own Natural swap file. When a user logs on to the application, the Natural UTM Interface checks whether there is sufficient space available for the new user in the Natural roll file. If there is not enough space, error message NUS0033 is output.
When a global swap pool is used, all Natural UTM applications which are connected to the same global swap pool must use the same Natural roll file.
The following Natural-specific definitions must be entered when
generating KDCROOT for a Natural UTM application:
MAX KB=400,SPAB=8192,NB=5120,TRMSGLTH=5120 (see Note 1) PROGRAM NUSTART,COMP=ASSEMB (see Note 2) PROGRAM NUERROR,COMP=ASSEMB (see Note 2) TAC NAT,PROGRAM=NUSTART,EXIT=NUERROR (see Note 2) EXIT PROGRAM=FREXIT,USAGE=FORMAT (see Note 3) PROGRAM FREXIT,COMP=ASSEMB (see Note 3)
| Note | |
|---|---|
| 1 | The area needed for the UTM KB has a minimum length of 400
bytes. The necessary KB length for operand
KB=nnn in the
MAX parameter of
KDCDEF
must be calculated as follows:
Fixed KB length is 400 bytes The UTM I/O areas |
| 2 | In a Natural UTM application there is as a rule only one
user-specific UTM partial program.
This program is the front-end part of the Natural UTM Interface,
which must be defined in the adequate parameters of
Any number of UTM transaction codes can be assigned, providing the naming rule is observed. The name of the DC transaction exit routine |
| 3 | The format exit module FREXIT must be defined
with the parameters EXIT and
PROGRAM.
|
All other definitions relating to the generation of
KDCROOT are either specific to UTM or else they are dependent upon
the values defined in the operands of the appropriate
parameters of macro
NATUTM.
The following Natural-specific points must be observed when defining the UTM resources:
The TERMN operand of the PTERM
command must be set to the value X1 or FG for
9755-type terminals and to the value X2 for 9756-type terminals.
These are special values and not described in the appropriate table in the
Siemens UTM documentation.
For all other types of terminals, the TERMN operand must
be set to the value shown in the tables.
PTERM ss19,lterm=ltdf1900,pronam=vr,ptype=t9755,TERMN=X1
The Natural UTM Interface supports the function keys K1,
K2, K3, K4, F1, F2,
F3, F4 and F5 (for P keys). The
function key which has been pressed can be identified by means of the UTM
return code, which must be defined using the SFUNC statement of
KDCDEF:
SFUNC K1,RET=26Z SFUNC K2,RET=27Z SFUNC K3,RET=28Z SFUNC K4,RET=29Z SFUNC F1,RET=21Z SFUNC F2,RET=22Z SFUNC F3,RET=23Z SFUNC F4,RET=24Z SFUNC F5,RET=25Z SFUNC nn,RET=nnZ
(for the PRKEY, see the parameter
PRKEY)
Using other function keys or using valid function keys that have not
been defined in KDCDEF results in an error message.
In an appropriate system configuration of IBM SNA (VTAM) and Siemens TRANSDATA DC, 3270-type terminals are supported by the Natural UTM Interface.
This means that Siemens terminals as well as 3270 terminals can be
connected to a Natural UTM application. Natural adjusts screen output to the
specific terminal type used. 3270-type terminals have to be defined as such to
KDCDEF in the PTERM command (see
Siemens UTM documentation).
For the support of Siemens and IBM function keys, the
SFUNC statements of KDCDEF have to be defined as
follows:
| Siemens Key | IBM Key | UTM Return Code |
|---|---|---|
| F1 | PF1 | 21Z |
| F2 | PF2 | 22Z |
| F3 | PF3 | 23Z |
| F4 | PF4 | 24Z |
| F5 | PF5 | 25Z |
| K1 | PA1 | 26Z |
| K2 | PA2 | 27Z |
| K3 | PF6 + PF13 | 28Z |
| K4 | PF7 + PF14 | 29Z |
| K5 | PF8 + PF15 | 30Z |
| K6 | PF9 + PF16 | 31Z |
| K7 | PF10 + PF17 | 32Z |
| K8 | PF11 + PF18 | 33Z |
| K9 | PF12 + PF19 | 34Z |
| K10 | PF20 | 35Z |
| K11 | PF21 | 36Z |
| K12 | PF22 | 37Z |
| K13 | PF23 | 38Z |
| K14 | PF24 | 39Z |
For terminals which are to be used in TTY mode, the TERMN
operand of the PTERM command must be set to
TERMN=X9.
The following restrictions apply to TTY mode:
Asynchronous transaction processing is not supported.
MULTI-PASS is not supported.
A UTM DC-transaction exit routine is defined in the front-end part of
the Natural UTM Interface. This routine is called at the beginning of a DC
transaction, when a DC transaction is restarted, at normal termination and at
abnormal termination (PEND ER). The user exit
UVGEXIT can be used in any
of these circumstances.
In the case of abnormal termination, the affected user is deleted from the internal terminal control table, the Natural recovery procedures are executed and the user's user area is released from the swap pool directory if necessary.
The DC-transaction exit routine NUERROR must be defined in
the adequate parameters of KDCDEF for the front-end part of the
Natural UTM Interface (generation of KDCROOT); see also
Generating
KDCROOT.
If the user exit STARTEX (default value of
parameter STRTALL ) is to be used,
EXIT PROGRAM=NUSTART,USAGE=START must be defined in the
KDCDEF parameter for the front-end part of the Natural
UTM Interface.
One of the effects of this is that the task initialization routines
(allocation of common memory pools, loading Natural, etc.) are activated
immediately following the start of each UTM task. Errors that occur are output
on the console and all users are sent an appropriate message; if
SYSLST=YES, errors are also
output to SYSLST.
If the UTM startup function is not used, the UTM task(s) are not initialized until they are activated when a user logs on. If an error occurs under these circumstances, the error message is sent to the terminal that caused the error. All other users are given an appropriate message when they try to log-on to the application.
If the user exits SHUTEX1 and/or SHUTEX2
(default values of parameters SHUTALL and
SHUTLST ) are to be used,
the following must be defined in the KDCDEF parameters
(KDCROOT) for the front-end part of the Natural UTM Interface:
EXIT PROGRAM=NUSTART,USAGE=SHUT
The statistics of the Natural UTM Interface are output when the last UTM task terminates.
If the UTM shutdown function is not used, the user exits defined with
SHUTALL and
SHUTLST
cannot be used and the statistics are not available.
The statistics that are collected and output by the Natural UTM Interface are:
MAIN DIRECTORY IS RESIDENT, N O T P A G E A B L E -------------------------------------------------- INITIALIZED WITH CONTROL DATA FROM NAT SYSTEM FILE TOTAL SIZE OF SWAP POOL IN KB : 32760 SIZE OF MAIN DIRECTORY IN KB : 2 TOTAL NO. OF SWAP POOL THREADS: 209 TOTAL NO. OF LOGICAL SWP(S) : 10 LAST STATUS OF THE SWAP POOL STATISTICS +-----------------------------------------------+ I Natural USER THREADS WITH LENGTH I I GREATER LOWER I I 152 KB I +-----------------------+-----------------------+ I + 2 KB: 0 I - 2 KB: 0 I I + 4 KB: 0 I - 4 KB: 17 I I + 6 KB: 0 I - 6 KB: 0 I I + 8 KB: 0 I - 8 KB: 1 I I + 10 KB: 0 I - 10 KB: 0 I I + 12 KB: 0 I - 12 KB: 0 I I + 14 KB: 0 I - 14 KB: 0 I I + 16 KB: 0 I - 16 KB: 0 I I + 18 KB: 0 I - 18 KB: 0 I I + NN KB: 0 I - NN KB: 0 I I AVER.LNG.NN: 0 KB I AVER.LNG.NN: 0 KB I +-----------------------------------------------+ |
LOGICAL SWP NO. 01 LOGICAL SWP NO. 02 ------------------ ------------------ LOGICAL SWP SIZE IN KB: 2402 LOGICAL SWP SIZE IN KB: 2690 DIRECTORY SIZE IN KB : 2 DIRECTORY SIZE IN KB : 2 SWP THREAD SIZE IN KB : 120 SWP THREAD SIZE IN KB : 128 NO. OF SWP ENTRIES : 20 NO. OF SWP ENTRIES : 21 MAX. USED ENTRIES : 0 MAX. USED ENTRIES : 0 NO. OF SWP GUESTS : 0 NO. OF SWP GUESTS : 0 NO. SUCCESSFUL LOCATES: 0 NO. SUCCESSFUL LOCATES: 0 NO. FAILED LOCATES : 0 NO. FAILED LOCATES : 0 LOGICAL SWP NO. 03 LOGICAL SWP NO. 04 ------------------ ------------------ LOGICAL SWP SIZE IN KB: 2858 LOGICAL SWP SIZE IN KB: 3026 DIRECTORY SIZE IN KB : 2 DIRECTORY SIZE IN KB : 2 SWP THREAD SIZE IN KB : 136 SWP THREAD SIZE IN KB : 144 NO. OF SWP ENTRIES : 21 NO. OF SWP ENTRIES : 21 MAX. USED ENTRIES : 0 MAX. USED ENTRIES : 1 NO. OF SWP GUESTS : 0 NO. OF SWP GUESTS : 0 NO. SUCCESSFUL LOCATES: 0 NO. SUCCESSFUL LOCATES: 1 NO. FAILED LOCATES : 0 NO. FAILED LOCATES : 0 LOGICAL SWP NO. 05 LOGICAL SWP NO. 06 ------------------ ------------------ LOGICAL SWP SIZE IN KB: 3194 LOGICAL SWP SIZE IN KB: 3362 DIRECTORY SIZE IN KB : 2 DIRECTORY SIZE IN KB : 2 SWP THREAD SIZE IN KB : 152 SWP THREAD SIZE IN KB : 160 NO. OF SWP ENTRIES : 21 NO. OF SWP ENTRIES : 21 MAX. USED ENTRIES : 1 MAX. USED ENTRIES : 0 NO. OF SWP GUESTS : 0 NO. OF SWP GUESTS : 0 NO. SUCCESSFUL LOCATES: 17 NO. SUCCESSFUL LOCATES: 0 NO. FAILED LOCATES : 0 NO. FAILED LOCATES : 0 LOGICAL SWP NO. 07 LOGICAL SWP NO. 08 ------------------ ------------------ LOGICAL SWP SIZE IN KB: 3530 LOGICAL SWP SIZE IN KB: 3698 DIRECTORY SIZE IN KB : 2 DIRECTORY SIZE IN KB : 2 SWP THREAD SIZE IN KB : 168 SWP THREAD SIZE IN KB : 176 NO. OF SWP ENTRIES : 21 NO. OF SWP ENTRIES : 21 MAX. USED ENTRIES : 0 MAX. USED ENTRIES : 0 NO. OF SWP GUESTS : 0 NO. OF SWP GUESTS : 0 NO. SUCCESSFUL LOCATES: 0 NO. SUCCESSFUL LOCATES: 0 NO. FAILED LOCATES : 0 NO. FAILED LOCATES : 0 LOGICAL SWP NO. 09 LOGICAL SWP NO. 10 ------------------ ------------------ LOGICAL SWP SIZE IN KB: 3866 LOGICAL SWP SIZE IN KB: 4118 DIRECTORY SIZE IN KB : 2 DIRECTORY SIZE IN KB : 2 SWP THREAD SIZE IN KB : 184 SWP THREAD SIZE IN KB : 196 NO. OF SWP ENTRIES : 21 NO. OF SWP ENTRIES : 21 MAX. USED ENTRIES : 0 MAX. USED ENTRIES : 0 NO. OF SWP GUESTS : 0 NO. OF SWP GUESTS : 0 NO. SUCCESSFUL LOCATES: 0 NO. SUCCESSFUL LOCATES: 0 NO. FAILED LOCATES : 0 NO. FAILED LOCATES : 0 |
------------------------------------------------------------ USAGE STATISTICS OF SWAP POOL AND NATURAL USER THREADS SWP SLOT NO. NAT. % DIAGRAM NO. LNG KB THREADS --- ------ ------- ----- ----------------------------------- 01 120 0 0,0 02 128 0 0,0 03 136 0 0,0 04 144 1 5,5 *** 05 152 17 94,4 *********************************** 06 160 0 0,0 07 168 0 0,0 08 176 0 0,0 09 184 0 0,0 10 196 0 0,0 DESERTERS: 0 0,0 M A I N D I R E C T O R Y S T A T I S T I C S A R E A NATSHARE: SWAP POOL START DATE 02-07-17 NATSHARE: SWAP POOL START TIME 11:52:14 NATSHARE: TOTAL NUMBER OF SWP SYNC. WAITS: 0 NATSHARE: TOTAL NUMBER OF ASYN. WRITE WAITS: 0 NATSHARE: TOTAL NUMBER OF DIALOGUE STEPS: 19 NATSHARE: TOTAL NUMBER OF SWAPS: 0 NATSHARE: TOTAL NUMBER OF WRITES TO ROLL FILE: 0 NATSHARE: TOTAL NUMBER OF SYNCHRONOUS WRITES: 0 NATSHARE: MAX NUMBER OF USER: 1 NATSHARE: MAX NUMBER OF DIALOGUES WITHOUT SWAPS: 19 NATSHARE: NUMBER OF SWAP POOL REORGANIZATION: 0 NATSHARE: NUMBER OF SWAP POOL REPAIR: 0 NATSHARE: NUMBER OF ABNORMAL ENDED SESSIONS: 0 NATSHARE: MAX. COMPR. L' OF NAT USER THREAD IN KB: 148 NATSHARE: REAL MAXSIZE NEEDED FROM Natural IN KB: 386 When Swap Pool Data Space is generated: NATSHARE: D A T A S P A C E ( D S F ) S T A T I S T I C S NATSHARE: NO. OF ESA DATA SPACE SLOTS: 30 NATSHARE: NO. OF WRITES INTO DATA SPACE: 0 NATSHARE: NO. OF FAILED WRITES (DATA SPACE FULL): 0 NATSHARE: NO. OF SUCCESSFUL DSP THREAD LOCATES: 0 NATSHARE: NO. OF FAILED DSP THREAD LOCATES: 0 NATSHARE: SWP STATISTICS PRINT DATE: 02-07-17 NATSHARE: SWP STATISTICS PRINT TIME: 11:52:14 |