This document covers the following topics:
Following any error, ETP automatically attempts to recover from the error and continue with the operation without any operator intervention. Of course, whether or not intervention is needed depends on the type of error.
There are five general types of possible errors:
Inaccessible master file (or its database), but with an intact Adabas log;
Inaccessible master file (or its database), and a damaged Adabas log;
Damaged replicate file (or its database) that is restorable to its current state;
Damaged replicate file (or its database) that needs to be restored to an earlier status;
The administration file has lost integrity, and must be restored to an earlier status.
ETP uses the basic Adabas restart/recovery process to correct the errors that can be restored from the undamaged Adabas log or master file. Such failures can be restored when the master file/database is again available. In these cases, Adabas restart/recovery recovers all participating databases and restores the integrity of the master and its log file, and of the replicate files and their confirmation files.
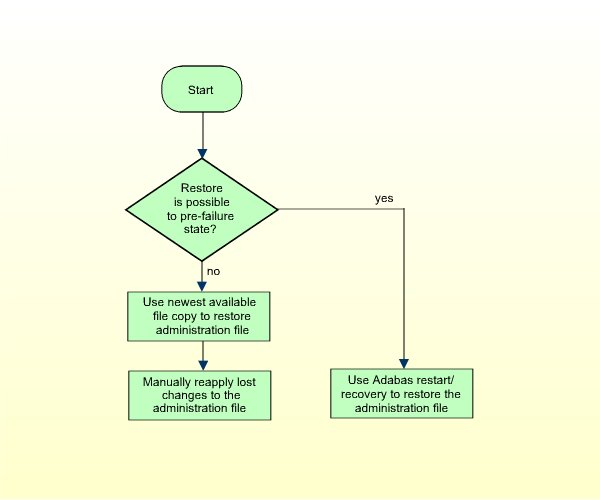
For those errors where a file must be restored to an earlier status,
the file must first be restored and then corrected from the Adabas log, using
the Adabas restart/recovery facility. If, however, a catastrophic
(data-damaging) error makes such restoring impossible, you must restore the
files to an earlier state from file copies (obtained with the Adabas
ADAULD or ADASAV utility). It is therefore specially
important to obtain copies of at least the most critical ETP files
regularly.
To permit restoring of lost or damaged files, the master, log and
administration files, you must obtain copies regularly with ADAULD
or ADASAV. Second, only information from the time before the
master file was last copied should be deleted from the log file. The date and
time when the copies were made should be recorded to ensure that the most
recent copy of each file is used, if it is needed. The log file should always
be copied at the same time as its master file.
If appropriate, replicate files and their confirmation files should
also be copied using ADAULD or ADASAV after the
master file has been copied. This eases automatic recovery if there has also
been damage to a replicate file's Adabas log information. Copying the replicate
files is not required because the replicate files can be restored from the
master/log file copy. The confirmation file should always be copied at the same
time as its replicate file, and the replicate file should always be copied
after its master file is copied.
When "partial replicate" files are damaged, you must use a copy of either the master file, the partial replicate file itself or of a full replicate to restore the replicate file. If the partial replicate is restored from the master or a full duplicate copy, you must perform reinitialization.
If a confirmation file is used by multiple replicate files, copy all replicate files and the confirmation file at the same time. If it becomes necessary to restore one of the files, all files must be restored.
The rest of the chapter describes the recommended procedures for restoring ETP operation after one of the general failures summarized earlier. In any of the following cases, the general recovery procedure is to:
Restore the data integrity of each database to the most recent level, using the autobackout/autorestart facility of Adabas;
Ensure that all links between the master files and their replicate files are active and running.
If the master file or its database is not available but is fully operable, local processing of related replicate files can still continue normally; that is, all read requests can be satisfied. In cases where local updates are made to an isolated master file, the updates will be applied to each remote replicate file by the replication task, once the isolation is removed and the task is restarted.
The figure below shows the general recovery sequence to follow when a failure occurs that isolates a master file from its replicate files. Such a failure is usually caused by the loss of a Net-Work (or other comparable database interconnecting system's) link.
|
|
Notes:
|
|
|
Notes:
|
If the failure not only isolated the master/replicate file but also interrupted an update transaction that changed the master file, the Adabas autobackout/ autorestart must first restore each affected database to its pre-transaction state. Autobackout removes any changes made during the failed transaction; autorestart then reruns the failed transaction to reapply the update to the master file.
If no update transaction was running when the failure occurred, you only need to re-establish the link and start the replication task or tasks to restore the ETP file integrity. Tasks running with a defined restart interval need not be restarted.
For a failure that damages a replicate file or its confirmation file,
you can usually recover the damaged file or files with the protection log, the
ADALOD utility, and using the file copy obtained with the Adabas
ADAULD or ADASAV utility to reconstruct the file to a
recent state before the failure. In most cases, however, it might be quicker to
simply reload the replicate/confirmation file from a recent copy.
Using the ETP maintenance utility, you can then restart the related replication task to apply uncompleted master file changes, if any, to the restored (and any other unsynchronized) replicate file. The figure above shows the general recovery sequence for such a failure.
In this situation, the Adabas database's log for the master file has been damaged, preventing recovery. Here, one of the following must be performed:
Restore the log file from the Adabas PLOG and the log file copy
obtained using the ADAULD or ADASAV utility;
Reinstall the master/log files from an earlier level, reload the replicate files at that same level, and then apply any pre-failure updates.
The figure below shows the sequence for recovering from a damaged log file.
|
|
Notes:
|
If both the master and its log file have been irreparably damaged, the possible sources of a new master/log file are:
Copy of the Adabas file, combined with the protection log;
Recent master/log file copy;
Full replicate file.
If the master and log files can be restored to their condition just before the failure by the Adabas file copy/protection log recovery, then you can restart the ETP task for that file and repeat any incomplete master file transaction related to the failure. ETP should then resynchronize the master with its replicate files at the next restart of the replication task.
If, however, the master/log files cannot be rebuilt to the pre-failure state you must determine which transactions are recoverable. Second, you must determine whether a recent master/log file copies or an available "full duplicate" replicate file can be used to restore the master and log files to a level to which the recoverable transactions can be applied to raise the master/log files to their state just before the failure.
If there is a master file copy that is newer than the most recently resynchronized full duplicate replicate file, you can use that master file copy to restore the master file. Otherwise, use that newest replicate file as source for restoring both the master file and any other "older" replicate files. After restoring the master and affected replicate files, you must reapply all update transactions to the master file that are not already in the restored files. These reapplied transactions will be reflected in the replicate files when you restart an ETP replication task for that master file.
The log file should be restored from the same source and at the same level as the master file. Even if the log is repairable at a newer level than the master file, there is a chance that it will not reflect the master file state accurately. Therefore, you should always obtain copies of the master and log files together, and the confirmation and replicate files together.
|
|
Note: |
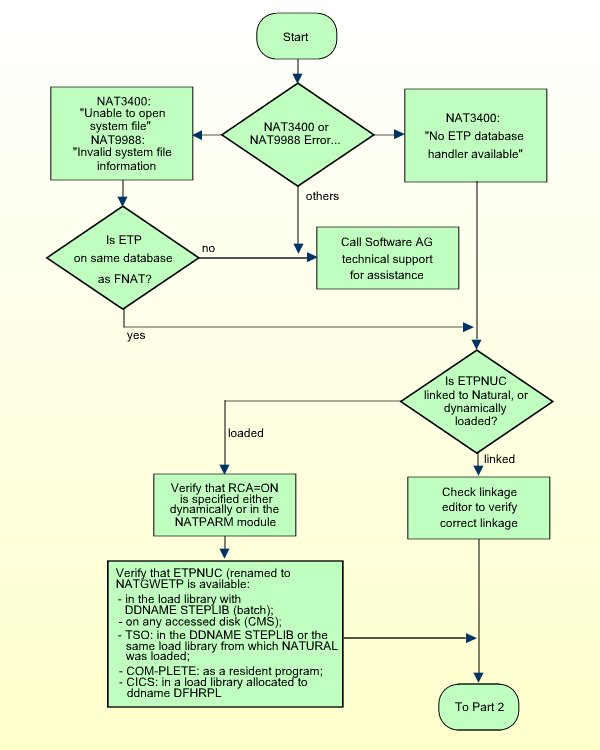
In some cases, a NAT3400 or NAT9988 error message can occur when ETP is
run. The error does not occur, however, when running Natural without ETP (that
is, where the ETPNUC module and Natural were not linked, or
ETPNUC could not be dynamically loaded). This is usually caused by
one of the following:
Incorrectly linking ETP to Natural;
The required amount of ETPSIZE (approx. 7 KB)
is not available.
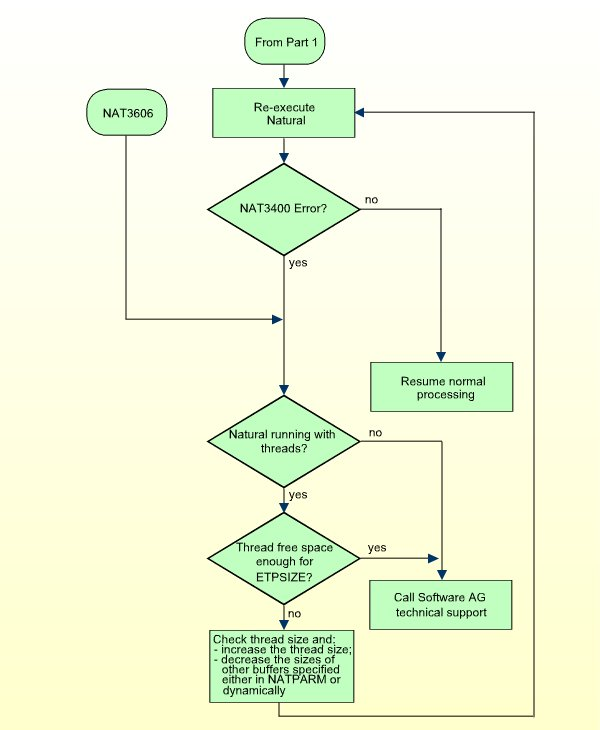
The figure below shows the general sequence for finding and removing the cause of a NAT3400 or NAT9988 error. See also ETP Installation. For NAT3606 error correction, see Part 2 of the figure below.